Presentation
Sever sudden pelvic pain. Ovarian mass was suspected on ultrasound.
Patient Data
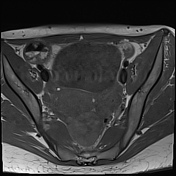

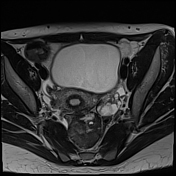

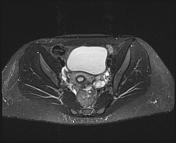

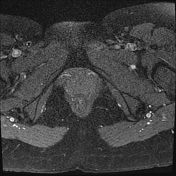

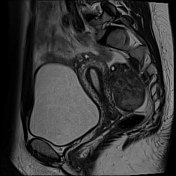

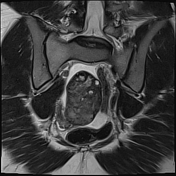

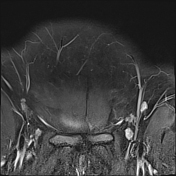

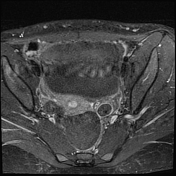

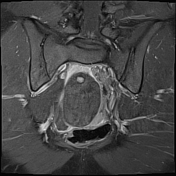

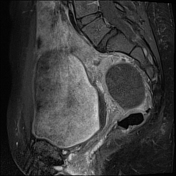




The right ovary is midline in position, large and heterogeneous measuring 6.7x 4.7 cm, mild pushing the uterus anteriorly and to the right side, with multiple small mainly peripheral follicles inside, one of them is hyperintense on T1W suggestive of blood or proteinaceous material. It is surrounded by a clear mild amount of fluid collection.
Slightly heterogeneous high signal intensity seen in T1W and central high signal on STIR represents congestion and edematous changes. No evidence of fatty component.
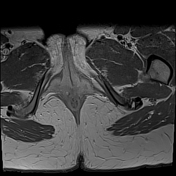
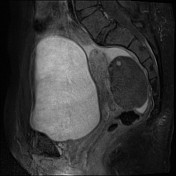
There is no normal enhancement seen in the right ovary after contrast administration.
The left ovary is normal in size, shape, and contour and shows a normal stromal enhancement pattern.
Features are highly in favor of right ovarian torsion with engorgement and hemorrhagic necrotic changes.
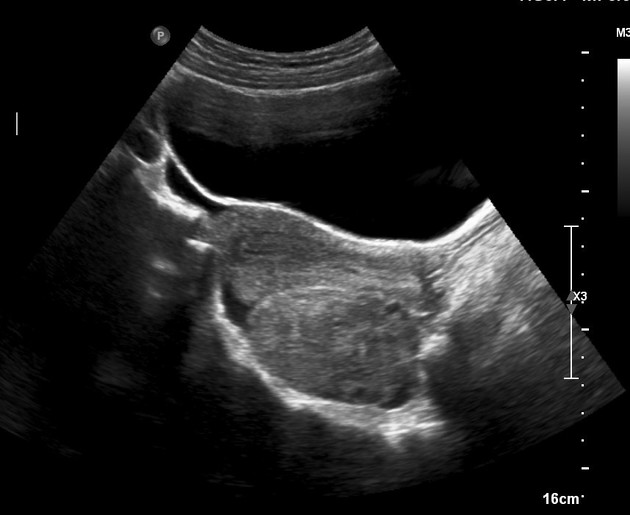
Complementary ultrasound was done after the MRI study and shows the right ovary is enlarged with echogenic stroma. No evidence of color flow seen inside confirming MRI diagnosis. Normal left ovary.
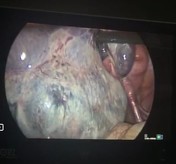

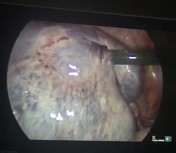
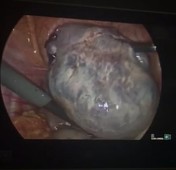
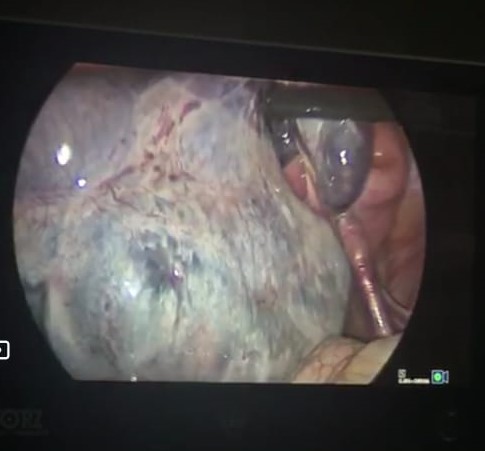
Laparoscopic images show grossly enlarged and engorged right ovary.
No underlying focal lesion was seen.
Case Discussion
The patient had an ultrasound scan twice, five and two days before the MRI scan.
The first examination was normal and the second was suspecting an ovarian tumor so that the MRI was arranged which reveals features of torsion and complementary ultrasound after MRI also confirming the MRI findings.
The patient was referring to the gynecologist who admitted the patient and surgery was done which showing that the ovary twisted 7 times around its vascular pedicle with hemorrhagic foci. No underlying pathology was seen.
According to the surgeon, surgical untwisting was done and salpingo-oophorectomy was not performed.



 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.