Presentation
Fatigue, dyspnea, fever (38 C). Amoxicillin was not effective.
Patient Data
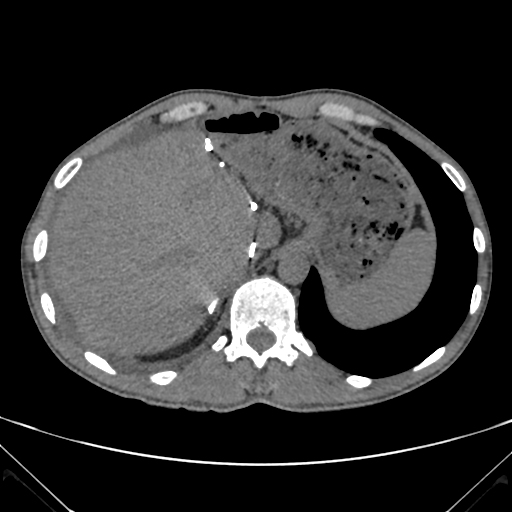
Hypodense structure in the right atrium, right Hydrothorax and free peritoneal fluid.


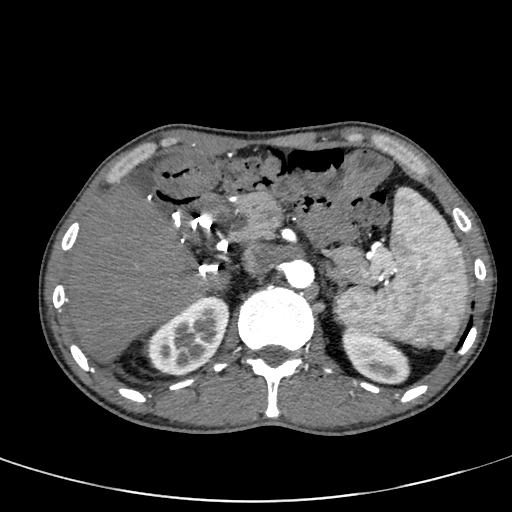
CT was performed two weeks later with contrast media administration.
Enlargement of the hypodense structure in the right atrium - thrombus from the right atrium to the cava inferior.
Patchy, mosaic enhancement of liver parenchyma with periportal edema due to hepatic congestion. Hepatic veins are not visible.
Hydrothorax, free peritoneal fluid.
Case Discussion
Elevated central venous pressure causes hepatic congestion and decreases hepatic blood flow. Increased hepatic venous pressure results in sinusoidal congestion, dilatation of fenestrae and exudation of protein and fluid into the space of Disse. This accumulation of exudate as well as decreased hepatic blood flow promote liver injury.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.