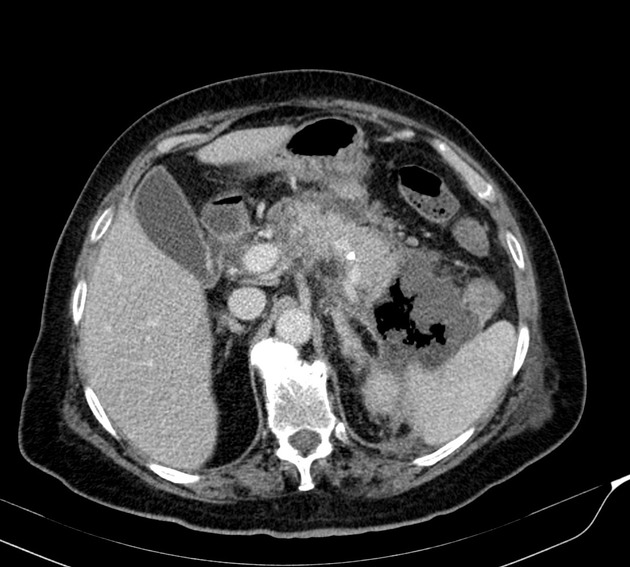
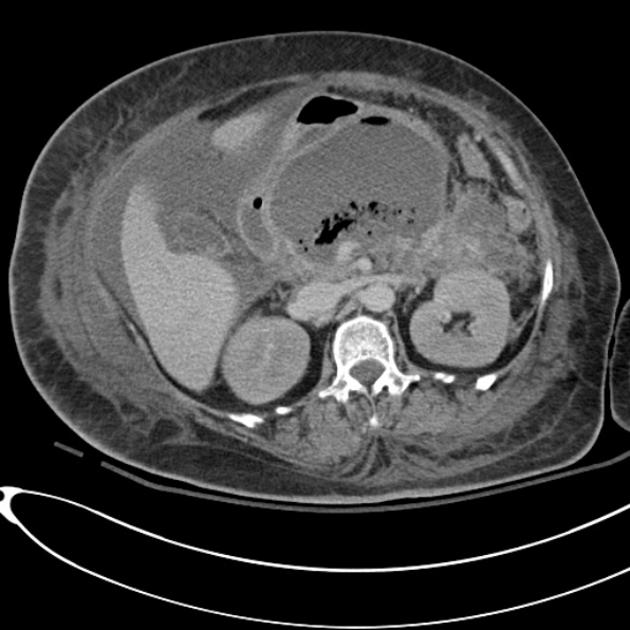
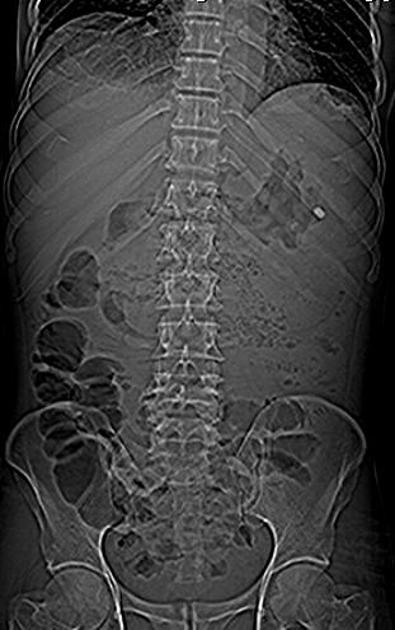
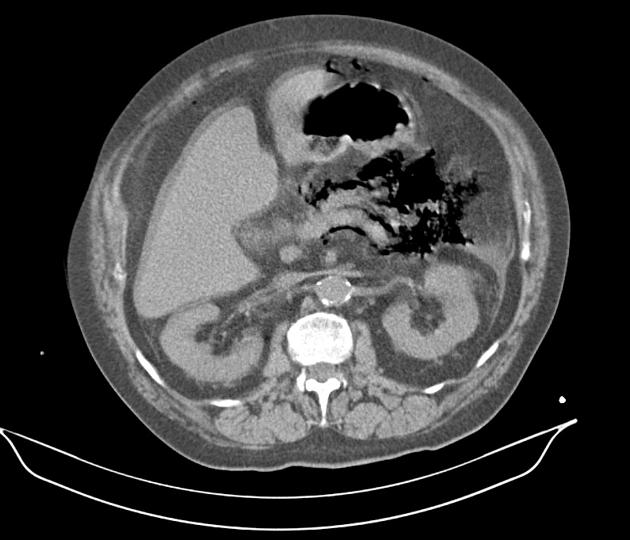
Emphysematous pancreatitis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Bruno Di Muzio had no recorded disclosures.
View Bruno Di Muzio's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- gangrenous pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis (EP)
Emphysematous pancreatitis is an unusual complication of acute pancreatitis caused by necrotising infection of the pancreas. It is associated with gas-forming bacteria and characterised by the presence of gas within or around the pancreas 1.
On this page:
Pathology
Infection with gas-forming bacteria such as
Escherichia coli
Clostridium perfringens
Staphylococcus spp.
Streptococcus spp
Klebsiella spp.
Pseudomonas spp.
Gas associated with infection is generally thought to consist of carbon dioxide and nitrogen secondary to the fermentation of glucose by some species of bacteria.
Radiographic features
Computed tomography is the imaging modality of choice because of its sensitivity and specificity in detecting gas bubbles 2.
Treatment and prognosis
This condition carries a high mortality rate. Percutaneous drainage of the fluid collection and, if there is no clinical response to support measures, surgical resection of the infected necrotic tissue.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Differential diagnosis
gas introduced by recent instrumentation, surgery (e.g. post-ERCP) or trauma
enteric fistula formation and reflux from an adjacent hollow viscus
References
- 1. Kvinlaug K, Kriegler S, Moser M. Emphysematous pancreatitis: a less aggressive form of infected pancreatic necrosis?. Pancreas. 2009;38 (6): 667-71. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181a9f12a - Pubmed citation
- 2. Wig JD, Kochhar R, Bharathy KG et-al. Emphysematous pancreatitis. Radiological curiosity or a cause for concern?. JOP. 2008;9 (2): 160-6. Pubmed citation
- 3. Niryinganji Révérien, Mountassir Shuruk, Siwane Abdellatif et al. The Emphysematous Pancreatitis: A Rare Complication of Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis. European Journal of Case Reports in Internal Medicine. 2020;(Vol 7 No 6). doi:10.12890/2020_001550
- 4. Martínez D, Belmonte M, Kośny P, Ghitulescu M, Florencio I, Aparicio J. Emphysematous Pancreatitis: A Rare Complication. European Journal of Case Reports in Internal Medicine. 2018;5(11):1. doi:10.12890/2018_000955 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- benign epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumours
- primary malignant epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumours
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumours
- haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumours
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumours
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic haemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumour
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumour
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumour
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (inflammatory pseudotumour)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumours
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumours
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.