Presentation
Left-sided weakness, diplopia and right-sided facial palsy.
Patient Data
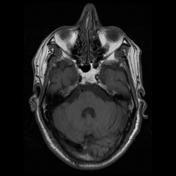

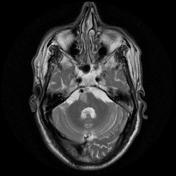

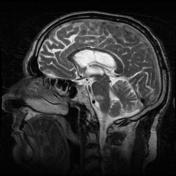

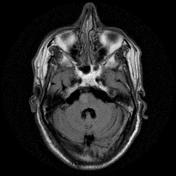



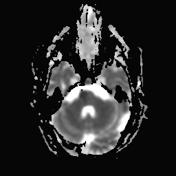

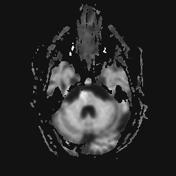

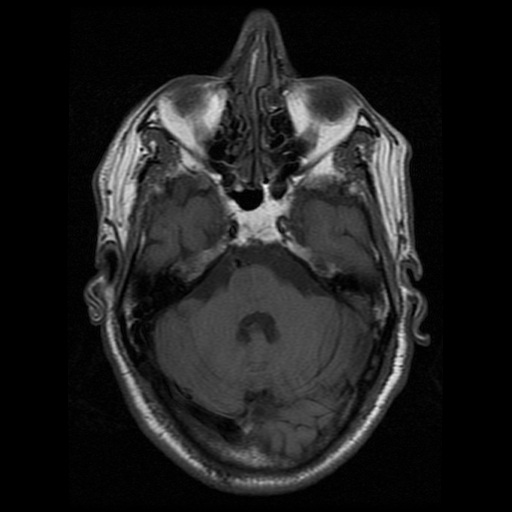
The right medial inferior pons shows a wedge-shaped area of restricted diffusion with high DWI and low ADC signal. It shows low T1 and high T2 / FLAIR signal intensity as well as subtle T1 hypointensity.
Multiple bilateral cerebral demyelinating foci with high T2/FLAIR signal intensity are seen with no restricted diffusion.
Mild dilatation of the ventricular system with peri-ventricular T2/FLAIR hyperintensity.
Widened extra-axial CSF spaces.
Normal sellar region. Normal cerebellum and cervico-medullary junction.
Case Discussion
This case shows typical right inferior medial pontine acute infarction; consistent with inferior medial pontine (Foville) syndrome. Atrophic brain changes with peri-ventricular arteriosclerotic leukoencephalopathy and bilateral cerebral small chronic vessel disease.
Inferior medial pontine (Foville) syndrome is characterized by:
- contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia due to corticospinal tract affection within the dorsal tegmentum of the pons at its inferior third.
- peripheral ipsilateral facial nerve palsy.
- conjugate gaze palsy with inability to look to the side of the lesion with diplopia.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.