Presentation
Out of hospital arrest. Intubated.
Patient Data
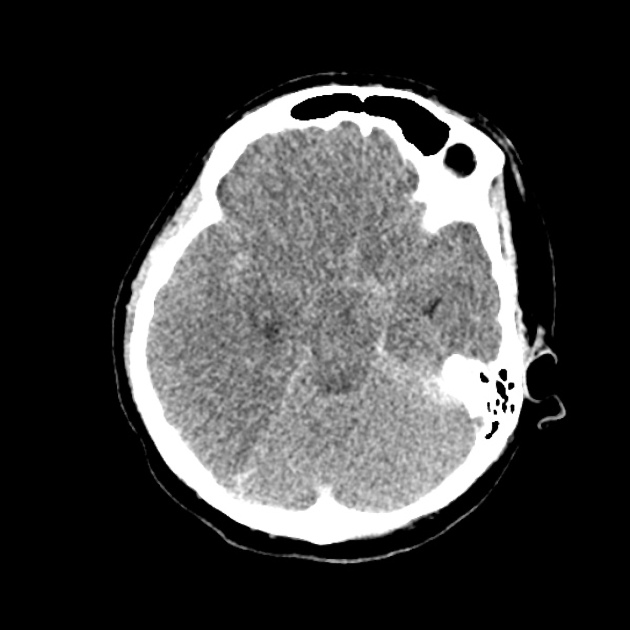
Reversal of normal attenuation of the supra and infratentorial brain - the cerebellum is denser ('white').
Loss of grey-white matter differentiation in the cerebral hemispheres.
Effacement of basal cisterns and sulci.
Impression of blood in the basal cisterns - pseudosubarachnoid hemorrhage.
Case Discussion
White cerebellum sign, also called reversal sign or dense cerebellum sign, is encountered when there is a diffuse decrease in density of the supratentorial brain parenchyma, with relatively increased attenuation of the thalami, brainstem and cerebellum.
This sign indicates irreversible brain damage and has a very poor prognosis.
One of the commonest causes is cerebral anoxia, typically from a prolonged cardiac arrest.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.