Presentation
Spiky like pubic pain radiating to the penis, severe urinary frequency, urgency, hesitancy, and intermittent retention. Background of recurrent urinary tract infections.
Patient Data

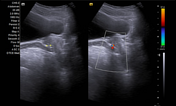
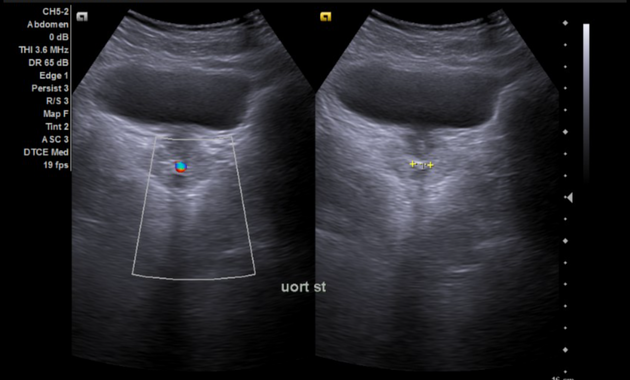
Transverse and longitudinal views of the urinary bladder and prostate.
Average size prostate with slightly increased urinary bladder wall thickness, suggestive of cystitis.
Repeat scanning post-void demonstrated minimal change in residual urine volume, and the patient stated micturition difficulty. Close interrogation of the prostatic urethra revealed a focal hyperechoic lesion with posterior acoustic shadows. On color Doppler, the lesion was associated with a twinkling artifact, suggesting urethral stone.
Case Discussion
Typical sonographic features of urinary tract calculi in grayscale are the same with hyperechoic solid objects and posterior acoustic shadows.
The presence of a twinkling artifact in color Doppler is suggestive of urethral calculus.
Also, attention to the patient complaints and insignificant change of post-void residual bladder volume are clues for the diagnosis.
Non-enhanced computed tomography is diagnostic. Cystoscopy is diagnostic and therapeutic.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.