Intercostal catheter
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Chest tube
- Chest tubes
- Intercostal drain
- Intercostal catheter (ICC)
- Intercostal catheters (ICCs)
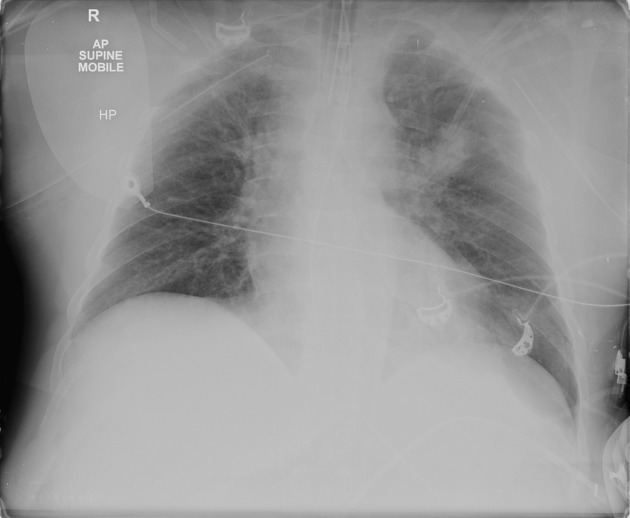
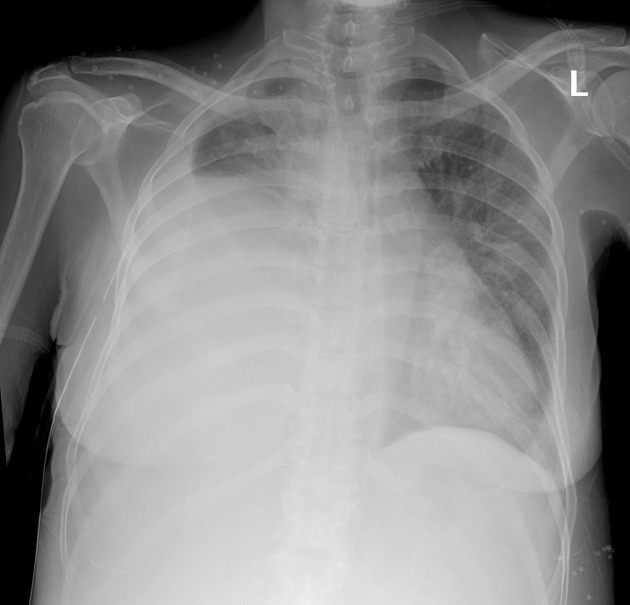
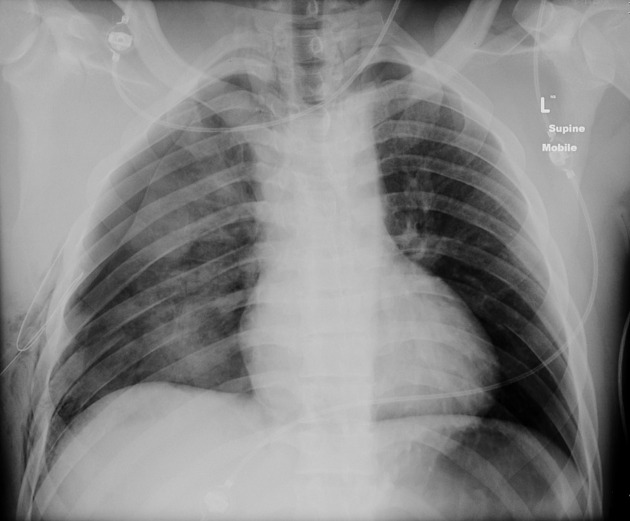
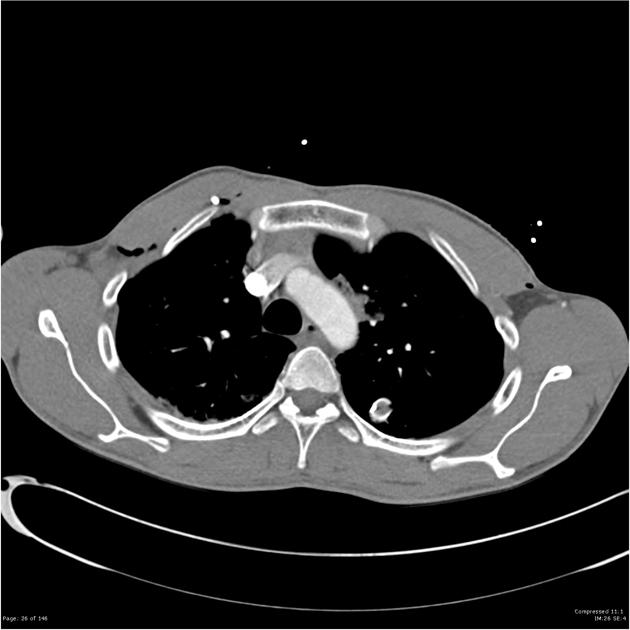
Intercostal catheters (ICC), or informally chest tubes, are inserted into the pleural space to drain fluid and/or air. They typically refer to large-bore (10-14 Fr) drains placed under direct vision rather than percutaneous pigtail catheters (6-8 Fr) placed under image guidance.
On this page:
Indication
The indications are wide and can include 1:
post-cardiothoracic surgery
Technique
consent
-
patient position
preferred: sitting at a 30-45° incline with the arm on the side of the procedure abducted
alternative: sitting upright and supported onto a table anteriorly or lateral decubitus
identify triangle of safety, insertions are preferably orientated slightly superior to the border of the inferior rib to minimise the risk of damaging the neurovascular bundle
sterile preparation and drape
local anaesthetic infiltration down to the level of parietal pleura
1-2 cm incision parallel to the rib
blunt dissection using index finger or blunt forceps and breech parietal pleura: will be accompanied by a release of blood, fluid or air
dilate insertion site with index finger
insert drain with forceps directed towards the lung apex for pneumothorax or basally for haemothorax or fluid drainage
-
drain size
10-14 Fr
smaller bore drains are recommended to minimise discomfort
larger bore drains are recommended for draining haemothoraces
there should be minimal resistance during drain insertion and an appropriate length should be passed within the pleural cavity
suture drain superficially and secure
connect the drain to an underwater seal drain system
-
confirmation: chest radiograph post procedure
in certain drains, the absence of ‘swinging and bubbling’ in the underwater seal mechanism are concerning signs of dysfunction
Complications
-
general complications
malpositioning
pain
pneumothorax/tension pneumothorax
infection
device failure/malfunction
-
complications arising from damage to local structures
heart and great vessels
oesophagus and stomach
intercostal nerves and vessels
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Kwiatt M, Tarbox A, Seamon MJ, Swaroop M, Cipolla J, Allen C, Hallenbeck S, Davido HT, Lindsey DE, Doraiswamy VA, Galwankar S, Tulman D, Latchana N, Papadimos TJ, Cook CH, Stawicki SP. Thoracostomy tubes: A comprehensive review of complications and related topics. (2014) International journal of critical illness and injury science. 4 (2): 143-55. doi:10.4103/2229-5151.134182 - Pubmed
- 2. Laws D, Neville E, Duffy J. BTS guidelines for the insertion of a chest drain. (2003) Thorax. 58 Suppl 2: ii53-9. Pubmed
- 3. Chadwick A, Halfyard R, Ali M. Intercostal Chest Drains: Are You Confident Going on the Pull? If Not Use the I-T-U Approach. J Intensive Care Soc. 2015;16(4):312-25. doi:10.1177/1751143715583856 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Thoracentesis
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (I)
- Pleural effusion (summary)
- Axilla
- Chest x-ray: lines and tubes (summary)
- Tension pneumothorax
- Medical devices in the thorax
- Buffalo pneumothorax
- Intercostal spaces
- Triangle of safety
- Lines and tubes (radiograph)
- Extrapleural haematoma
- Non-expandable lung
- Pneumothorax
- Traumatic rib fractures with lung contusion and pneumothorax
- Pneumothorax
- Chest tube in axilla
- Post intubation tracheal injury with pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax and massive subcutaneous emphysema
- Pulmonary contusion after gunshot wound
- Basal pneumothorax
- Misplaced nasogastric tube resulting in pneumothorax
- Ruptured pulmonary hydatid cyst
- Traumatic pneumothorax with malpositioned intercostal catheter
- Fractured left pleural catheter
- Tension pneumothorax
- Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Malpositioned chest tube - intra-abdominal
- Air embolism following CT-guided lung biopsy
- Kinked intercostal catheter
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- Pneumocath in pulmonary artery and left atrium
- Tension pneumothorax
- Right lower lobe collapse
- Misplaced chest tube
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph
- radiography
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- oesophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting
- cardiomediastinal contour
- chest radiograph zones
- tracheal air column
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm
- nipple shadow
-
lines and stripes
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-oesophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-oesophageal recess
- spaces
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT
-
chest radiograph
- airways
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary oedema
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- aetiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organising pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumours
- minimally invasive tumours
- invasive tumours
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumours
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumour spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumour cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumours by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.