Presentation
Patient was referred to CT scan for exclusion of pulmonary embolism.
Patient Data
Age: 80 years
Gender: Male
From the case:
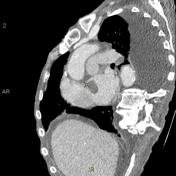
Intracardiac thrombi - left ventricle and atrium



Download
Info
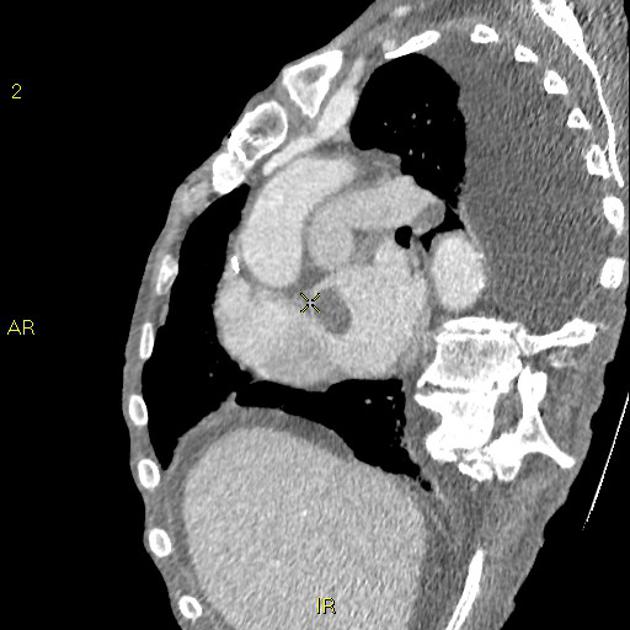
No pulmonary artery embolism noted.
Bilateral pleural effusion noted (left>right), which may explain the patient's dyspnea.
Furthermore, there is a thrombus in the left atrium and one in the apex of the left ventricle.
Case Discussion
Cardiac thrombi are seen in a variety of clinical settings and can result in severe morbidity or even death from embolic events. It can occur following myocardial infarction with ventricular thrombus formation, or with atrial fibrillation and mitral stenosis where atrial thrombi predominate.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.