Gastric duplication cysts are rare congenital foregut duplication cysts affecting the stomach. Gastrointestinal tract duplication cysts (GTDCs) most commonly affect the ileum, followed by the oesophagus, large bowel, and jejunum; gastric location accounts for less than 10% of all gastrointestinal duplications.
On this page:
Epidemiology
A review of four large series comprising 281 cases of gastrointestinal tract duplication cysts, demonstrated that duplications of the stomach constituted about 7% 1.
Clinical presentation
Clinical manifestations are dependent on location, size, and mucosal pattern. Symptoms, if present, usually appear before one year of age 2:
upper abdominal obstruction
abdominal pain
palpable mass
Pathology
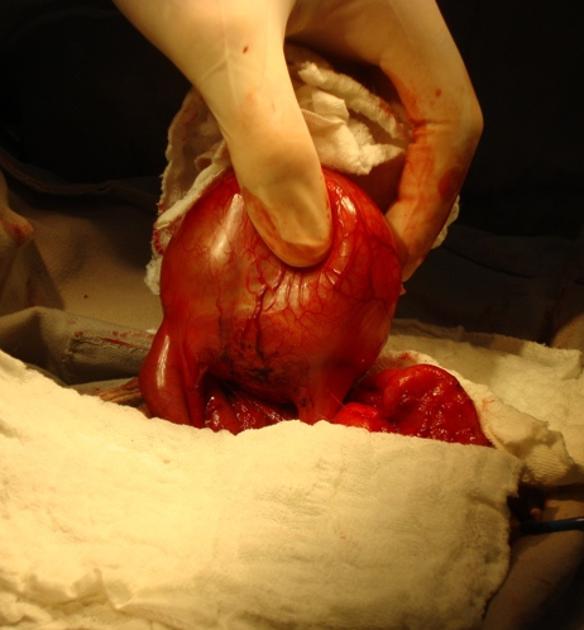
By definition, the gastric duplication has some defining characteristics as a well-developed layer of smooth muscle and an epithelial lining representing some part of the alimentary tract, and are attached to some part of the stomach sharing a common muscle wall and blood supply 3.
Duplication cysts may also contain heterotopic tissue which can include:
gastric mucosa
pancreas: ectopic pancreatic tissue
lymphoid tissue
respiratory epithelium
Location
The majority are non-communicating, spherical cysts and the greater curve is the most common site of its occurrence 1.
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
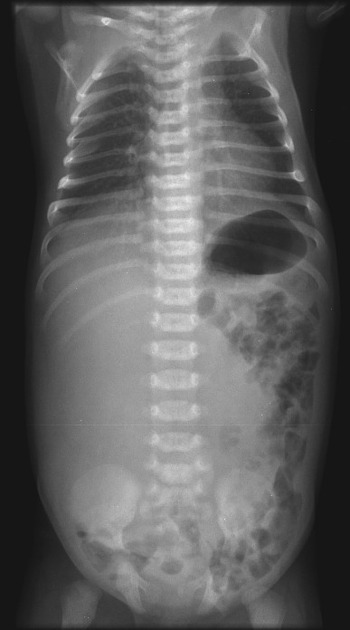
An abdominal plain radiograph can demonstrate a soft tissue mass displacing air-filled bowel loops. There can be occasional calcification in the cysts wall 6.
Fluoroscopy
A barium study may show a filling defect due to extrinsic compression from these cystic masses.
Ultrasound
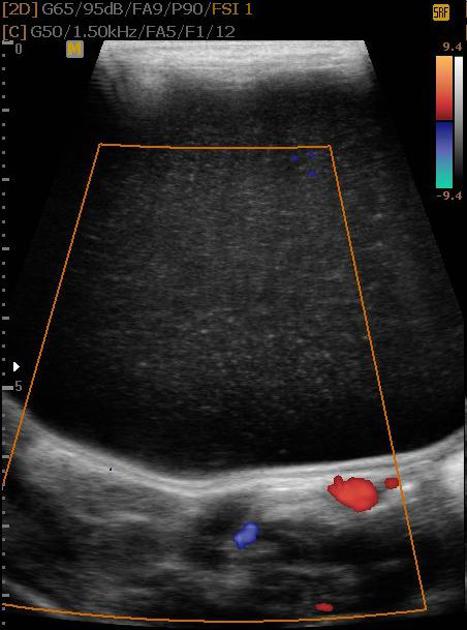
Sonography plays an important role in these patients and many authors have demonstrated that the combination of an echogenic inner mucosal layer and hypoechoic outer muscular layer are highly suggestive of a gastrointestinal tract duplication cyst 4.
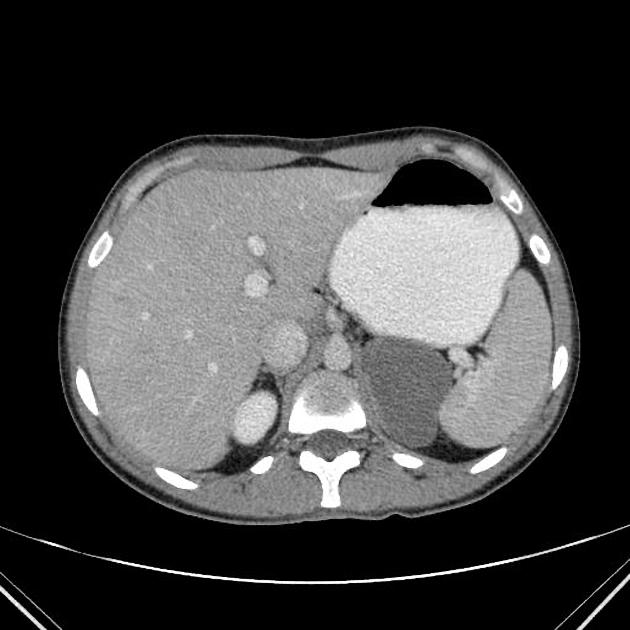
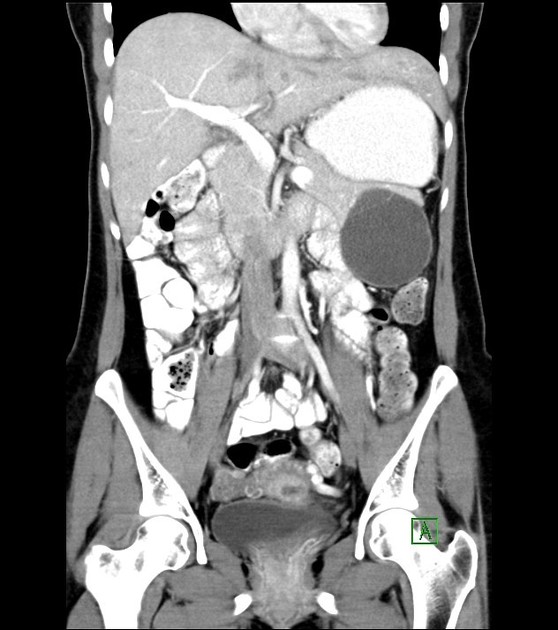
CT
CT scans will show a fluid-attenuation cystic mass in close contact with the stomach.
MRI
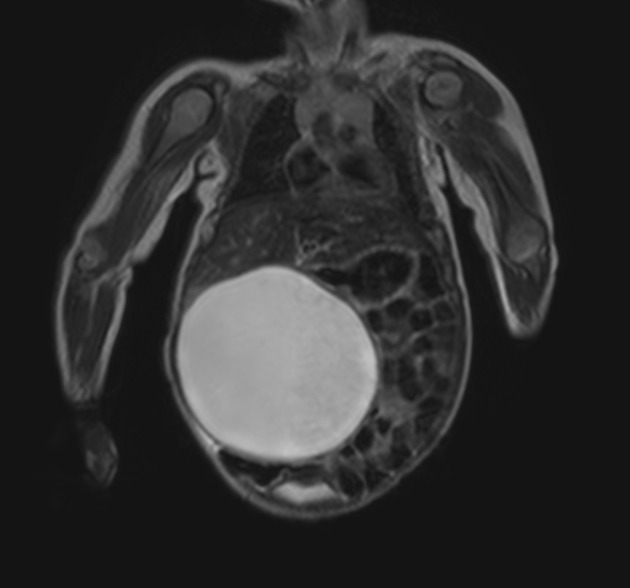
Magnetic resonance demonstrates features common to cysts with typical signal characteristics being:
T1: low signal
T2: high signal
T1 C+ (Gd): the cyst wall can show slight enhancement 6
Treatment and prognosis
Complications
Recognised complications include:
torsion 8
gastric adenocarcinoma: very rare, only six cases in literature 13
The above complications are especially likely if duplication cysts contain ectopic gastric mucosa (which occurs in 20-50% of duplications) or ectopic pancreatic tissue 6.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging differential considerations include:
it can sometimes be challenging to differentiate from a cystic adrenal lesion on the left (especially if large with little intervening tissue)






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.