Presentation
Wrist pain and restricted motion.
Patient Data
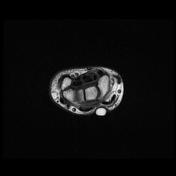

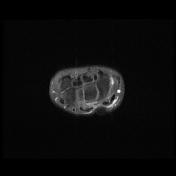

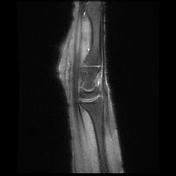

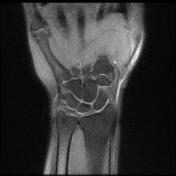

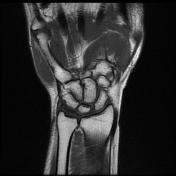

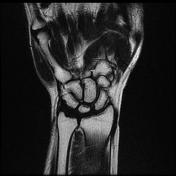

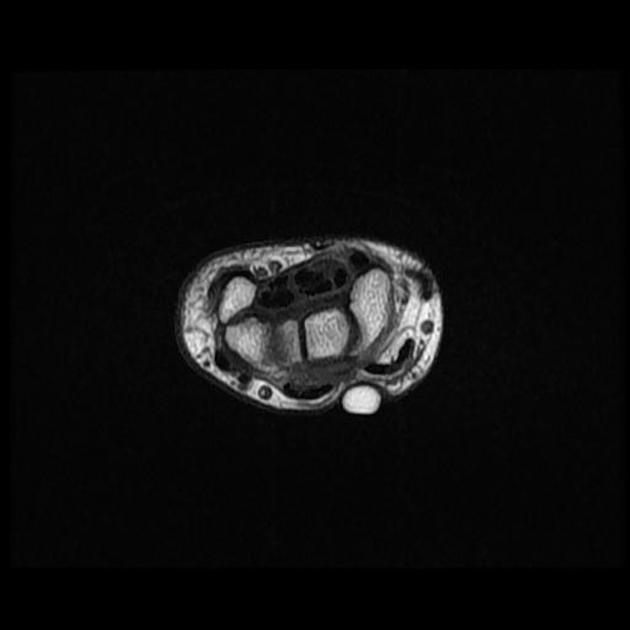
There is a high signal within the extensor pollicis longus (EPL) tendon just distal to Lister's tubercle as it crosses over the second extensor compartment tendons (ECRL and ECRB) and is flattened by the overlying extensor retinaculum.
There is localized tenosynovitis around this area and a small amount of increased fluid within the EPL and ECRL tendon sheaths.
Case Discussion
The ECRB, ECRL, and EPL tendons intersect distal to Lister’s tubercle and radiocarpal joint. The tubercle acts as a pulley, changing the EPL tendon angle when it crosses superficially over the ECRL and ECRB tendons. This creates a mechanically disadvantageous arrangement, where the motion of the thumb and hand may cause friction between these tendons.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.