Presentation
Seizures.
Patient Data
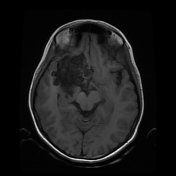

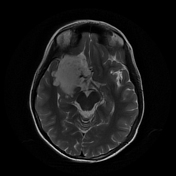

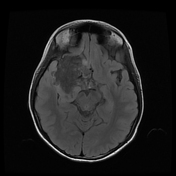

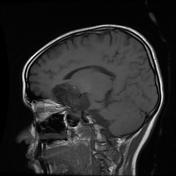

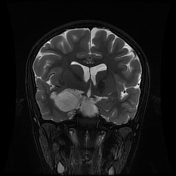

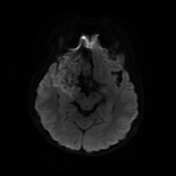

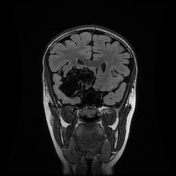

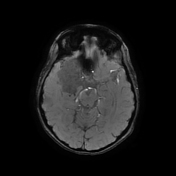

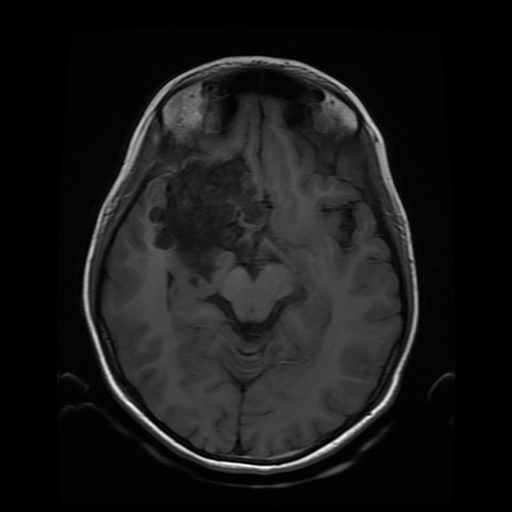
The study reveals an extra-axial cystic lesion, measuring approx. 58 x 50 x 42mm (AP x TD x CC) in the right frontotemporal region. The lesion is causing a significant mass effect on the right temporal lobe including the hippocampus with possible extension into convexity sulci. Compression of the right basifrontal lobe is also seen. The lesion partially encases the supra clinoid segment of the right internal carotid artery, right middle, anterior cerebral arteries, and abutting intracranial part of the right optic nerve/optic chiasma. The lesion appears heterogeneously hyperintense on T2, DWI with intralesional T1 hyperintense areas. No significant perilesional edema is seen. A mild anterior midline shift is seen towards the left side (6.6mm) with mild descending transtentorial herniation.
A possible incidental connatal cyst is seen on the right side. Otherwise, the ventricular system is unremarkable with no significant compression or hydrocephalus.
Case Discussion
The above findings are characteristic of an epidermoid cyst. This is the likely cause of seizures due to the compression of the right temporal lobe and hippocampus.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.