Presentation
Vision loss on right side
Patient Data
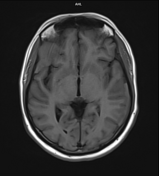

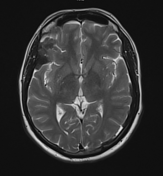

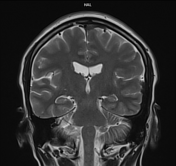

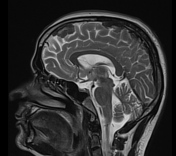

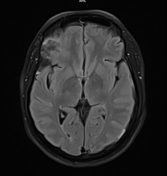

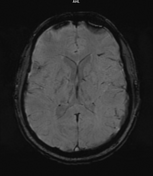


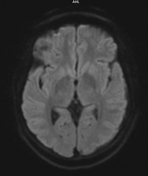

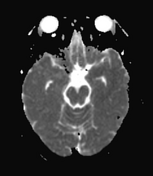

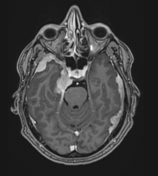

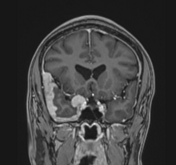

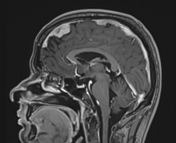

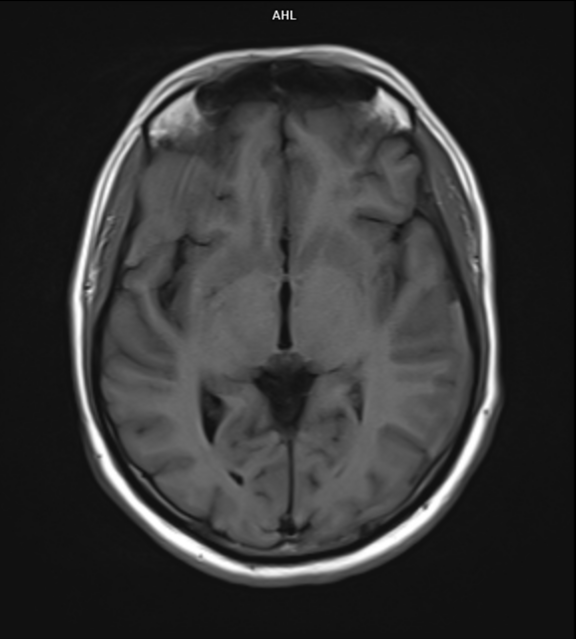
Multifocal mass-like nodular homogenously enhancing dural thickening overlying the bilateral temporal lobes, left parieto-occipital lobe, and along the falx cerebri in the anterior aspect. It appears isointense on T1W images and hypointense on T2W/FLAIR images with no evidence of diffusion restriction. No evidence of calcification or hemorrhage was seen within it. It causes mild compression over the intracanalicular segment of the right optic nerve that is likely responsible for the patient symptom of vision loss.
There is associated mild diffuse smooth enhancing dural thickening overlying the bilateral cerebral hemisphere.
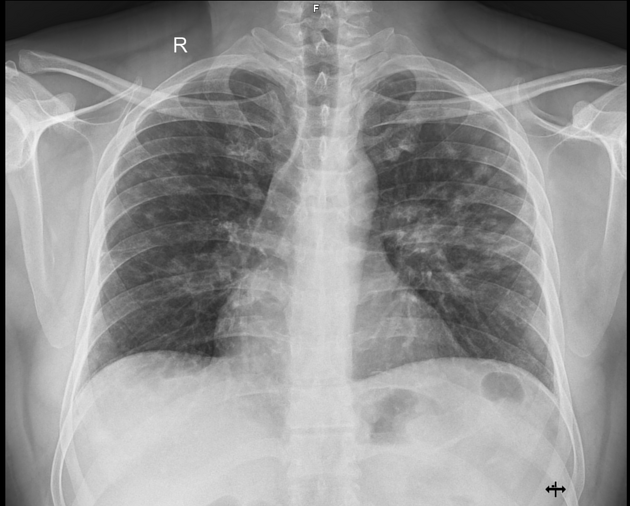
Multiple small nodular opacities are seen in the bilateral upper and mid zones, more on the left side.
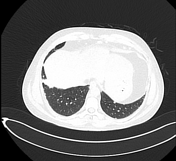

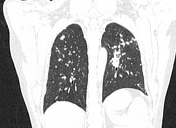

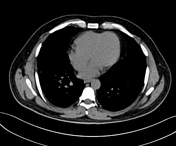

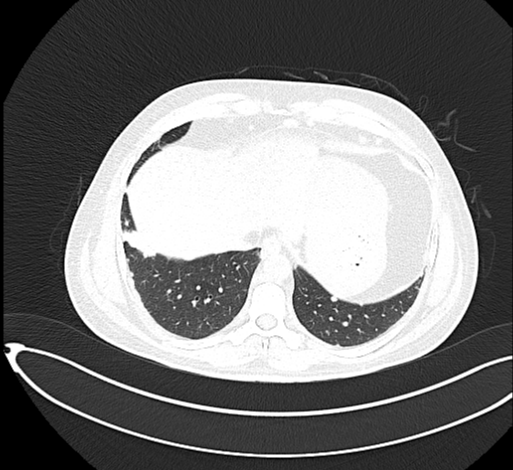
Multiple small variable-sized nodules are scattered in the bilateral lung with upper lobe predominance and more confluent in the left upper lobe in the para hilar region.
No significant mediastinal/hilar lymphadenopathy was seen.
-----Granulomatous etiology (Sarcoidosis/ tuberculosis) is the likely possibility.
Case Discussion
The patient went for transbronchial lung biopsy and histopathological report shows non-caseating granulomas.
The patient had significantly improved his vision after initiation of steroid therapy.
So overall the case is sarcoidosis involving the meninges of brain and lung parenchyma.
Co-authors:
Dr. Mukund Prasad, Mch (Neurosurgery).
Dr. Ranjan Kumar, DMRD, FRCR.
Dr. Saket Sharma, DM (Pulmonary medicine).




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.