Anterior communicating artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Francis Deng had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Francis Deng's current disclosures- Anterior communicating artery (ACOM)
- ACOM
- ACOMs
- Anterior communicating arteries
- AComm
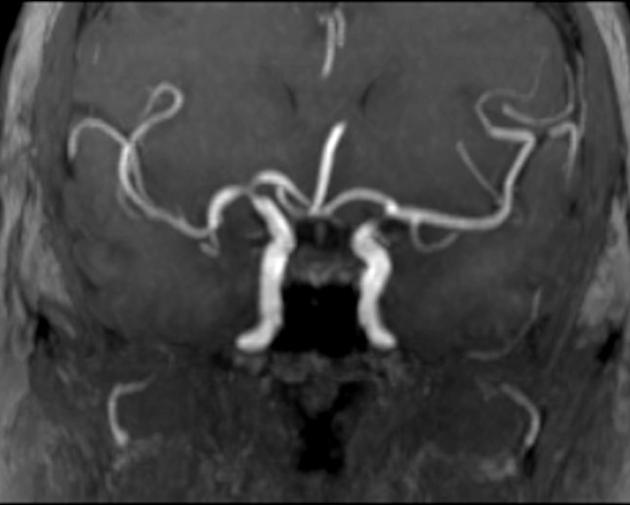
The anterior communicating artery (often abbreviated ACom or AComm) arises from the anterior cerebral artery and acts as an anastomosis between the left and right anterior cerebral circulation. Approximately 4 mm in length, it demarcates the junction between the A1 and A2 segments of the anterior cerebral artery.
Branches
The anterior communicating artery gives off numerous small branches that go on to supply the following structures:
anterior columns of the fornix
para-olfactory areas
Variant anatomy
anterior communicating artery duplication: incidence 18%
anterior communicating artery fenestration: incidence ~15% (range 12-21%)
anterior communicating artery origin of frontopolar artery, resulting in an anterior cerebral artery "trifurcation" or "triplication" appearance: incidence ~7.5% (range 2-13%)
absent anterior communicating artery: incidence 5% (at surgical dissection) 2
If the vessel is not well seen on routine angiography, cross-compression view of the anterior cerebral artery/anterior communicating artery complex can be performed.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. (2015) ISBN: 0702052302 - Google Books
- 2. Dimmick S & Faulder K. Normal Variants of the Cerebral Circulation at Multidetector CT Angiography. Radiographics. 2009;29(4):1027-43. doi:10.1148/rg.294085730 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Brain arterial vascular territories
- Hypothalamus
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (A)
- Circle of Willis
- Lamina terminalis
- Azygos anterior cerebral artery
- Amnestic syndrome of the subcallosal artery
- Intracranial arterial fenestration
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Orbitofrontal artery
- Congenital absence of the internal carotid artery
- Cistern of the lamina terminalis
- Fornix (brain)
- Anterior cerebral artery hypoplasia or absence
- Pericallosal artery
- ِAnterior communicating artery aneurysm
- ACOM and right M1 fenestrations
- Anterior communicating artery aneurysm with subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Rupture of anterior communicating artery aneurysm
- Ruptured ACom aneurysm
- Ruptured intracranial aneurysm: small aneurysm with large haemorrhage
- Ruptured intracranial aneurysm: small aneurysm with large haemorrhage
- Median artery of the corpus callosum
- Anterior communicating artery
- Anterior communicating artery fenestration
- Anterior communicating artery aneurysm
- Colloid cyst with anterior communicating artery aneurysm
- Anterior communicating artery aneurysm and left canal wall down mastoidectomy
- Anterior communicating artery aneurysm
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage due to ruptured berry aneurysm
- Anterior communicating artery aneurysm
- Ruptured ACom aneurysm with subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Anterior cerebral arterial variations
- Cross compression view of the ACOM
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway


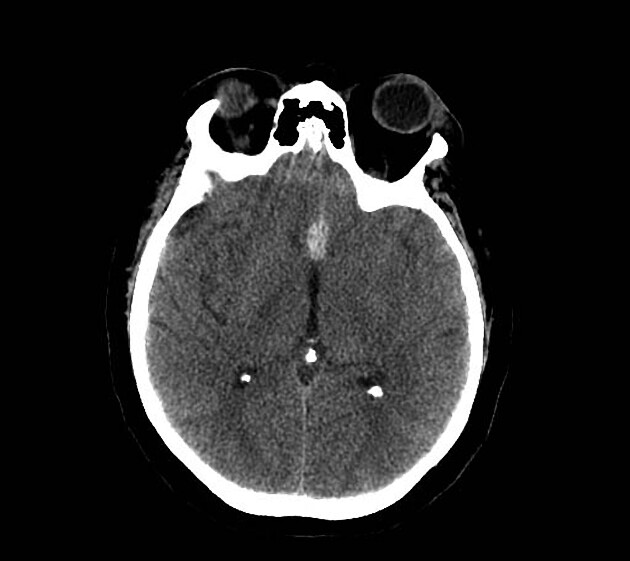


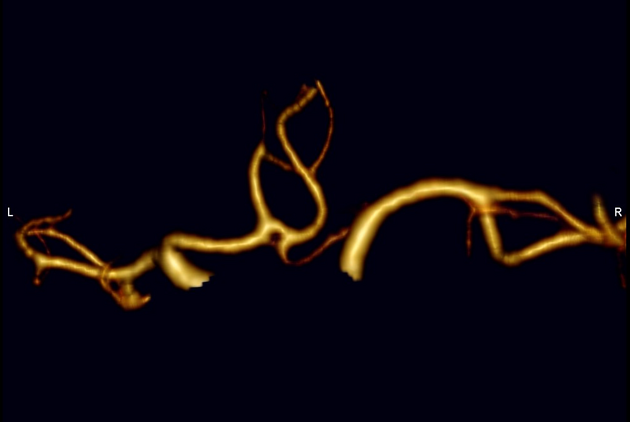
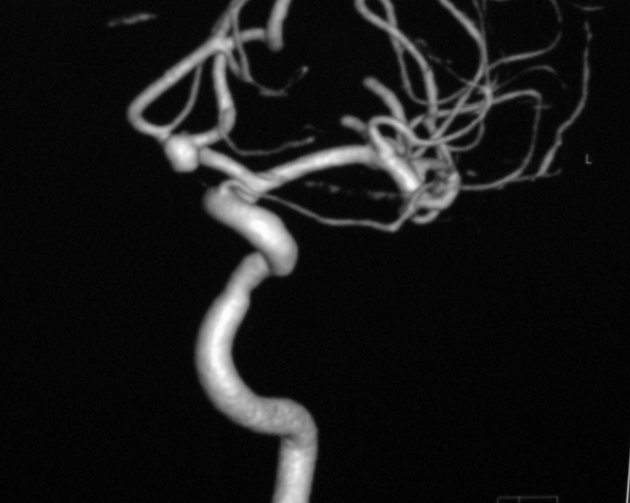
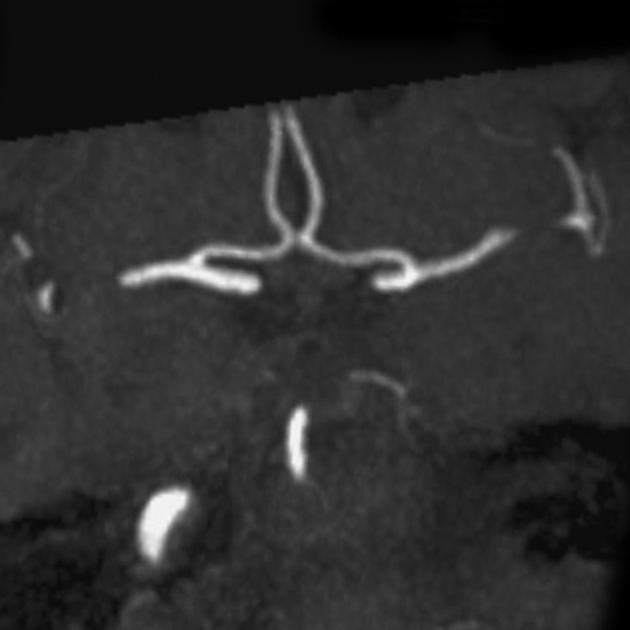



 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.