Presentation
Lower abdominal pain. White cell count 11.9 (ref. 4.0-11.0). ?colitis ?diverticulitis.
Patient Data


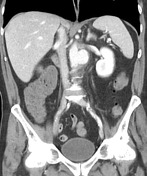

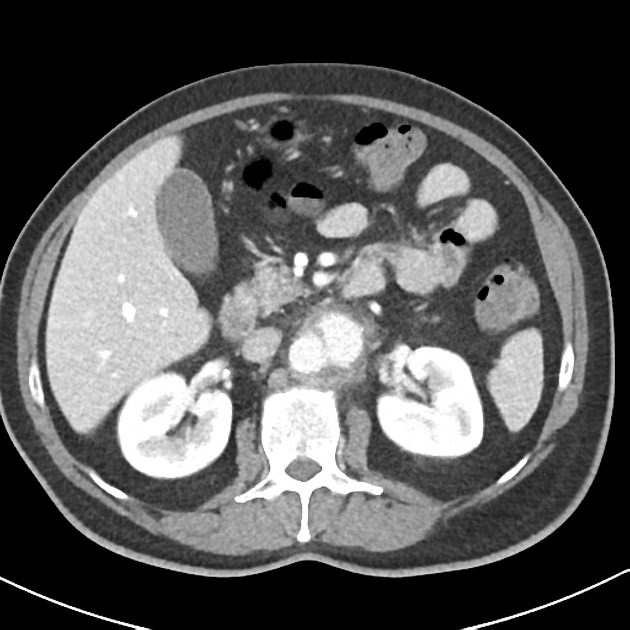
There is a saccular aneurysmal dilatation extending anterolaterally on the left side of the infrarenal abdominal aorta, with a neck of 2.2 cm (longitudinal), depth of 2.3 cm (transverse) and longitudinal extension of 3.5 cm. A thick fat stranding surrounds this vascular dilation and, contrasting to the remainder aorta, no atheromatous calcifications are present in its walls. Inferiorly in the abdominal aorta, a intimal flap with atheromatous calcification is identified crossing the center of the opacified aortic lumen and may represent a chronic dissection.
The liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands are normal. No abnormality of the bowel is identified. There is no free fluid or free gas.
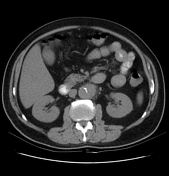
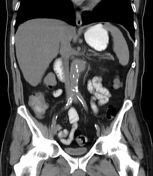
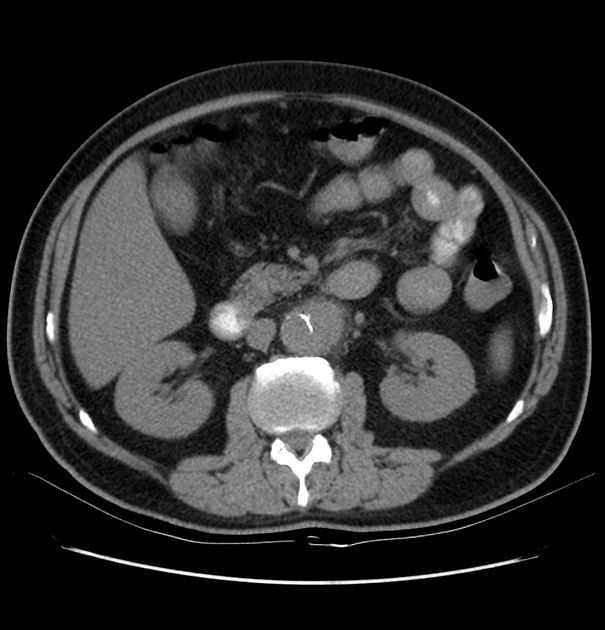
Selected images of the previous CT 5 days prior
Exams performed in the community 5 days prior to the presentation to the ED. Non-contrast images demonstrating the same saccular aneurysm, but with significantly smaller dimensions.
Case Discussion
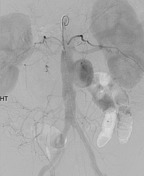
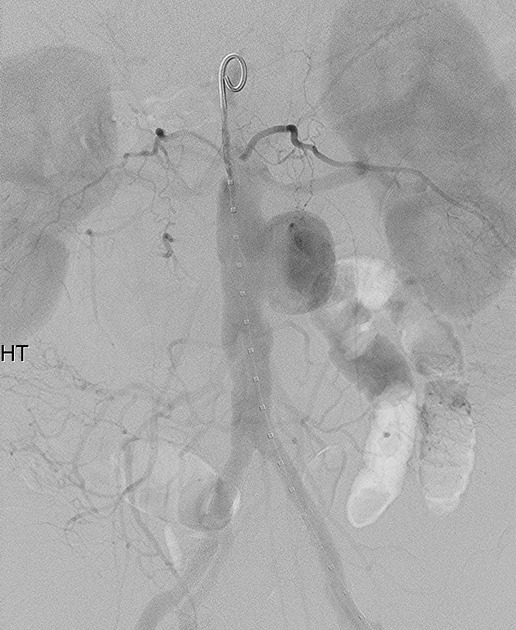
The diagnosis of a mycotic aneurysm was achieved based on the imaging and clinical data. These aneurysms are caused by infection of the arterial wall, usually bacterial. It is a complication of the hematogenous spread of bacterial infection, classically from the heart.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.