Basilar artery fenestration
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised David Puyó had no recorded disclosures.
View David Puyó's current disclosures- Basilar fenestration
- Fenestration of the basilar artery
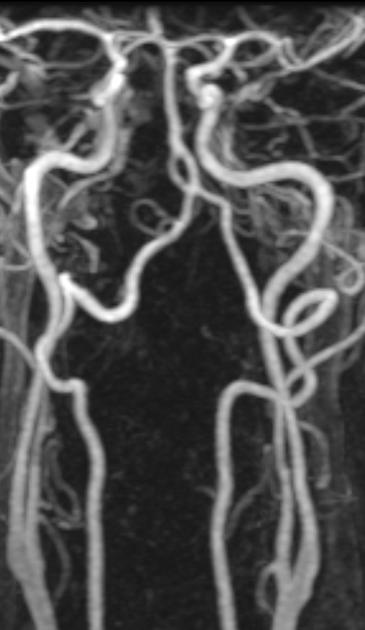
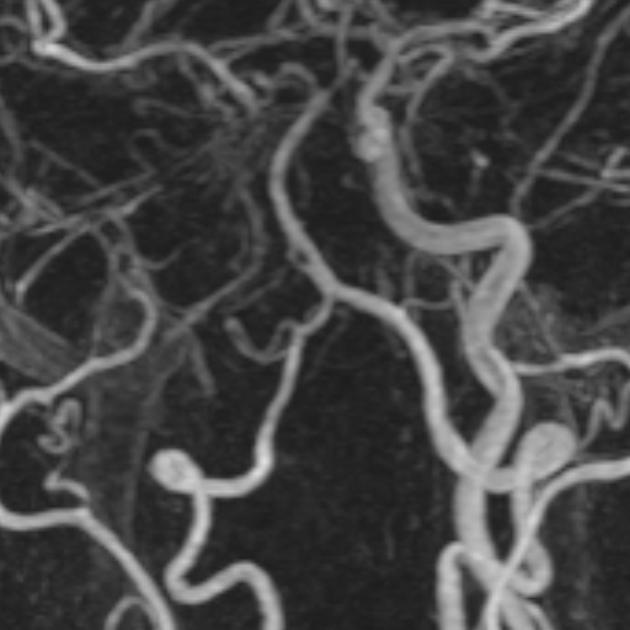
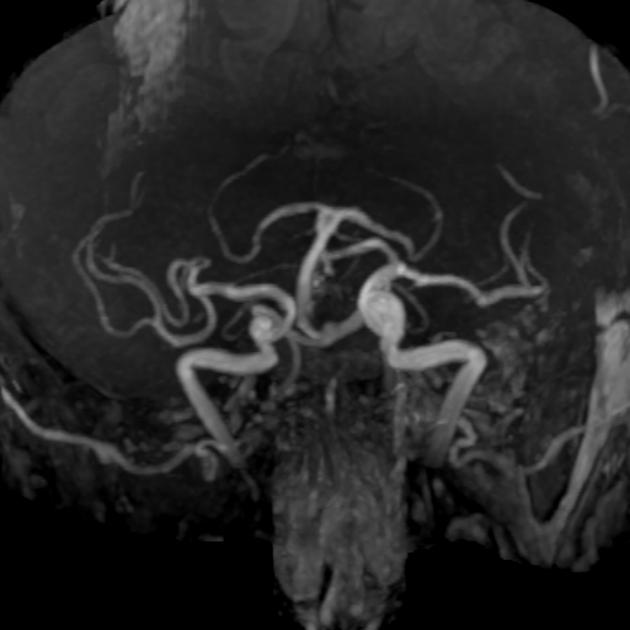
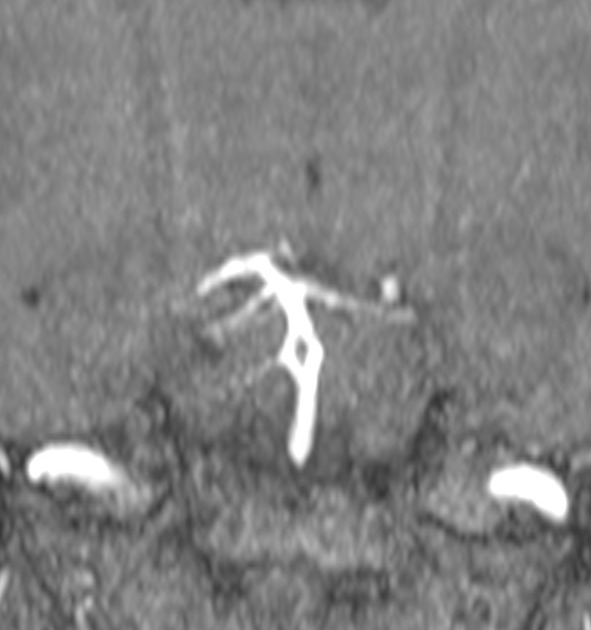
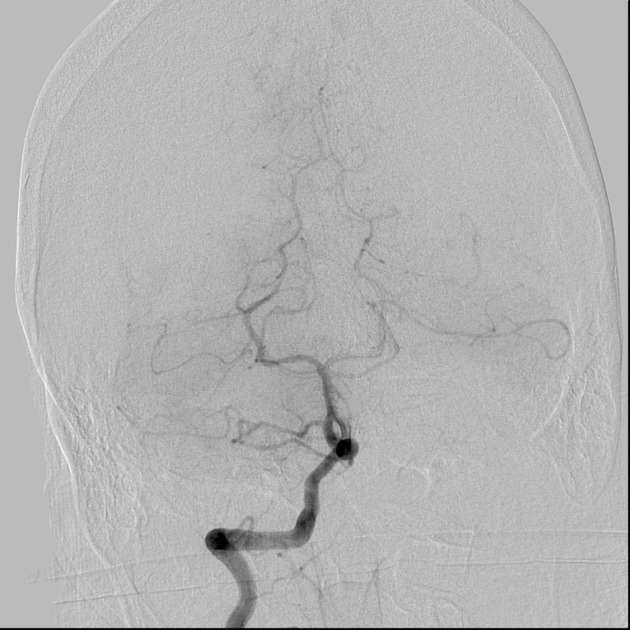
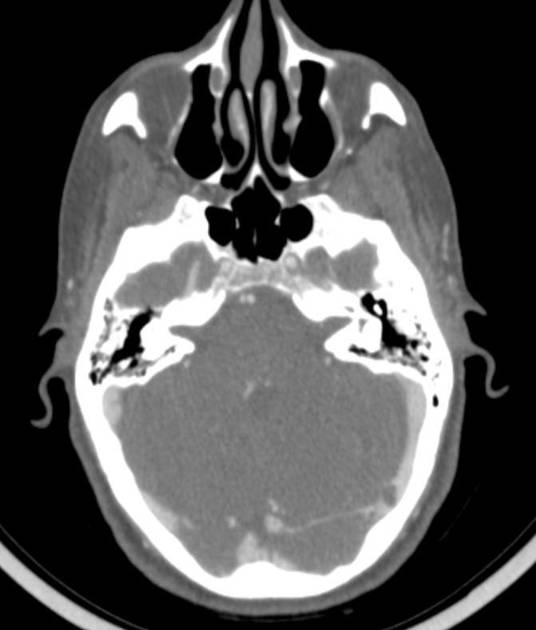
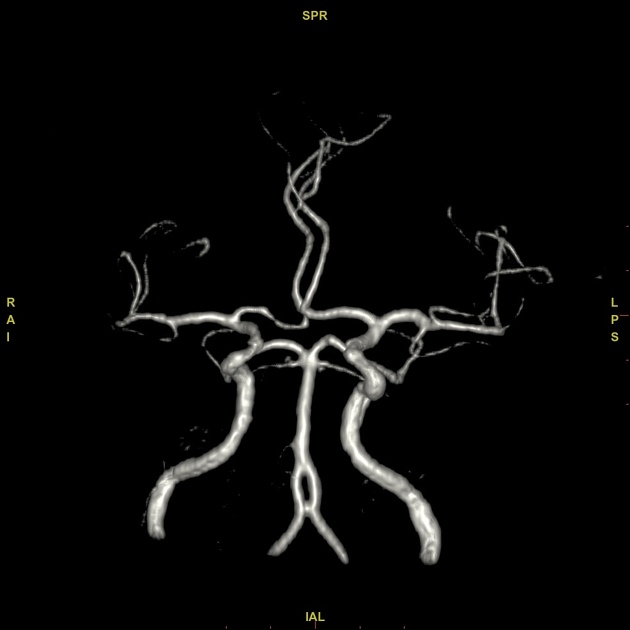
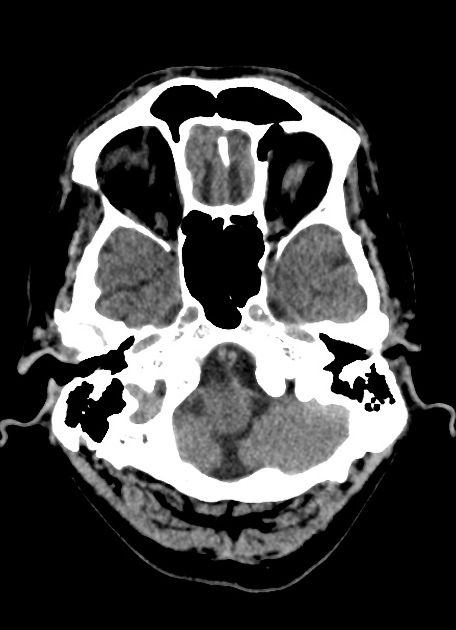
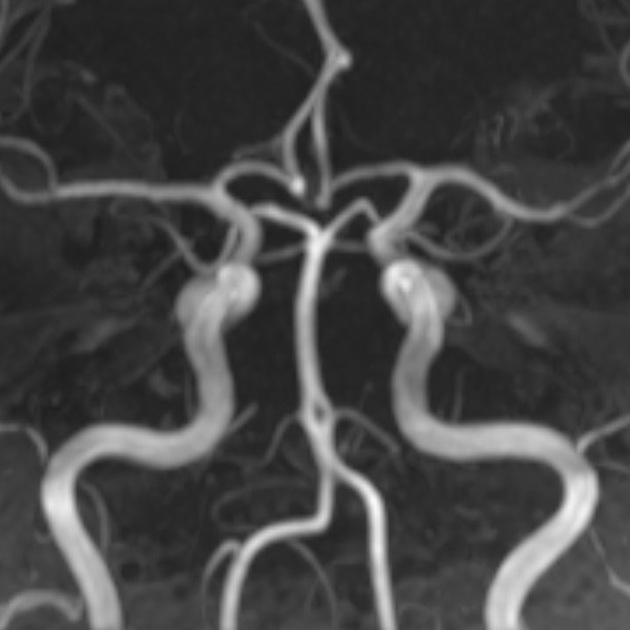
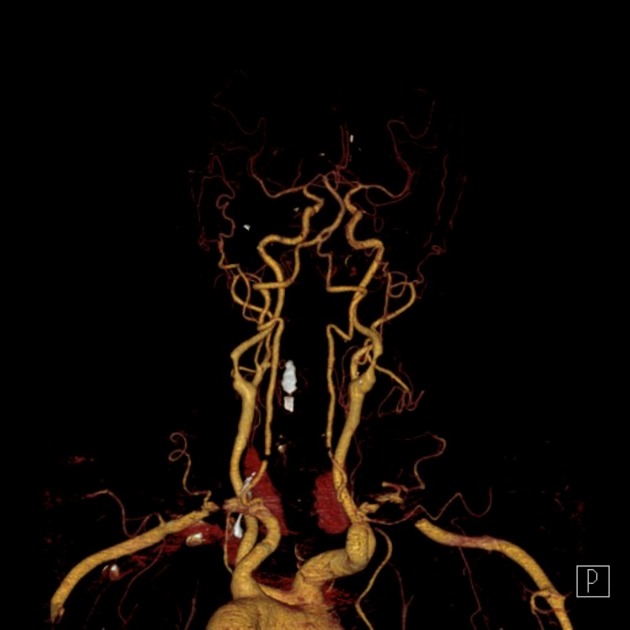
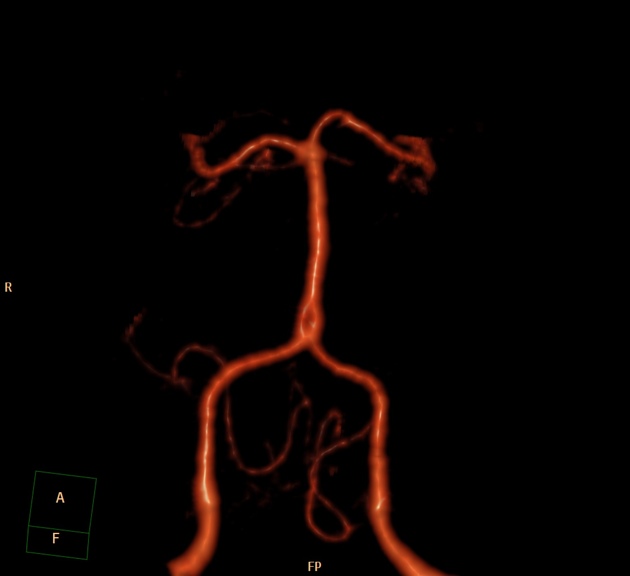
Basilar artery fenestration (or more simply, basilar fenestration) is the most common intracranial arterial fenestration and most common congenital anomaly of the basilar artery. This anatomic variant is characterised by duplication of a portion of the artery that are connected proximally and distally.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Its reported prevalence is highly variable depending on the technique used:
- angiography: 0.6% 3 (presumably low due to preferential laminar flow in only one lumen at a time)
- CT angiography: 2.4% 2
- MR angiography: 1-2% 19
- autopsy: up to 5% 5
Pathology
An arterial fenestration is a segmental duplication wherein a single lumen divides into two lumens, both lined by endothelium, that rejoin to one distally.
Fenestrations vary in size. At one extreme, basilar septation is a rare variant considered to be a miniature/aberrant basilar fenestration 8. At the other extreme, complete duplication can be considered extreme fenestration of the basilar artery 9.
Aetiology
Fenestration is thought to occur due to failed fusion of plexiform primitive longitudinal neural arteries 4.
Location
Basilar fenestration typically occurs at the lower end of the basilar artery just as the vertebral arteries join. However, it can also be seen in the mid-basilar and distal tip.
Treatment and prognosis
Basilar fenestration is generally considered an anatomic variant not requiring observation or treatment. However, adverse sequelae have been reported in the literature.
Complications
Fenestration may predispose to basilar artery aneurysm formation, presumably due to abnormal flow dynamics, but the magnitude of risk is inconsistent across studies 1,6,12. Fenestration-associated aneurysms most often occur at the vertebrobasilar junction, followed by the basilar trunk, and are usually saccular in morphology 7. The reported prevalence of aneurysms in cases of basilar fenestration is 7% 3.
Thromboembolic posterior circulation infarcts have been reported with basilar artery fenestration 10-18.
Differential diagnosis
The main differential consideration for a small fenestration is an acquired focal arterial dissection with a raised intimal flap dividing true and false lumens.
References
- 1. Tasker A & Byrne J. Basilar Artery Fenestration in Association with Aneurysms of the Posterior Cerebral Circulation. Neuroradiology. 1997;39(3):185-9. doi:10.1007/s002340050389 - Pubmed
- 2. Bharatha A, Aviv R, White J, Fox A, Symons S. Intracranial Arterial Fenestrations: Frequency on CT Angiography and Association with Other Vascular Lesions. Surg Radiol Anat. 2008;30(5):397-401. doi:10.1007/s00276-008-0340-7 - Pubmed
- 3. Dimmick S & Faulder K. Normal Variants of the Cerebral Circulation at Multidetector CT Angiography. Radiographics. 2009;29(4):1027-43. doi:10.1148/rg.294085730 - Pubmed
- 4. Cademartiri F, Stojanov D, Dippel D, Van Der Lugt A, Tanghe H. Noninvasive Detection of a Ruptured Aneurysm at a Basilar Artery Fenestration with Submillimeter Multisection CT Angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(10):2009-10. PMC8148929 - Pubmed
- 5. Wollschlaeger G, Wollschlaeger P, Lucas F, Lopez V. Experience and Result with Postmortem Cerebral Angiography Performed as Routine Procedure of the Autopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1967;101(1):68-87. doi:10.2214/ajr.101.1.68 - Pubmed
- 6. Guo X, Gao L, Shi Z et al. Intracranial Arterial Fenestration and Risk of Aneurysm: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;115:e592-8. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2018.04.106 - Pubmed
- 7. Sturiale C, Stifano V, Della Pepa G et al. Intracranial Aneurysms of the Posterior Circulation Associated with a Fenestration: A Systematic Review. J Neurosurg Sci. 2019;63(5). doi:10.23736/s0390-5616.18.04225-x
- 8. Small J, Macey M, Wakhloo A, Sehgal S. CTA Evaluation of Basilar Septations: An Entity Better Characterized as Aberrant Basilar Fenestrations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42(4):701-7. doi:10.3174/ajnr.a7008 - Pubmed
- 9. Goldstein J, Woodcock R, Do H, Phillips C, Dion J. Complete Duplication or Extreme Fenestration of the Basilar Artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20(1):149-50. - Pubmed
- 10. Kloska S, Schlegel P, Sträter R, Niederstadt T. Causality of Pediatric Brainstem Infarction and Basilar Artery Fenestration? Pediatr Neurol. 2006;35(6):436-8. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.06.013 - Pubmed
- 11. Gold J & Crawford J. An Unusual Cause of Pediatric Stroke Secondary to Congenital Basilar Artery Fenestration. Case Reports in Critical Care. 2013;2013:1-3. doi:10.1155/2013/627972 - Pubmed
- 12. Tanaka M, Kikuchi Y, Ouchi T. Neuroradiological Analysis of 23 Cases of Basilar Artery Fenestration Based on 2280 Cases of MR Angiographies. Interv Neuroradiol. 2006;12(1_suppl):39-44. doi:10.1177/15910199060120s103 - Pubmed
- 13. Wu X, Lin A, Zhu J, Cai B. Basilar Artery Fenestration: An Unusual Possible Cause of Ischaemic Stroke? BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018:bcr-2017-222910. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-222910 - Pubmed
- 14. Miyamoto N, Ueno Y, Hira K et al. Characteristics of Clinical Symptoms, Cerebral Images and Stroke Etiology in Vertebro-Basilar Artery Fenestration-Related Infarction. Brain Sciences. 2020;10(4):243. doi:10.3390/brainsci10040243 - Pubmed
- 15. Ha S, Kim H, Kim B. Bilateral Pontine Infarction with Basilar Artery Fenestration: A Case Report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(32):e21530. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000021530 - Pubmed
- 16. Scherer A, Siebler M, Aulich A. Virtual Arterial Endoscopy as a Diagnostic Aid in a Patient with Basilar Artery Fenestration and Thromboembolic Pontine Infarct. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002;23(7):1237-9. PMC8185723 - Pubmed
- 17. Woo S, Seo M, Kim Y et al. Extreme Duplication-Type, Nonseparated Fenestration of the Basilar Artery in a Patient with Pontine Infarction: Confirmation with Virtual Arterial Endoscopy. J Clin Neurol. 2006;2(1):74. doi:10.3988/jcn.2006.2.1.74 - Pubmed
- 18. Berry A, Kepes J, Wetzel M. Segmental Duplication of the Basilar Artery with Thrombosis. Stroke. 1988;19(2):256-60. doi:10.1161/01.str.19.2.256
- 19. Arráez-Aybar L, Villar-Martin A, Poyatos-Ruiperez C, Rodriguez-Boto G, Arrazola-Garcia J. Prevalence of Fenestrated Basilar Artery with Magnetic Resonance Angiography: A Transversal Study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012;35(6):487-93. doi:10.1007/s00276-012-1053-5 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Vertebral artery fenestration
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Fenestration of the right vertebral artery V3 segment
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Basilar artery fenestration
- Striatocapsular haemorrhage and fenestrated basilar artery
- Basilar artery distal tip fenestration
- Fenestrated basilar artery
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.