Presentation
Recurrent attacks of aphasia, diplopia and bilateral lower limb weakness.
Patient Data


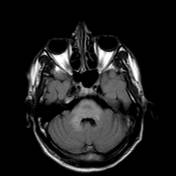


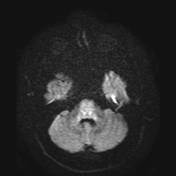




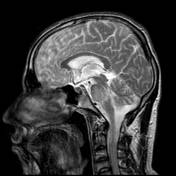

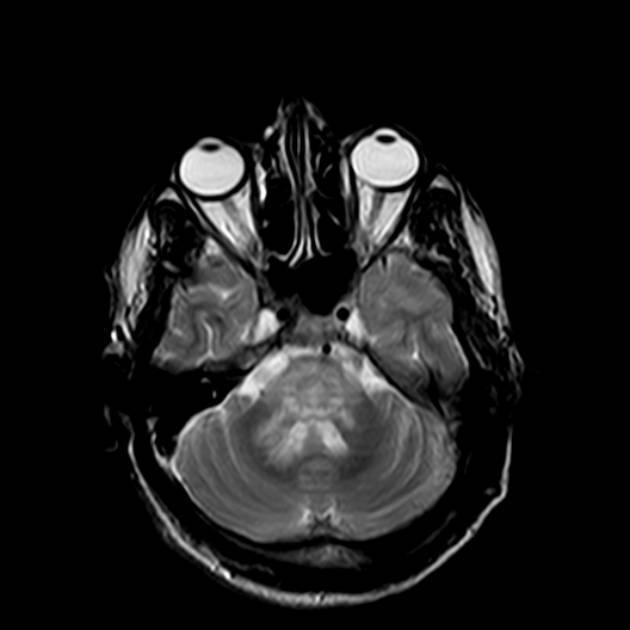
Abnormal signal of the midbrain, pons, middle cerebellar peduncles and anterior medulla.
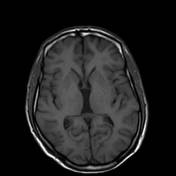
Left basal ganglia multiple small foci of CSF like signal, likely chronic ischemic foci.
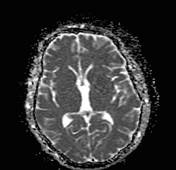
Bilateral high parietal multiple subcortical patches of abnormal signal.
Case Discussion
The patient has a history of Behçet disease.
Behçet disease (BD) is a multisystem vasculitis of unknown origin.
Neurologic involvement includes typical and atypical parenchymal neuro-Behçet disease, dural sinus thrombosis, cerebral arterial aneurysm, occlusion, dissection, and meningitis
Parenchymal neuro-Behçet primarily affects the brainstem (especially the mesodiencephalic junction, around the cerebral peduncles and the pons) or the basal ganglia, thalami, or subcortical white matter.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.