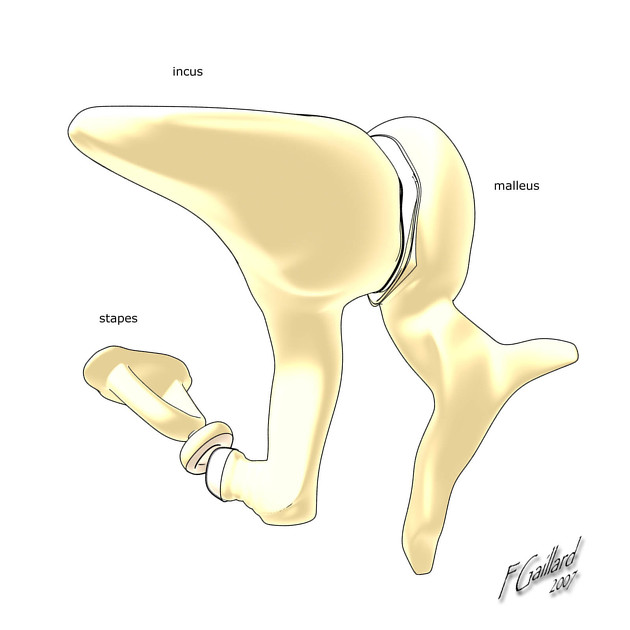
Congenital anomalies of the ossicles are most frequently associated with external ear abnormalities also, although they can occur in isolation.
Clinical presentation
These anomalies result in conductive hearing loss.
Pathology
When bilateral, they are most frequently genetic with autosomal dominant inheritance. Unilateral anomalies are usually sporadic.
Isolated ossicular anomalies can be classified as:
- class I: stapedial ankylosis
- class II: stapedial ankylosis with other associated anomalies
- class III: ossicular anomalies without stapedial ankylosis
- class IV: oval/round dysplasia
They are associated with numerous syndromes including:
- Klippel-Feil syndrome
-
Wildervanck syndrome (or cervico-ocular-acoustic dysplasia)
- typically diffuse ossicular ankylosis
- Madelung dyschondro-osteosis
- otopalatodigital syndrome
- Pyle disease
- craniometaphyseal dysplasia




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.