Presentation
History of laparoscopic cholecystectomy with iatrogenic common bile duct injury that underwent repair surgery.
Patient Data
Transhepatic cholangiography
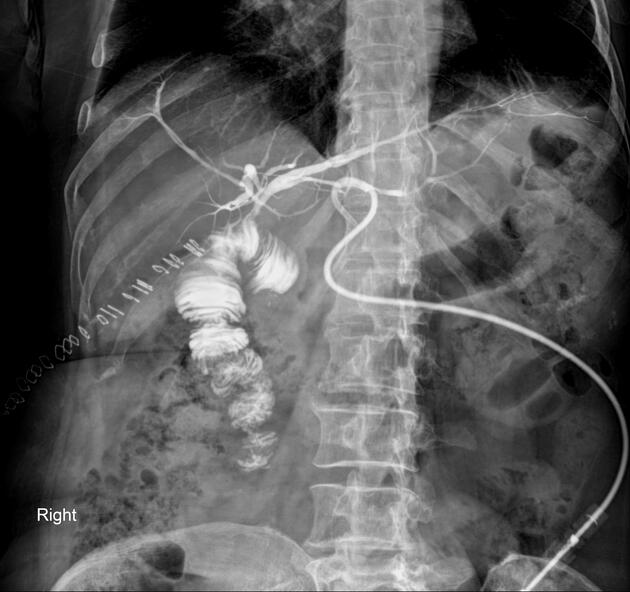
By injecting contrast medium through a catheter in the left intrahepatic bile ducts, evidence of hepaticojejunostomy is seen.
Intrahepatic and remnant parts of extrahepatic bile ducts appear normal without stricture and filling defects.
The contrast medium passed quickly into the jejunom.
Multiple surgical staplers are seen in the right upper quadrant areas.
Case Discussion
Bile duct injuries are a potentially serious surgical issue linked to high morbidity, mortality, and extended hospitalization. They usually occur infrequently as a complication of technically challenging laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedures or in the context of hepatobiliary trauma.
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) is an invasive technique used when interventions like percutaneous transhepatic biliary drain (PTBD) placement are needed to decompress or divert a blocked biliary system and control bile leakage, allowing for inflammation to subside and promote healing.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.