Presentation
Left-sided hemiparesis. CT to rule out ischemia.
Patient Data




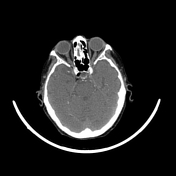

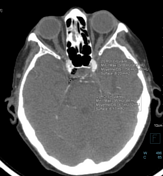
Well-circumscribed hypodensity (gas attenuation, with a mean -756 UH) within the right cavernous sinus.
Another hypodensity in the posterior aspect of the right cavernous sinus, demonstrating fat density (- 67 UH)
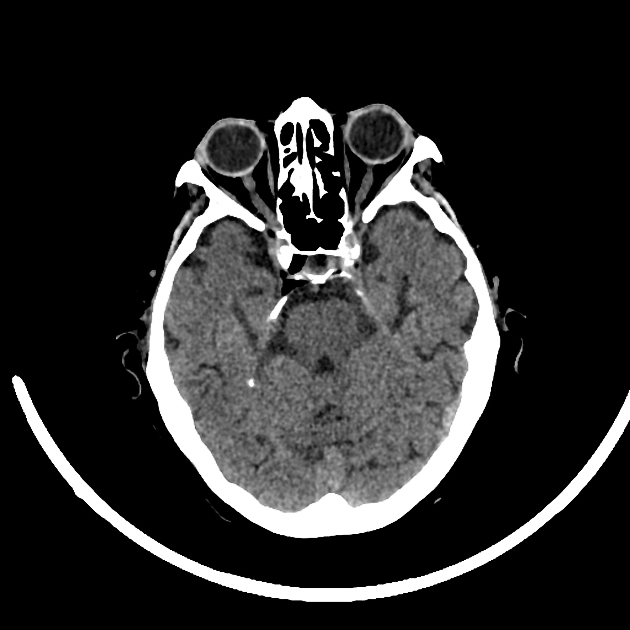
lacunar infarct in the left caudate nucleus
Left temporal hypodensity in keeping with a chronic ischemic stroke
No intracranial hemorrage or mass. No hydrocephalus.
Bilateral enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces, in keeping with degenerative changes.
Calcified atheromatous plaques in the carotid bulbs and in the C4 segments of the internal carotid arteries. No significant arterial stenosis.
Linear ill-defined filling defect within the right internal carotid artery, suggestive of flow artifact rather than dissection.


Compared to the previous CT, there is stability of the fat density material within the right cavernous sinus
Case Discussion
Gas in the cavernous sinus can be seen in a variety of conditions such as trauma and infections, but can also be iatrogenic after IV access. This case demonstrates air embolism in the cavernous sinus with associated adipose tissue in the sinus wall, which is a normal variant with no clinical significance.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.