Presentation
Crush injury. Tachycardic but normotensive after fluid resuscitation and blood transfusion.
Patient Data
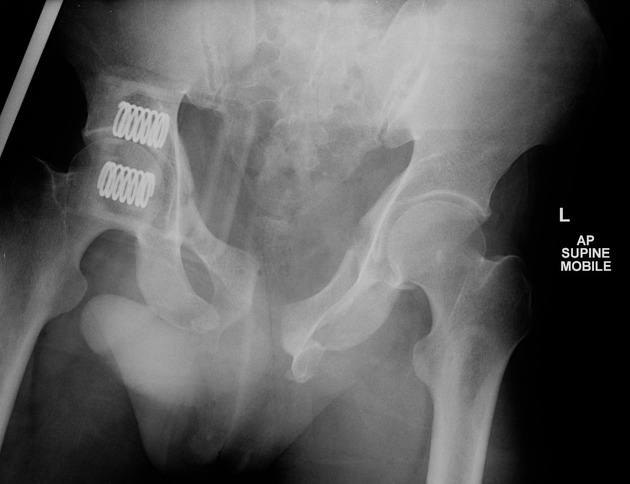
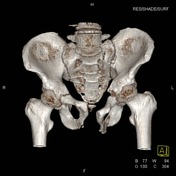
Pubic symphysis distasis with bilateral ischial and inferior pubic rami fractures, and mild widening of the left sacro-iliac joint, in keeping with an "open book" pelvic fracture. Pelvic binder in situ.
Case courtesy Dr Chris Lawson, The Royal Melbourne Hospital.
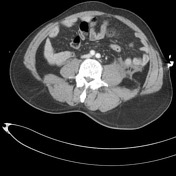

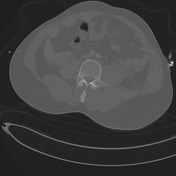

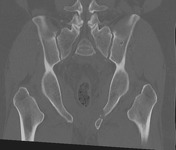


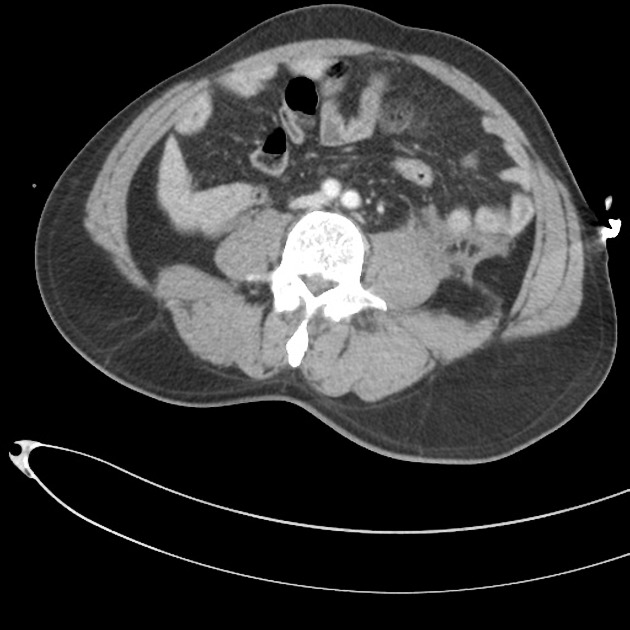
Multiple pelvic fractures through the left sacral mass, left ischium/acetabulum, left superior pubic ramus, right inferior and superior pubic ramus. Widening of the left sacro-iliac joint. Pubic symphysis diastasis.
Associated large hematoma involving adjacent musculature and extra-peritoneal pelvis. Ill defined linear regions of increased density within the pelvic hematoma may represent sites of active bleeding. Hematoma also tracks superiorly along the paracolic gutters and over the psoas muscles.
No solid organ traumatic injury.
Case courtesy Dr Bruno Di Muzio and Dr Di Pascoe, The Royal Melbourne Hospital.
The patient was transferred to radiology, and underwent a successful pelvic angio-embolization. While this was being organized a urethrogram was performed in the emergency department.
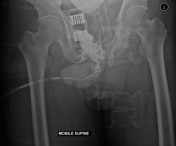
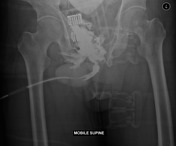
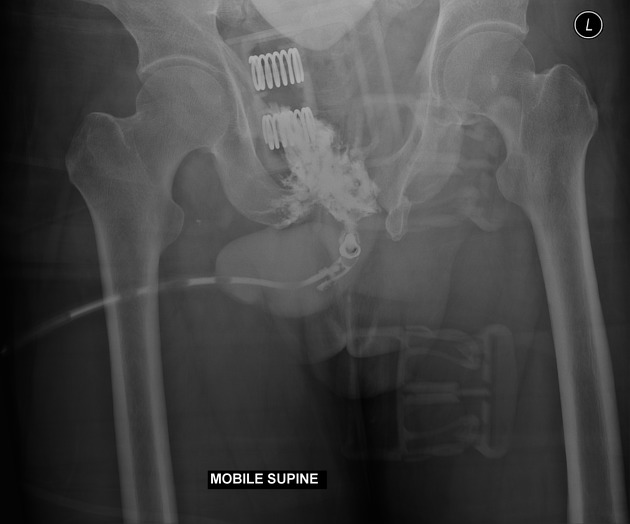
Performed in the emergency department with mobile x-ray (not fluoroscopy).
Multiple pelvic fracture are again demonstrated. Contrast leaks from the urethra with no visible filling of the posterior urethra, consistent with a traumatic urethral injury. Contrast from prior CT fills the partially imaged bladder.
Case Discussion
Traumatic urethral injuries are not an uncommon injury associated with severe pelvic fractures.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.