Presentation
Acute right eye proptosis and painful right eye movement.
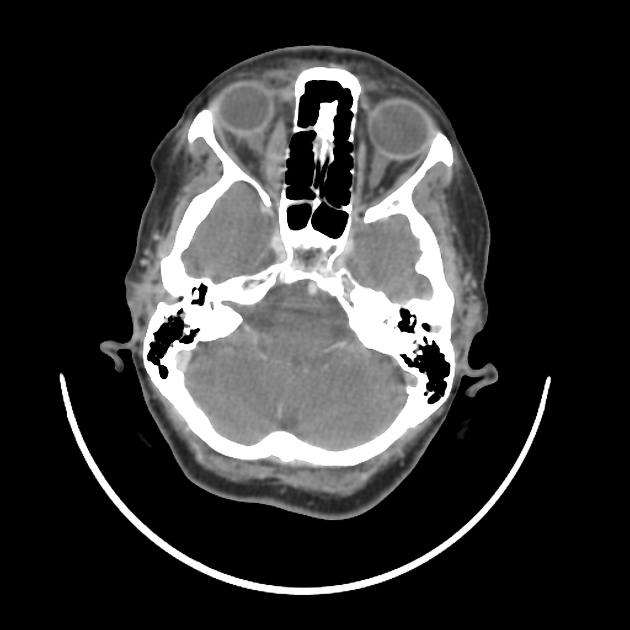
The right medial rectus muscle is diffusely enlarged with moderate homogeneous enhancement with relative involvement of its tendineous insertion. Smudging of the retro-orbital fat is noted as well as mild pre-orbital cellulitis.
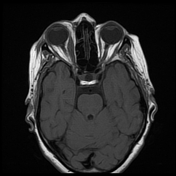

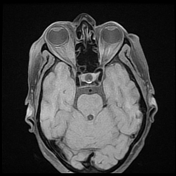

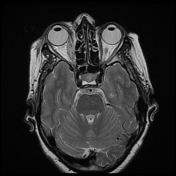

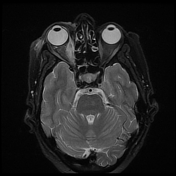

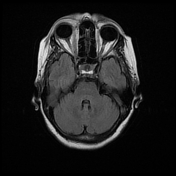

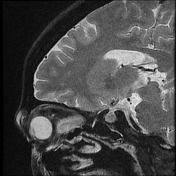

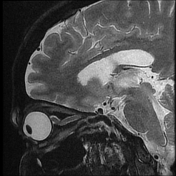

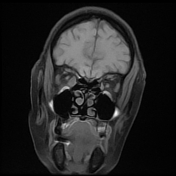





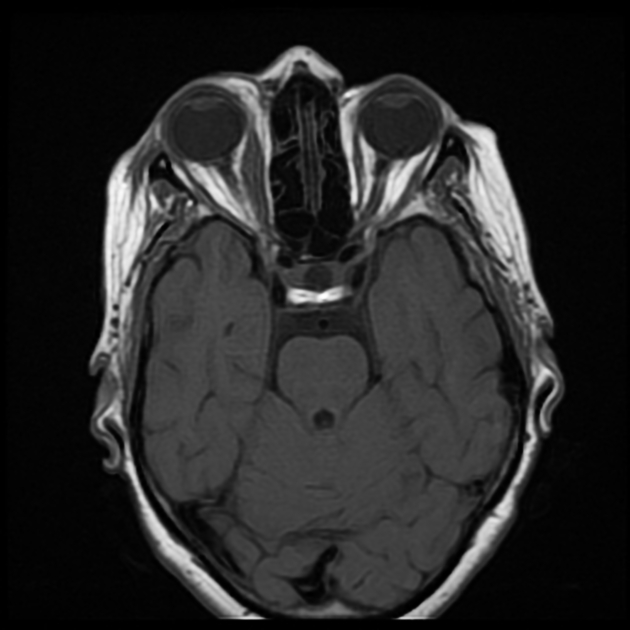
The right medial rectus muscle as well as its tendineous insertions is diffusely enlarged with mildly hypointense T1 as well as hyperintense T2 and FLAIR signal intensity with intense homogeneous post-contrast enhancement. Pre-orbital cellulitis with mild inflammatory changes of the retro-orbital fat is noted with heterogenous post-contrast enhancement. Intact cavernous sinus on either side.
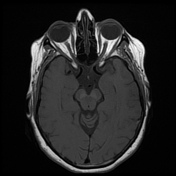

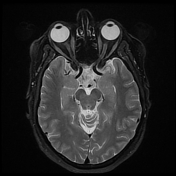

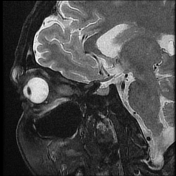

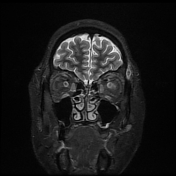

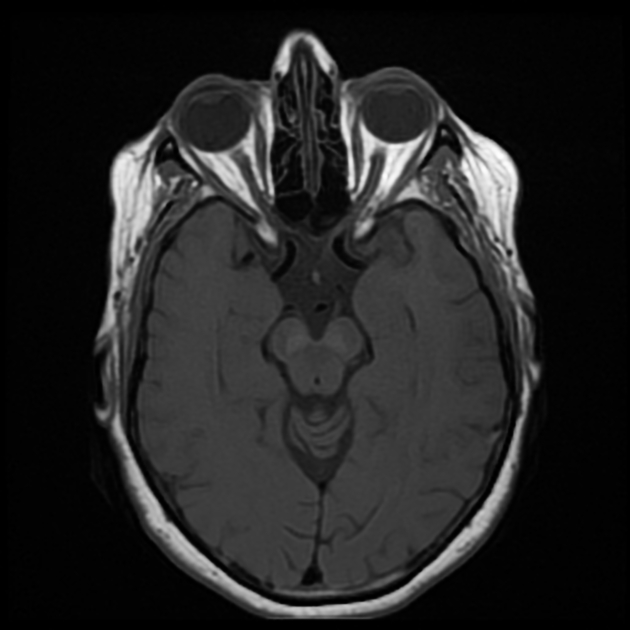
Follow-up MRI of the orbits after treatment with corticosteroids appears unremarkable.
Case Discussion
Right orbital pseudotumor with pre-orbital cellulitis.
Orbital pseudotumor is an idiopathic inflammatory lesion of the orbit most commonly involving the extra-ocular muscles (most commonly the lateral rectus muscle), but can involve any of the orbital contents including the retro-orbital fat and the lacrimal gland.
The differential diagnosis of orbital pseudo-tumor of the orbit is:
- Thyroid orbitopathy (Grave's disease): usually sparing the anterior tendon of the extra-ocular muscles and is limited to the muscle belly. The inferior and medial rectus muscles are commonly involved followed by the superior and lateral rectus & oblique muscles (I'M SLOw!)
- Orbital lymphoma: homogeneously enhancing intraorbital mass usually separable from the extra-ocular muscles. Painless swelling with proptosis.
- Tolosa-Hunt syndrome: the orbital inflammatory lesion involves the orbital apex with extension into the cavernous sinus.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.