Stress shielding after osteosynthesis humeral head displaced fracture
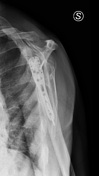
Presentation
Fell on outstretched arm.
Patient Data
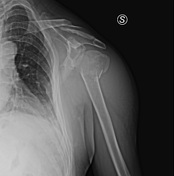
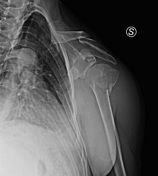
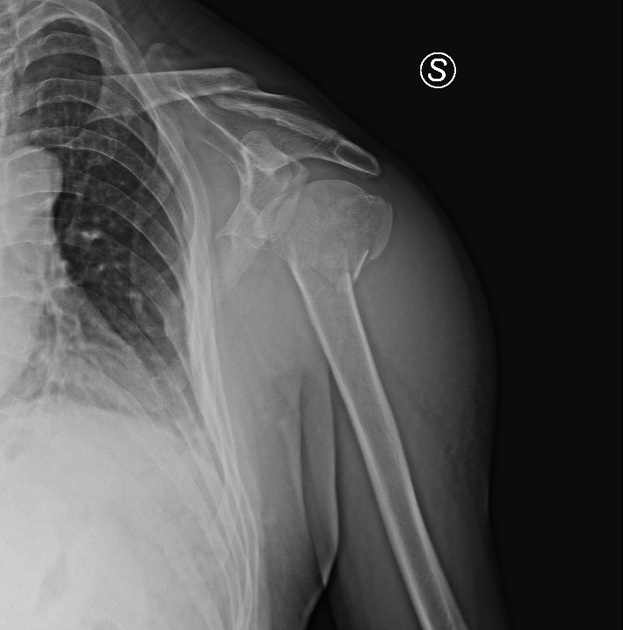
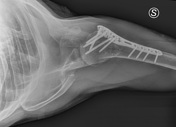
A valgus-impacted displaced proximal humeral fracture.
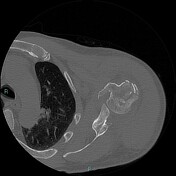

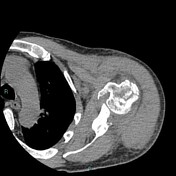

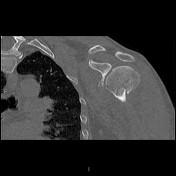

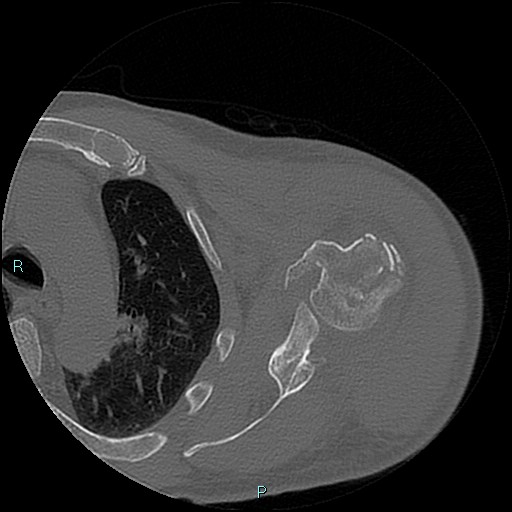
Displaced proximal humeral fracture involving the surgical neck, greater tuberosity, and lesser tuberosity with hemarthrosis. These fractures are denoted as four part fractures in Neer classification of proximal humeral fractures. There are consolidated outcomes of displaced fracture of the clavicle.
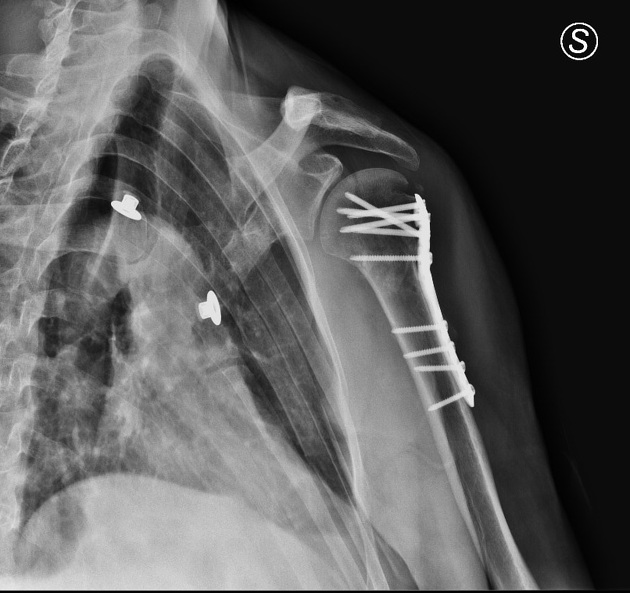
Post operative x-ray
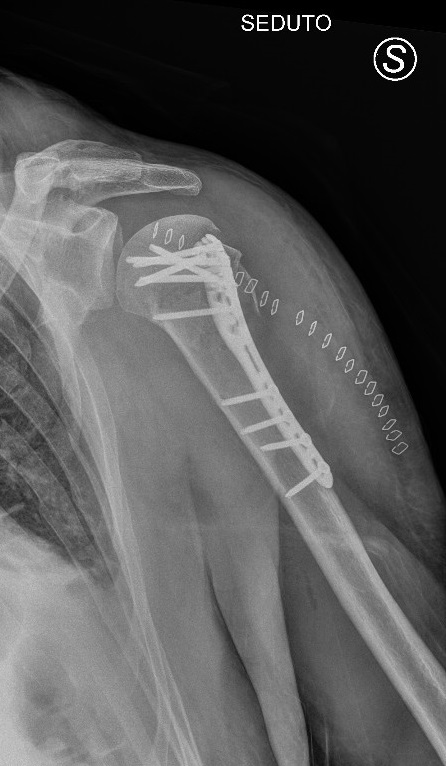
Osteosynthesis with locking plate and screw fixation for proximal humerus fracture with realignment of the fracture.
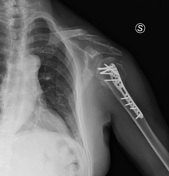
Follow up after two months
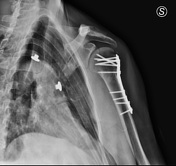
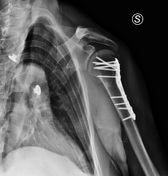
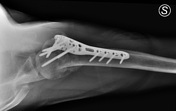
Diffuse bone osteoporosis caused by rigid plate and screw fixation with thinning of the cortex.
Follow up after four months

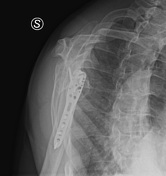
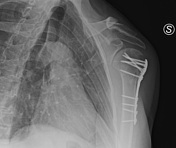
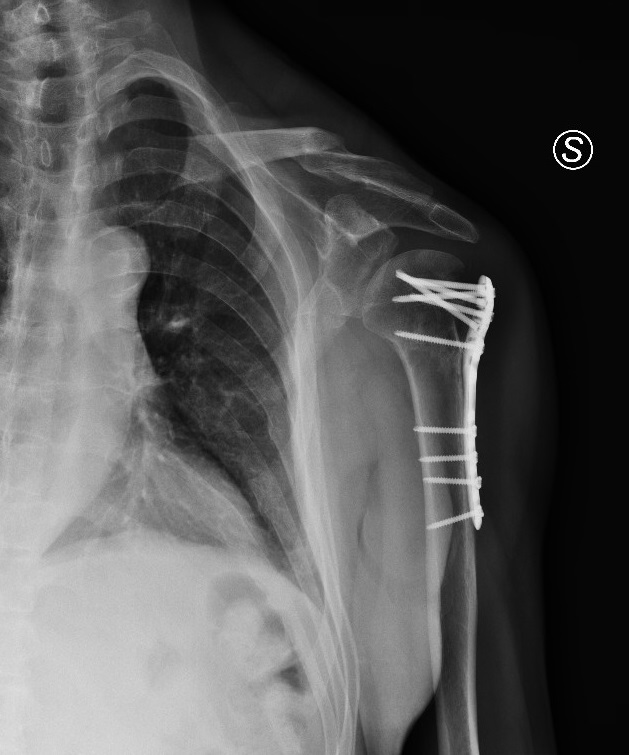
A pronounced reduction of cortical bone in the diaphysis of the plated bone.
Case Discussion
Stress shielding occurs when metal implants, such as bone plate and screw fixation, are used to repair fractures or in joint replacement surgery. Rigid metal plates stabilize the fracture site, maintain contact between bone fragments, and allow early mobility of the limb, but the higher stiffness of the implant results in bone loss as a result of decreased physiologic loading of the bone, influenced by plate geometry, plate stiffness, and plate location, according to Wolff's law. Osteoporosis caused by rigid plate and screw fixation occurs by thinning of the cortex under the plate as a result of endosteal resorption.
Case Courtesy of Dr.ssa Laura Braccaioli
Radiographer: TSRM Fabio Imola




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.