Scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC) & dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI)
Presentation
Post-traumatic wrist instability
Patient Data


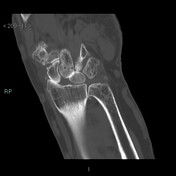

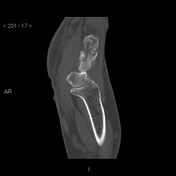


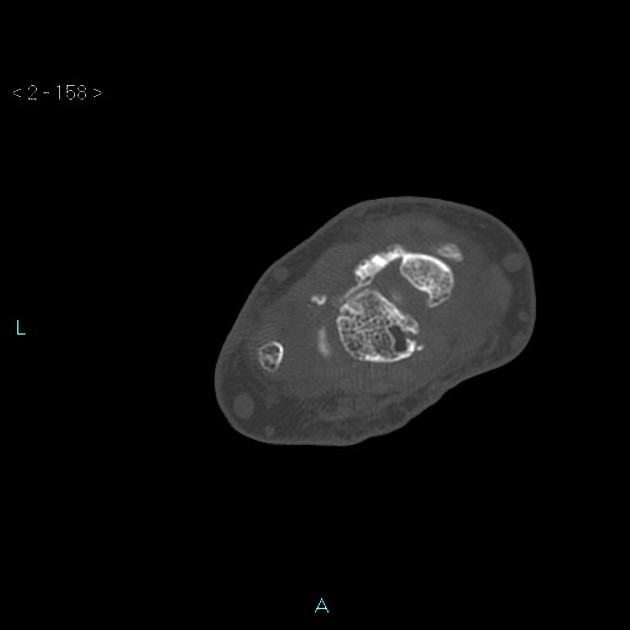
There is marked diastasis of the scapholunate articulation due to complete tear of the scapholunate ligament, with proximal migration, between the two bones, of the capitate (SLAC stage III: radioscaphoid involvement, scaphocapitate and lunocapitate).
The lunate is directed in the dorsal direction with respect to the capitate (DISI).
Associated radioscaphoid joint space reduction due to degenerative joint disease.
Scaphotrapeziotrapezoid (STT) osteoarthritis.
Negative ulnar variance.
Case Discussion
Scaphoid pseudarthrosis and untreated chronic ligament injuries can produce changes in the biomechanics of the carpus that give rise to arthrosis of the wrist. In this case, the instigating injury was a ruptured scapholunate ligament.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.