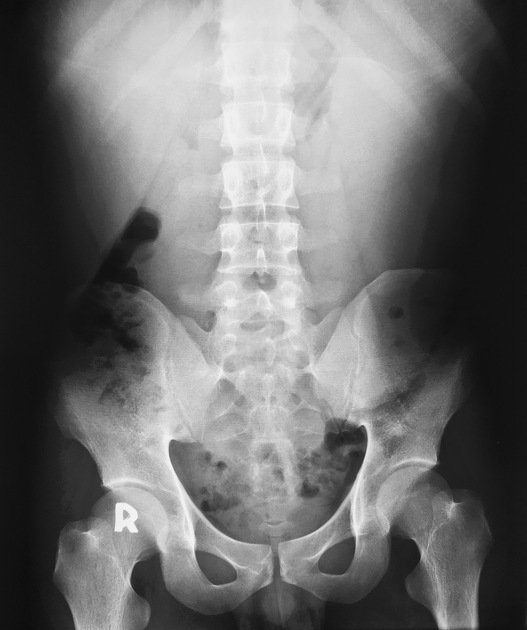
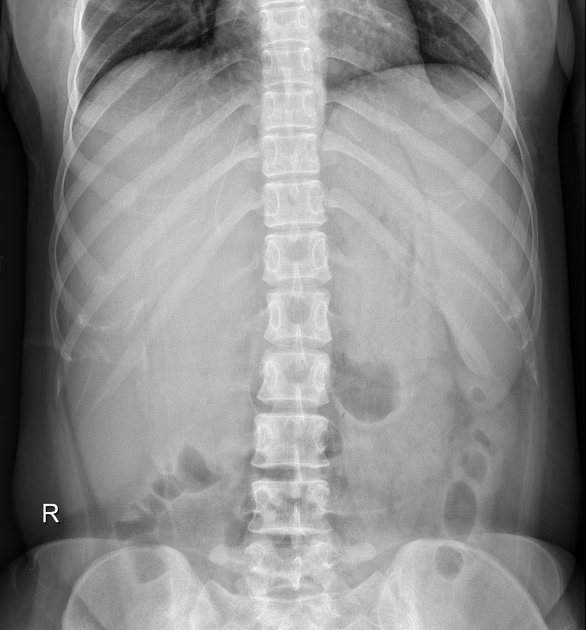
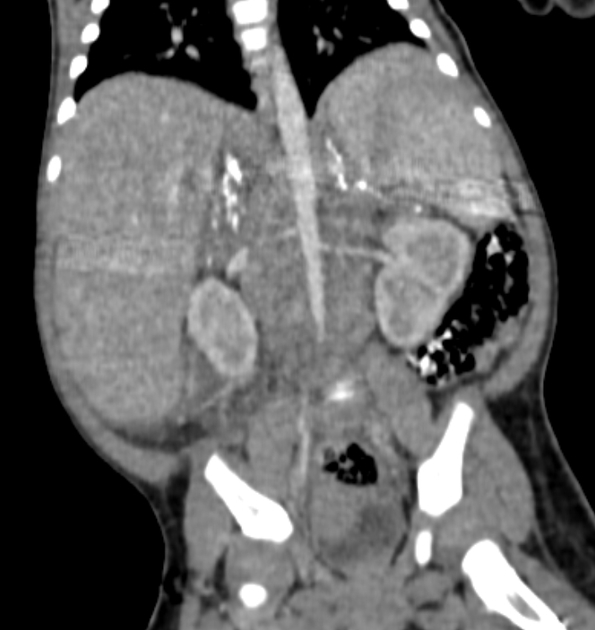
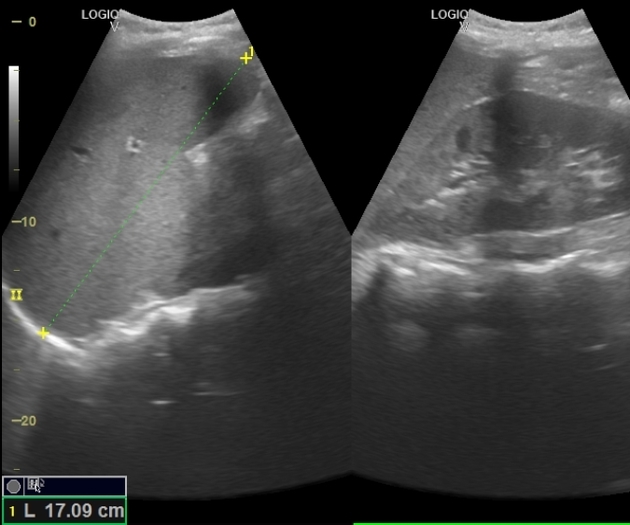
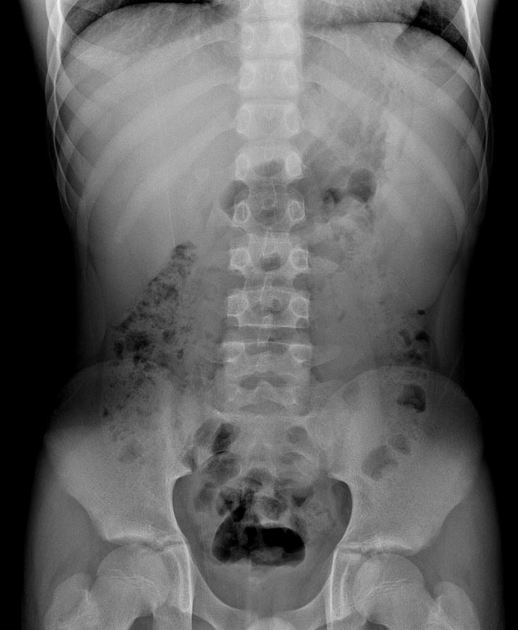
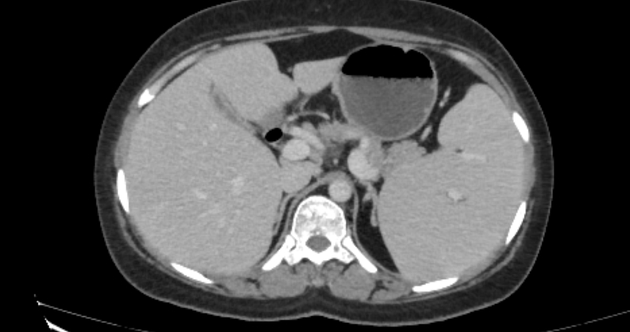
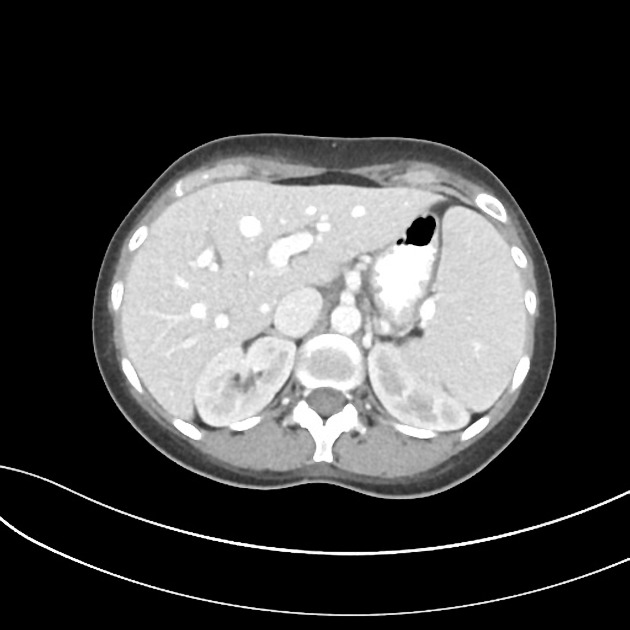
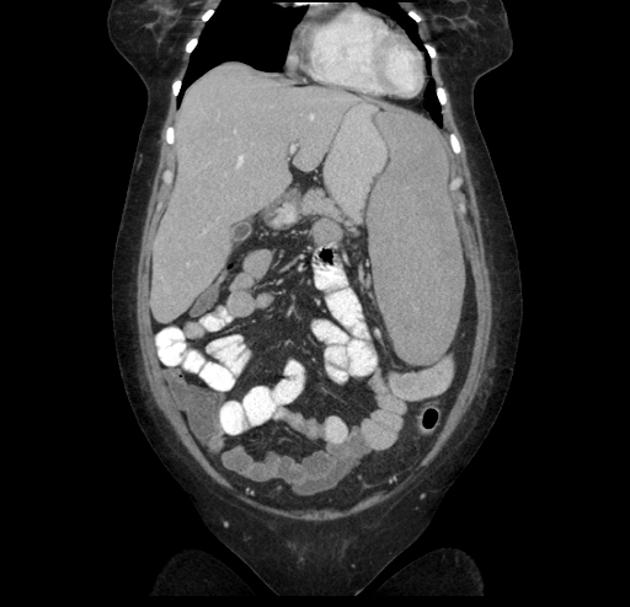
Hepatosplenomegaly is simply the simultaneous presence of a pathologically-enlarged liver (hepatomegaly) and spleen (splenomegaly).
Pathology
Aetiology
Infection
Many infections can produce a mild concurrent enlargement of the liver and spleen. This list is by no means exhaustive.
- viral
- bacterial
- fungal
- parasitic disease
Malignancy
- lymphoma
- leukaemia 5
-
multiple metastases (e.g. from primaries melanoma, pancreatic, breast, hepatic angiosarcoma)
- splenic metastases not usually seen unless advanced metastatic disease
Haematological
- extramedullary haematopoiesis
- thalassaemia
- sickle cell disease: normal/atrophic spleen more common
- systemic mastocytosis
- myelofibrosis and other myeloproliferative neoplasms
- haemochromatosis
- haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
Storage diseases/metabolic/infiltrative disorders
- lysosomal storage disorders 6
- glycogen storage diseases
- porphyria
- amyloidosis
- sarcoidosis
- hypervitaminosis A
Connective tissue disorders
Others
- cirrhosis (early)
- portal hypertension (non-cirrhotic)
- Graves disease 2




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.