Presentation
Headache
Patient Data
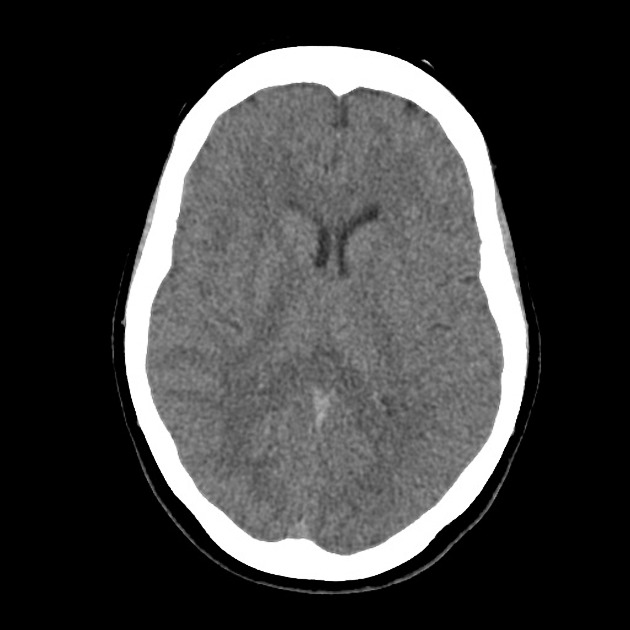
The fourth ventricle appears and enlarged and distorted by a low-density mass of near CSF density. No hydrocephalus.


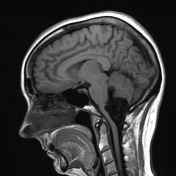

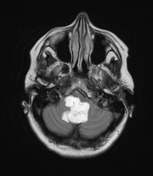

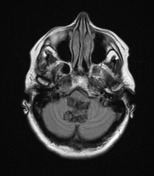

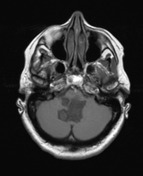

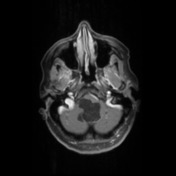

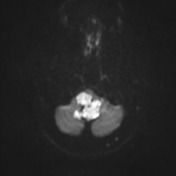

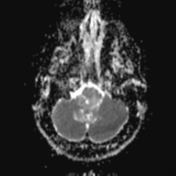



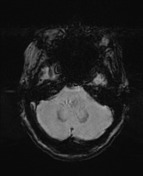

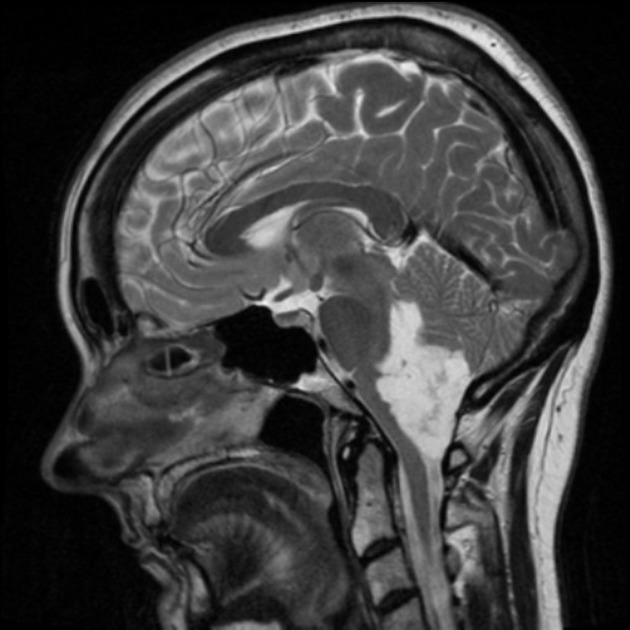
A large lobulated non-enhancing mass occupies and expands the fourth ventricle and extends inferiorly through the midline foramen of Magendie. It has scalloped margins, very high T2 signal which only partially attenuates on FLAIR. It is of low T1 signal without calcification or enhancement. Diffusion-weighted imaging demonstrates very high DWI signal and intermediate ADC values similar to the adjacent cerebellum. Appearances are characteristic of an epidermoid cyst.
Case Discussion
The patient went on to have surgery which confirmed the pre-operative diagnosis of an epidermoid cyst. The 4th ventricle is actually not that uncommon a location for this entity, but far less common than the cerebellopontine angle.
Histology
MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: The sections show the lining and contents of an epidermal cyst. The lining is composed of squamous epithelium with a discernible granular layer. The contents comprise laminated keratin. No mesenchymal or appendageal components are identified. There is no evidence of tumor.
DIAGNOSIS: Epidermoid cyst




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.