Presentation
Presented with vertigo. No other neurological symptoms or signs.
Patient Data
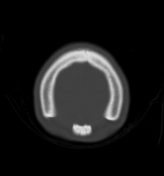

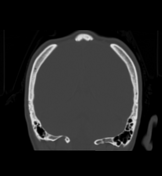

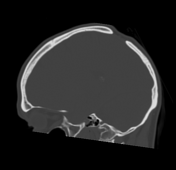

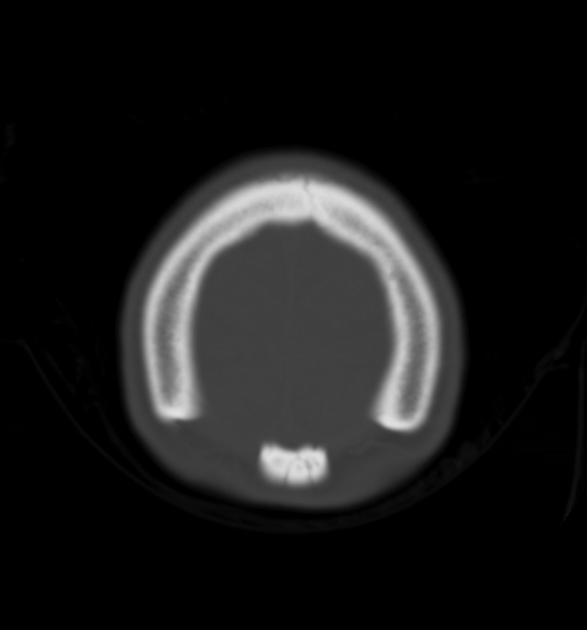
Paired, rounded parietal bone deficits of around 20 mm diameter located just lateral to the intersection of the sagittal and lambdoid sutures, consistent with enlarged parietal foramina.
Case Discussion
Enlarged parietal foramina were diagnosed in this case as an incidental finding.
This is typically an incidental finding caused by an autosomal dominant genetic mutation, but can be part of a congenital syndrome such as Potocki-Shaffer syndrome. Whilst generally asymptomatic and benign, there may be associated cortical, venous or meningeal anomalies.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.