Presentation
Man with cerebral palsy. New onset of swelling over dorsum of right hand and disuse of right arm.
Patient Data

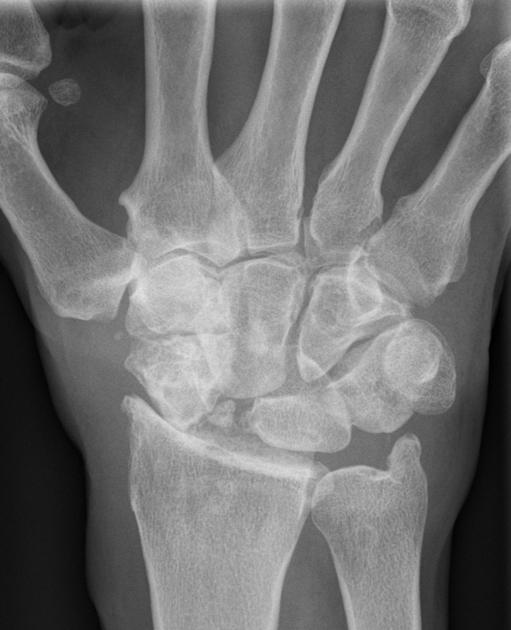
Anterior-posterior wrist radiograph shows advanced degenerative arthritis in the radioscaphoid > scaphoid-trapezium-trapezoid (STT) > scapholunate > capitolunate articulations. The radiolunate articulation is relatively spared. There is abnormal widening of the scapholunate interval with an osseous fragment interposed within the scapholunate interval. This is suggestive of chronic scaphoid non-union. There is loss of parallelism of the first and second carpal arc, with collapse of the mid-carpal joint.
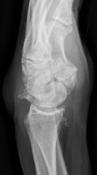
The lateral wrist radiograph demonstrates significant dorsal tilting of the lunate with dorsal subluxation of the capitate. The findings are in keeping with a dorsal intercalated segmental instability (DISI) deformity.
For those with an eye for detail, there is soft tissue swelling over the dorsum of the wrist.
The soft tissue swelling over the dorsum of the wrist was further investigated with an ultrasound examination (not shown) and this confirmed an acute rupture of extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) and extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) with hematoma/synovial effusion in the second extensor compartment.
Case Discussion
SLAC (scapholunate advanced collapse) refers to a specific pattern of osteoarthritis and subluxation which results from untreated chronic scapholunate dissociation or from chronic scaphoid non-union. In the case example, the likely culprit is chronic scaphoid non-union. The pattern of sequential degenerative arthritis of the wrist includes arthritis between the scaphoid, lunate, and radius (57%), arthritis between the scaphoid, trapezium, and trapezoid (27%) and a combination of these two patterns (15%).1




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.