Presentation
Persistent low back pain.
Patient Data





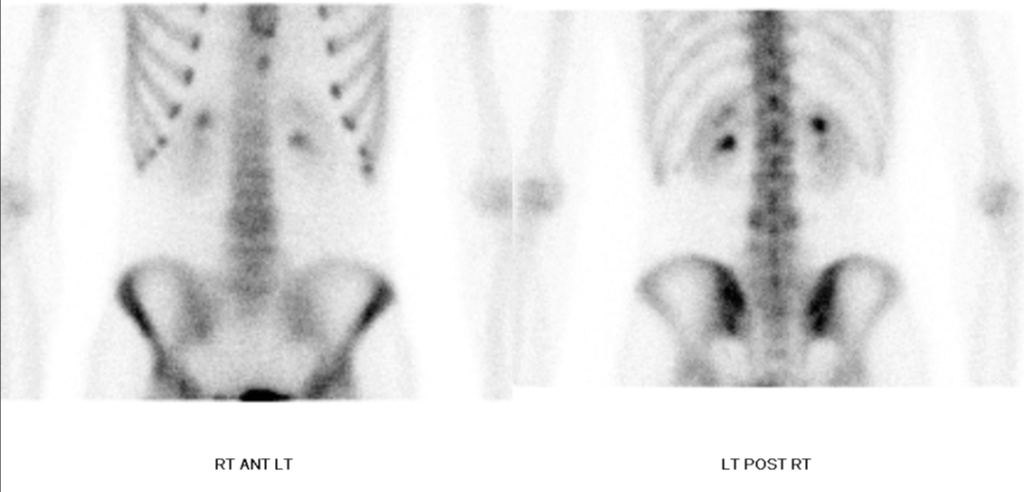
Limited planar images of the lumbar spine obtained 3 hours after radiotracer injection show mild increased osteoblastic activity involving the posterior elements of L4.
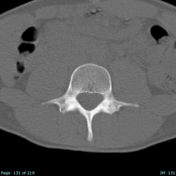
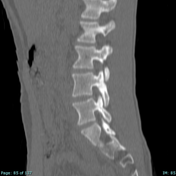
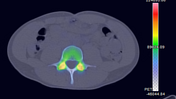
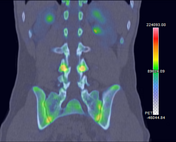
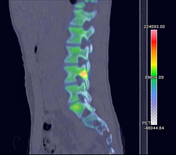
SPECT MIP and SPECT-CT of the lumbar spine show the uptake to localize to the pars interarticularis of L4. Uptake is greater on the right versus the left.
CT from SPECT-CT acquisition shows subtle sclerosis without fracture lucency or lithesis, consistent with a grade I stress reaction (Hollenberg classification system).
Case Discussion
Injury of the pars interarticularis is a well-recognized cause of low back pain in adolescent athletes. It is a spectrum of findings including, in its earliest form, a bone stress injury, and progressing to spondylolysis (a non-displaced fracture of the pars interarticularis) and eventually spondylolisthesis (anterior subluxation of the effect vertebra in relation to the one below).
Bone scintigraphy is very sensitive for the detection of bone stress injuries. Bone stress, typically due to repetitive microtrauma, results in osseous remodeling and amplified osteoblastic activity, resulting in abnormally increased uptake of the radiotracer.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.