Patient Data






CT shows a hepatic nodule in segment VI that is hyperdense compared to steatotic liver parenchyma. After contrast administration is noted a progressive peripheral enhancement that is centripetal and has a delayed homogenization.
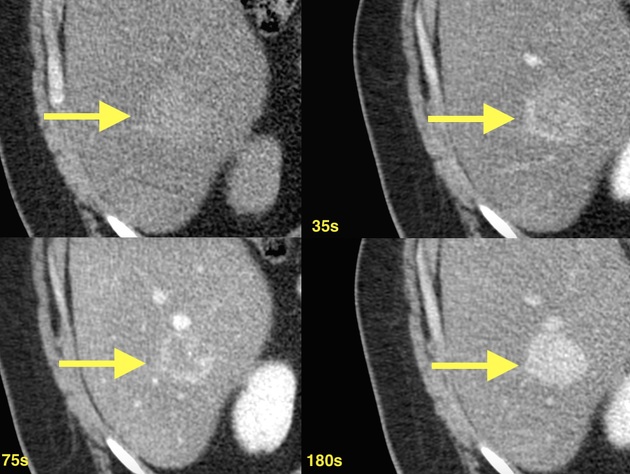
CT shows a hepatic nodule in segment VI that is hyperdense compared to steatotic liver parenchyma. After contrast administration is noted a progressive peripheral enhancement that is centripetal and has a delayed homogenization.
Case Discussion
Diffuse hepatic steatosis is a common imaging finding, and can lead to difficulties assessing the liver appearances, specially on ultrasound exam.
Hepatic hemangioma is a benign non-neoplastic hypervascular liver lesions. They are frequently diagnosed as an incidental findings on imaging and most patients are asymptomatic.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.