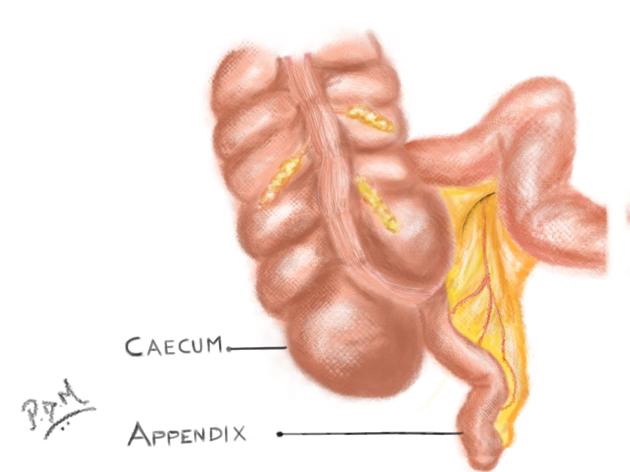
Caecum
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Cecum
- Caeca
- Ceca
- Caecums
- Cecums
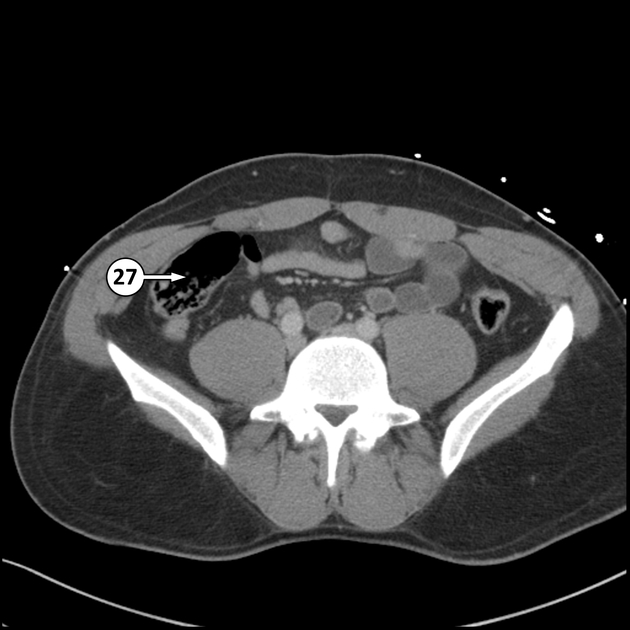
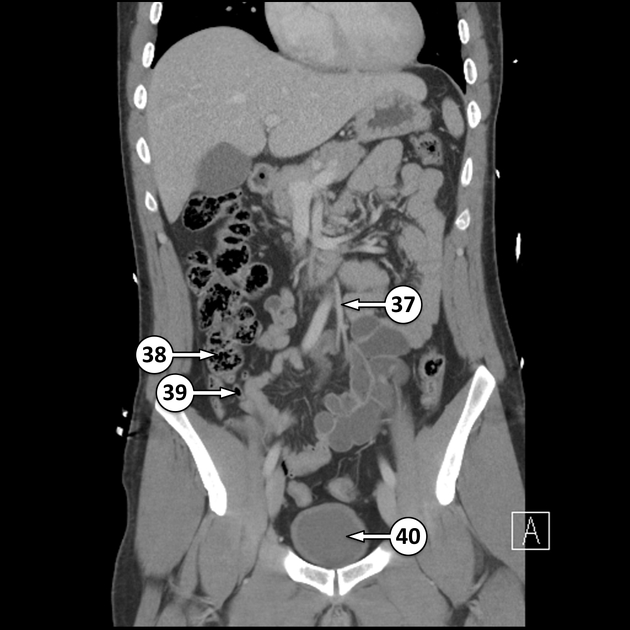
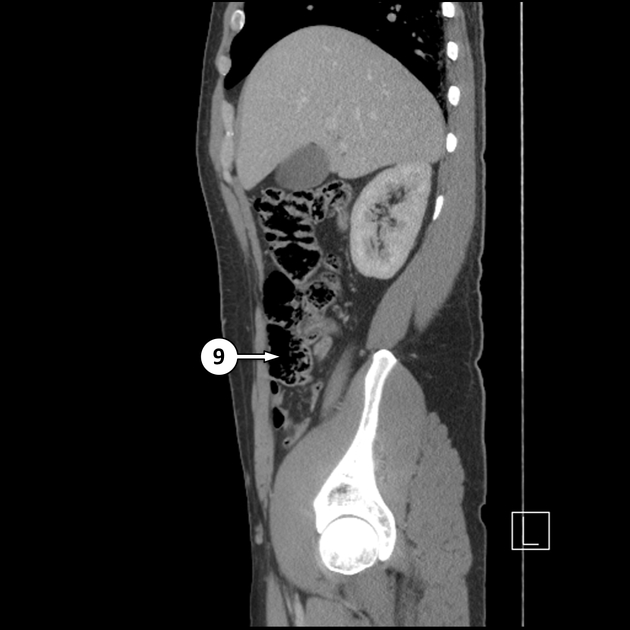
The caecum (plural: caeca or caecums) is the first part of the large bowel and lies in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Blind-ending sac of bowel that lies below the ileocaecal valve, above which the large intestine continues as the ascending colon. The caecum measures 6 cm in length and can have a maximum diameter of 9 cm before it is considered abnormally enlarged. The vermiform appendix typically arises from the posteromedial surface, 2 cm inferior to the ileocaecal valve 1.
The caecum is covered by peritoneum, except posteriorly where it has a layer of loose connective tissue and it has a variable mesentery 1.
The superior margin of the caecum is defined by the ileocaecal ostium. Upper and lower flaps consisting of smooth muscle protrude into the lumen around the ostium forming the ileocaecal valve 2. Its competence is often shown by the lack of contrast reflux into the terminal ileum on contrast enema studies.
Relations
anterior: parietal peritoneum, anterior abdominal wall, and loops of small bowel
posterior: iliacus muscle, psoas muscle, femoral nerve, lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, genitofemoral nerve and variably, the appendix
medial: ileocaecal valve and terminal ileum
lateral: right paracolic gutter, anterior superior iliac spine
superior: ascending colon
inferior: the lateral third of the inguinal ligament
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Arterial supply
anterior and posterior caecal arteries from the colic artery, a branch of the ileocolic artery from the superior mesenteric artery
Venous drainage
run with corresponding arteries to the superior mesenteric vein, a tributary of the portal venous system
Lymphatic drainage
lymphatic network runs parallel to the arterial supply, to paracolic lymph nodes, which drain to the superior mesenteric group
Innervation
sympathetic supply via the superior mesenteric plexus
parasympathetic supply via fibres from the anterior and posterior vagal trunks
Variant anatomy
subhepatic caecum: failure of the caecum to migrate to its typical position during midgut rotation in embryogenesis 3
-
right colonic mesentery fails to fuse to the lateral peritoneum 4
occurs in ~15% of the population 4
Related pathology
History and etymology
Caecum is short for the Latin term "intestinum caecum", which means blind gut.
References
- 1. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy et al. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 2. Cornelius Rosse, Penelope Gaddum-Rosse, William Henry Hollinshead. Hollinshead's Textbook of Anatomy. (1997) ISBN: 0397512562 - Google Books
- 3. B. S. Mitchell, Ram Sharma. Embryology. (2009) ISBN: 9780702032257 - Google Books
- 4. Toprak H, Bilgin M, Atay M, Kocakoc E. Diagnosis of Appendicitis in Patients with Abnormal Position of the Appendix Due to Mobile Caecum. Case Rep Surg. 2012;2012:921382. doi:10.1155/2012/921382 - Pubmed
- 5. Silva A, Beaty S, Hara A et al. Spectrum of Normal and Abnormal CT Appearances of the Ileocecal Valve and Cecum with Endoscopic and Surgical Correlation. Radiographics. 2007;27(4):1039-54. doi:10.1148/rg.274065164 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Bowel and mesenteric trauma
- Subhepatic appendicitis
- Barium studies of the small bowel
- Organomegaly
- Large bowel obstruction
- Ileum
- Necrotising enterocolitis
- Typhlitis
- Lesser sac hernia
- Caecal bascule
- Appendiceal mucocele
- Right hemicolectomy
- Ascending colon
- Midgut volvulus
- Duplex appendix
- Abdominal hernia
- Amoebic colitis
- Cecal volvulus
- Indirect inguinal hernia
- CT colonography reporting and data system
- Caecum adenocarcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma of the cecum
- Complicated Crohn disease
- Appendicitis
- Cecal volvulus
- Acute appendicitis
- Subhepatic acute appendicitis
- Acute appendicitis with appendicolith
- Mobile caecum syndrome
- Appendicular mucocele with pseudomyxoma peritonei
- Intestinal obstruction due to adhesions
- Caecal adenocarcinoma
- Incomplete intestinal malrotation
- Barium enema (anatomy quiz)
- Gallstone ileus
- Meckel diverticulitis
- Appendicitis with localised perforation and abscess formation
- Appendicitis and appendicolith
- Caecal volvulus
- Subhepatic caecum
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- coeliac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.