Presentation
Headache, visual disturbance
Patient Data
Age: 45 years
Gender: Male
From the case:
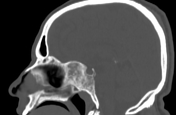
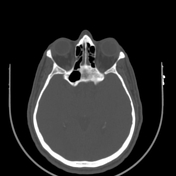
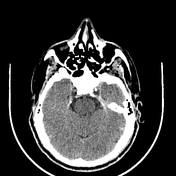
Sphenoid bone fibrous dysplasia





Download
Info
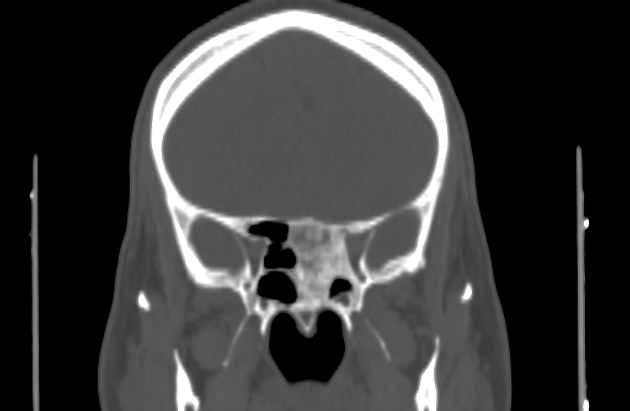
Note is made of bone expansion, with ground-glass opacity in the sphenoid sinus region with sclerotic rim, involving the base of the skull, causing regional mass effect, obliterating both sphenoid sinuses, indenting the left optic canal, subsequently compressing intracanalicular part of the optic nerve.
Case Discussion
Ground-glass attenuation of sphenoid bone likely sphenoid bone fibrous dysplasia.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.