External auditory canal osteoma
Last revised by Tariq Walizai
on 5 Oct 2024
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Ibrahim D, Walizai T, Anan R, et al. External auditory canal osteoma. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 16 Feb 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-46947
Permalink:
rID:
46947
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Dalia Ibrahim had no recorded disclosures.
View Dalia Ibrahim's current disclosures
Last revised:
5 Oct 2024,
Tariq Walizai
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures
Revisions:
11 times, by
9 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Synonyms:
- EAC osteoma
- External ear canal osteoma
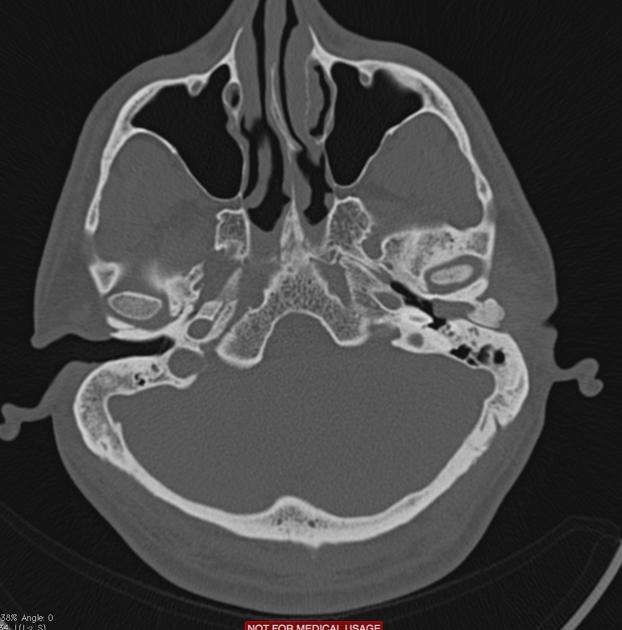
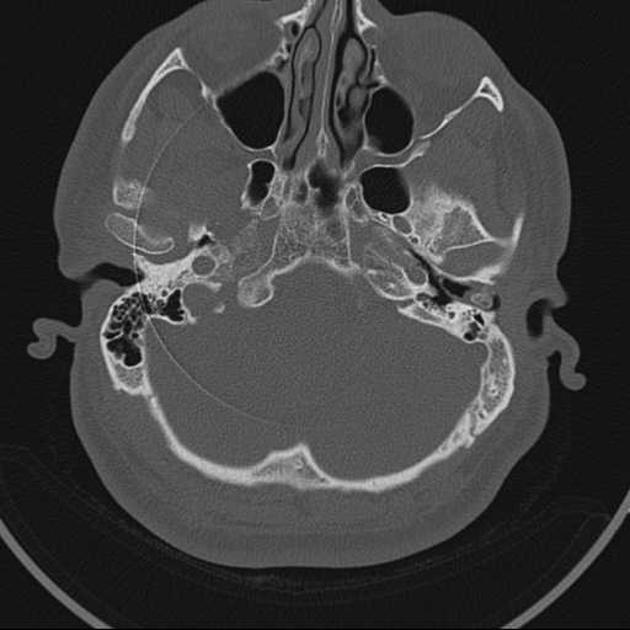
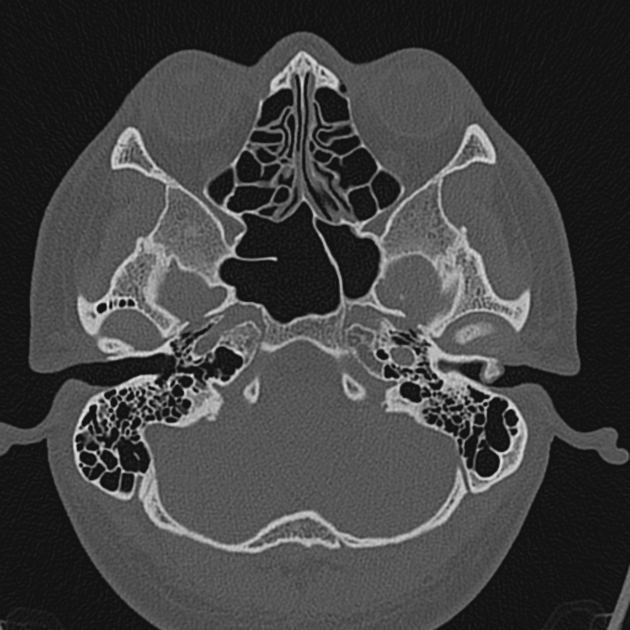
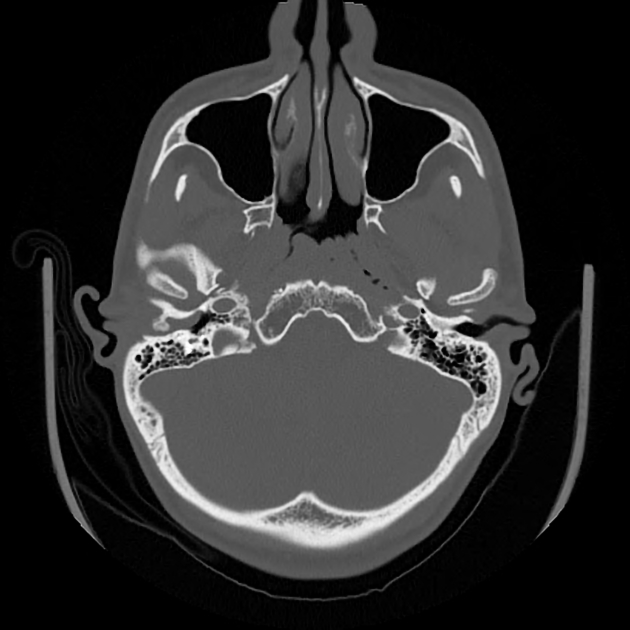
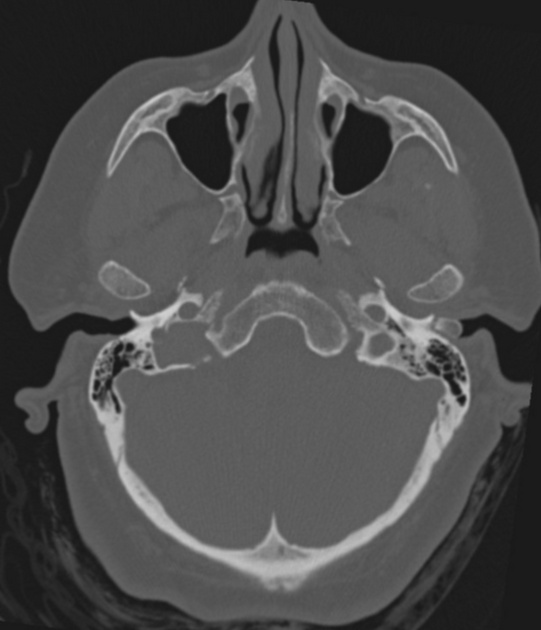
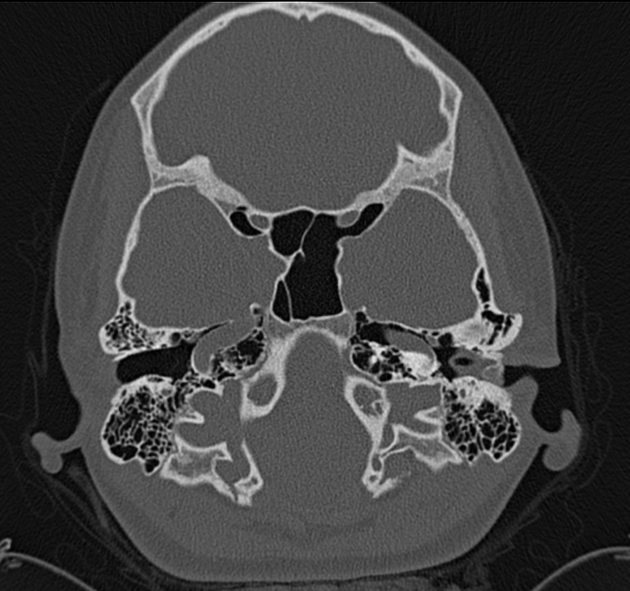
External auditory canal osteomas are rare focal pedunculated bony overgrowths of the osseous external auditory canal.
Radiographic features
solitary pedunculated bony overgrowth of the external auditory canal usually at the bony cartilaginous junction
unilateral
large lesions may be associated with earwax, debris or secondary cholesteatoma
Differential diagnosis
external auditory canal exostoses (surfer's ear): bilateral multiple broad based bony overgrowths
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Harnsberger HR, MBBS CMG, Michel MA et-al. Diagnostic Imaging Head and Neck. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN:1931884781. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Sente M. External auditory canal osteoma. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2009;137 (1-2): 73-6. Pubmed citation
- 3. Graham MD. Osteomas and exostoses of the external auditory canal. A clinical, histopathologic and scanning electron microscopic study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1979;88 (4 Pt 1): 566-72. Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Cases:
Multiple choice questions:





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.