Caudate nucleus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yvette Mellam had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
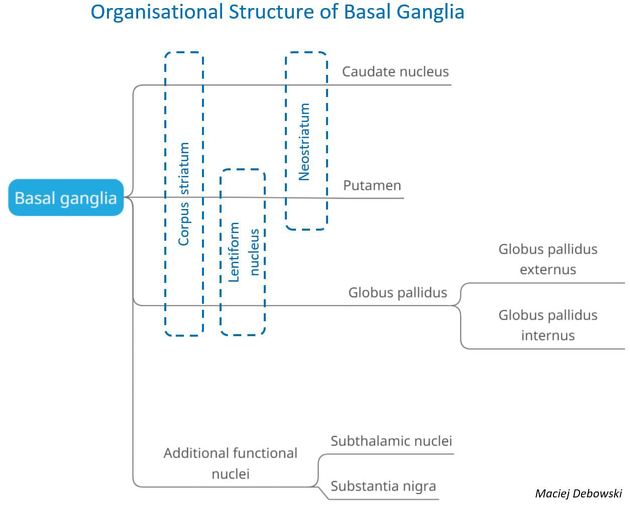
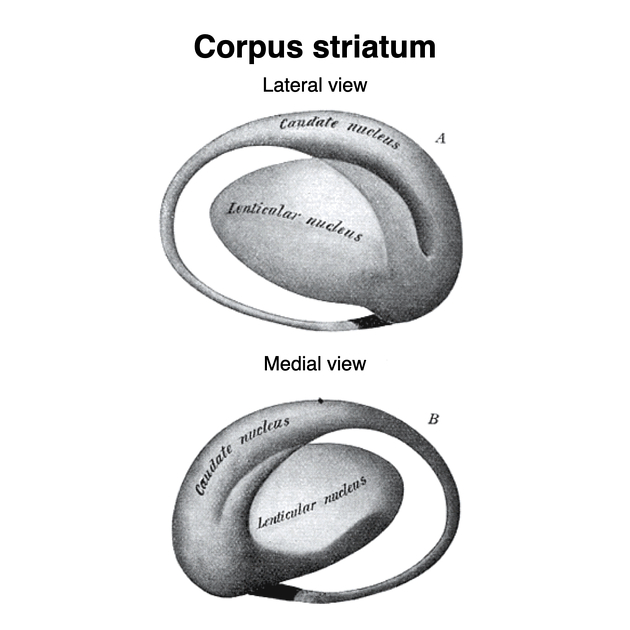
View Yvette Mellam's current disclosuresCaudate nuclei are paired nuclei which along with the globus pallidus and putamen are referred to as the corpus striatum, and collectively make up the basal ganglia. The caudate nuclei have both motor and behavioural functions, in particular maintaining body and limb posture, as well as controlling approach-attachment behaviours, respectively 3.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The caudate nucleus is divided into three parts (from anterior to posterior):
-
head
bulbous segment
-
body
thin component that curves superiorly and posteriorly
-
tail
thins distally, and at its distal most portion continues into an expanded amygdaloid body
Relations
The caudate nucleus is located lateral to the lateral ventricles, with the head lateral to the frontal horn, and body lateral to the body of the lateral ventricle. The tail of the caudate nucleus terminates immediately above the temporal horn of the ventricle. It is bound laterally by the anterior crus of the internal capsule.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Arterial supply
The head of the caudate nucleus is supplied by the recurrent artery of Heubner, a small branch from the A2 (sometimes the A1) segment of the anterior cerebral artery. The superior aspect of the head and the body of the caudate are supplied by the lenticulostriate perforators from the middle cerebral artery. The tail of the caudate is supplied by the anterior choroidal artery.
Related pathology
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Standring S (editor). Gray's Anatomy (39th edition). Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Ross LMMP. Atlas of anatomy. George Thieme Verlag. (2007) ISBN:3131421215. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Villablanca JR. Why do we have a caudate nucleus?. Acta neurobiologiae experimentalis. 70 (1): 95-105. Pubmed
- 4. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9780702033957 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Putamen
- Major depressive disorder
- Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration
- Striatum
- Hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC)
- Canavan disease
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Organophosphate poisoning (CNS manifestations)
- Schizophrenia
- Recurrent artery of Heubner
- Wilson disease (CNS manifestations)
- Globus pallidus
- Basal ganglia
- Biotin-thiamine-responsive basal ganglia disease
- Bicaudate index
- Striatocapsular infarct
- Substantia nigra
- Lacunar stroke syndrome
- Claustrum
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour
- Non-ketotic hyperglycaemic hemichorea
- Hypoglycaemic encephalopathy
- Early hyperacute ischemic stroke
- Lenticulostriate infarct possibly secondary to snake bite
- Tandem lesion
- Caudate head cavernoma
- Corpus striatum (Gray's illustration)
- Hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum (H-ABC)
- Fahr disease
- Human brain - lateral view
- Japanese encephalitis
- Maple syrup urine disease
- Epstein-Barr virus encephalitis
- Superior cerebellar artery infarction from contralateral brain swelling
- Non-ketotic hyperglycaemic hemichorea
- Huntington disease
- Huntington disease
- Perforator infarct
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway












 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.