Presentation
Fell onto right hip with tenderness on palpation. Post-operative internal fixation for right proximal femur fracture performed 3 days after initial presentation.
Patient Data
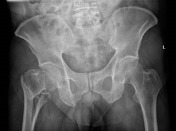
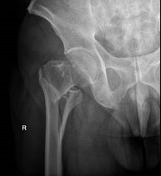

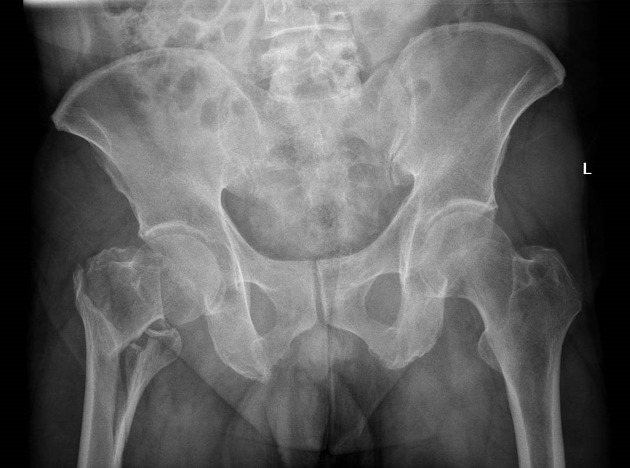
There is a mildly displaced, comminuted intertrochanteric fracture of the right femur. The femoral heads are enlocated. No pelvic fracture is seen.
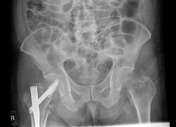
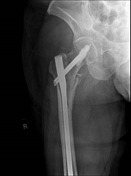

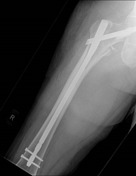
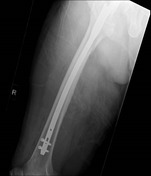
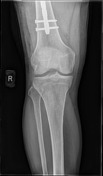
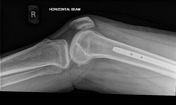
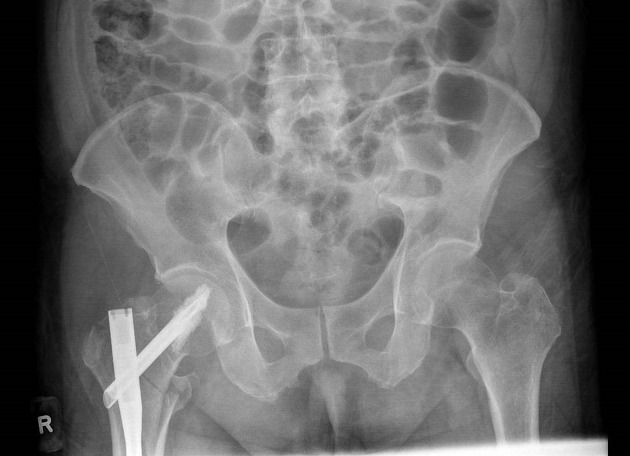
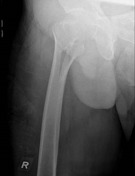
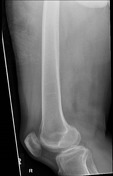
Internal fixation of the right proximal femoral fracture is seen with expected post-surgical soft tissue changes in the right proximal thigh in the gluteal region. The knee joint is congruent albeit with a small suprapatellar effusion.
Case Discussion
In this case, the patient has sustained a mildly displaced intertrochanteric fracture, which is often stabilised using surgical means. Doing so will prevent propagation and completion, subsequent displacement, or other injuries that may require a more invasive surgical approach 1. A proximal femoral nail (PFN) fixation is one of the surgical treatments for proximal femoral fractures and is used in this case.
Implant position, fragment position and fracture healing can be evaluated with an anteroposterior view and lateral radiograph of the implant. Radiographers performing post-operative imaging for such patients should ideally ensure that the entire length of the PFN can be assessed in a single image.
Post-operative notes on the implant used:
Synthex long TFNA 10 mm 360 mm
helical blade 105 mm
4 mL cement
distal locking bolt 46 mm and 48 mm
Notably, the Synthex long TFNA includes a helical blade, which categorises it as a PFN or, more specifically, a proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA).
It is important to note that due to the absence of an antirotation pin, there is a risk of the implant being mistaken for a long gamma nail if clinical information is not provided or the radiographs are not closely examined. Accurate distinction is hence crucial for proper identification and subsequent management of the fracture.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.