Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Weerakkody Y, Silverstone L, Farhadi M, et al. Broncholith. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 25 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-24032
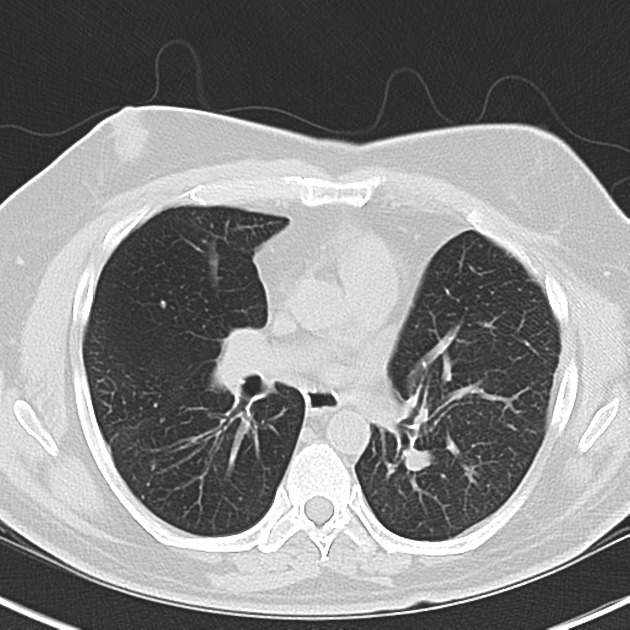
Broncholith refers to focal calcified endobronchial material which usually follows erosion by a granulomatous peribronchial lymph node (e.g. TB) 13. This can cause distal atelectasis, bronchiectasis or mucoid impaction.
dry cough
haemoptysis
fever, chest pain, rigors: due to obstructive pneumonia
-
lithoptysis: coughing up of broncholith(s)
A broncholith is usually formed by erosion by and extrusion of a calcified adjacent lymph node into the bronchial lumen and is usually associated with long-standing foci of necrotising granulomatous lymphadenitis. Other causes of broncholithiasis include
aspiration of bone tissue or in situ calcification of aspirated foreign material
erosion by and extrusion of calcified or ossified bronchial cartilage plates
migration to a bronchus of calcified material from a distant site, e.g. pleural plaque or the from the kidney (nephrobronchial fistula)
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
CT
Calcified opacity within a bronchus. There may be associated distal lung collapse or airway dilatation / mucoid impaction.
Broncholithiasis is more common on the right, and obstructive changes particularly affect the right middle lobe.
Treatment and prognosis
In some cases they may be left alone while in other cases, they can be removed safely by rigid bronchoscopy with the aid of Nd-YAG laser photocoagulation 9.
Imaging differential considerations include 4
-
1. Seo JB, Song KS, Lee JS et-al. Broncholithiasis: review of the causes with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2002;22 Spec No (suppl 1): S199-213. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
-
2. Conces DJ, Tarver RD, Vix VA. Broncholithiasis: CT features in 15 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157 (2): 249-53. doi:10.2214/ajr.157.2.1853800 - Pubmed citation
-
3. Shin MS, Ho KJ. Broncholithiasis: its detection by computed tomography in patients with recurrent hemoptysis of unknown etiology. J Comput Tomogr. 1983;7 (2): 189-93. Pubmed citation
-
4. Eurorad teaching files : Case 11427
-
5. Arrigoni MG, Bernatz PE, Donoghue FE. Broncholithiasis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1971;62 (2): 231-7. Pubmed citation
-
6. Ferretti G, Coulomb M, Blanc-Jouvan F et-al. Diagnosis of broncholithiasis. Role of high resolution tomodensitometry. J Radiol. 1995;75 (10): 531-6. Pubmed citation
-
7. Menivale F, Deslee G, Vallerand H et-al. Therapeutic management of broncholithiasis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005;79 (5): 1774-6. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2003.10.124 - Pubmed citation
-
8. Ryberg AA, Gengler JS, Angelillo VA et-al. Broncholithiasis: case report and literature review. Nebr Med J. 1996;81 (1): 14-7. Pubmed citation
-
9. Nollet AS, Vansteenkiste JF, Demedts MG. Broncholithiasis: rare but still present. Respir Med. 1999;92 (7): 963-5. Pubmed citation
-
10. Theriault M, Eddy K, Borgaonkar J, et al. Diseases Involving the Central Bronchi: Multidetector CT for Detection, Characterization, and Differential Diagnosis. Radiographics: a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 38 (1) 2018
-
11. Krishnan S, Kniese CM, Mankins M, et al. Management of broncholithiasis. (2018) Journal of thoracic disease. 10 (Suppl 28): S3419-S3427. doi:10.21037/jtd.2018.07.15 - Pubmed
-
12. Andy Adam, Adrian K. Dixon, Cornelia Schaefer-Prokop et al. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology, 2 Volume Set. (2020) ISBN: 9780702075247 - Google Books
-
13. Bankier A, MacMahon H, Colby T et al. Fleischner Society: Glossary of Terms for Thoracic Imaging. Radiology. 2024;310(2):e232558. doi:10.1148/radiol.232558 - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.