Prepontine cistern
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Raymond Chieng had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Raymond Chieng's current disclosures- Basilar cistern
- Prepontine cistern
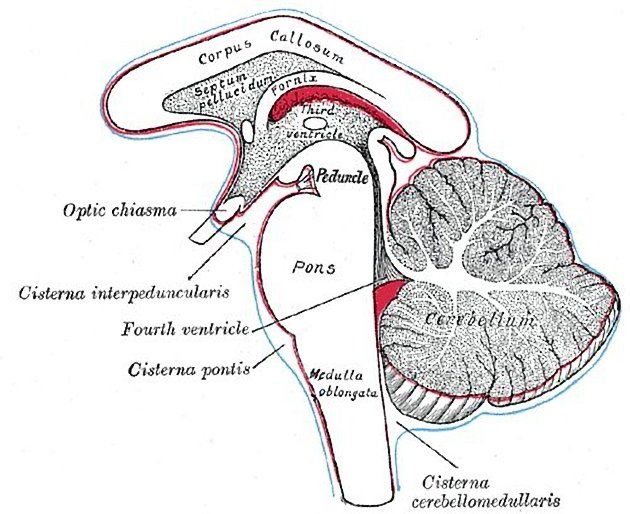
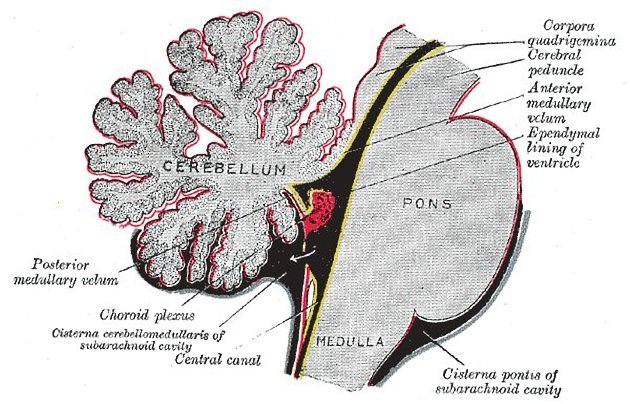
The prepontine cistern, or simply pontine cistern, is an unpaired CSF-filled subarachnoid cistern located ventral to the pons and dorsal to the clivus.
It is bounded by arachnoid membranes which separate it from surrounding cisterns.
superiorly the mesencephalic leaf of the membrane of Liliequist, above which is the interpeduncular cistern
inferiorly the medial pontomedullary membrane, below which is the premedullary cistern
laterally the anterior pontine membranes, lateral to each are the cerebellopontine cisterns through which most CSF enters the prepontine cistern
A number of vessels and a cranial nerve course through this cistern and the content is somewhat variably described depending on how the borders of the cistern are defined. Using the arachnoid membranes as landmarks result in the least structures, limited to merely the basilar artery, some of its branches (pontine perforators and the origin of the AICA) and the transverse pontine veins 6.
Preganglionic fibres of the trigeminal nerve pass through the prepontine cistern before entering Meckel's cave through porus trigeminus 7.
The abducens nerve (CN VI), often cited as traversing the prepontine cistern is more accurately considered coursing in the anterior pontine membrane and thus, not strictly speaking within the cistern but rather in its wall 6.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Stranding S. Gray's anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (2005) ISBN:0443071683. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Ross LMMP. Atlas of anatomy. George Thieme Verlag. (2007) ISBN:3131421215. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Altafulla J, Bordes S, Jenkins S, Litvack Z, Iwanaga J, Loukas M, Tubbs RS. The Basal Subarachnoid Cisterns: Surgical and Anatomical Considerations. (2019) World neurosurgery. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.087 - Pubmed
- 5. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2020) ISBN: 9780702029714
- 6. Matsuno, Haruo, Rhoton, Albert L., Peace, David. Microsurgical Anatomy of the Posterior Fossa Cisterns. (1988) Neurosurgery. 23 (1): 58. doi:10.1227/00006123-198807000-00012 - Pubmed
- 7. Kamel H & Toland J. Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176(1):247-51. doi:10.2214/ajr.176.1.1760247 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Subarachnoid cisterns
- Premedullary cistern
- Porus trigeminus
- Clivus
- Dorello canal
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Basilar artery
- Medial pontomedullary membrane
- Anterior pontine membrane
- Bern score
- Trigeminal ganglion
- Möbius syndrome
- Pons
- Abducens nerve
- Cerebellopontine angle cistern
- Liliequist membrane
- Trigeminal schwannoma
- Trigeminal neuralgia protocol (MRI)
- Ruptured saccular aneurysm
- Interpeduncular cistern
- Tension pneumocephalus
- Ecchordosis physaliphora
- Intracranial neurenteric cyst
- Ruptured basilar artery aneurysm
- Meningioma - cavernous sinus
- Brainstem glioma
- Cavernoma - mesial temporal lobe
- Brainstem glioma
- Giant aneurysm of the internal carotid artery
- Epidermoid cyst compressing the trigeminal nerve
- Epidermoid cyst - posterior cranial fossa
- Epidermoid cyst with abducent nerve palsy
- Diffuse pontine glioma
- Epidermoid cyst - intracranial
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
- Suprasellar arachnoid cyst
- Posterior circulation infarct due to basilar artery thrombosis
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum [+][+]
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem [+][+]
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)[+][+]
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)[+][+]
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)[+][+]
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy[+][+]
- CNS development[+][+]
- cerebral vascular supply[+][+]
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.