Lateral collateral ligament calcification is rare that can cause acute knee pain.
On this page:
Clinical presentation
Most patients with lateral collateral ligament calcification are asymptomatic while a small proportion will have lateral knee pain.
Radiographic features
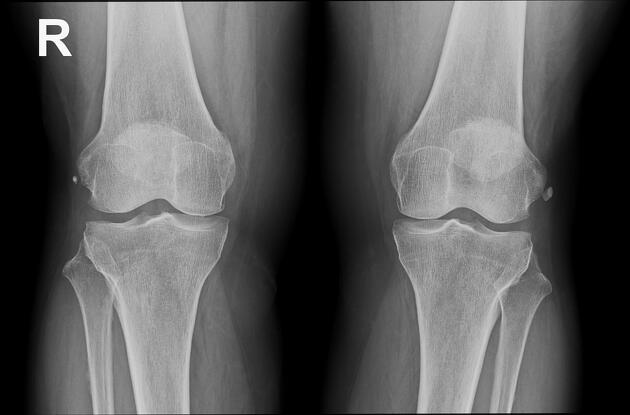
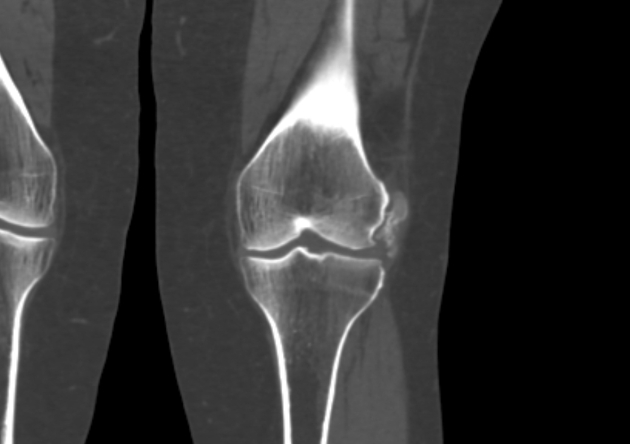
Plain radiograph
Calcification is adjacent to the lateral femoral condyle, often linear or curvilinear in shape and paralleling the femoral cortex.
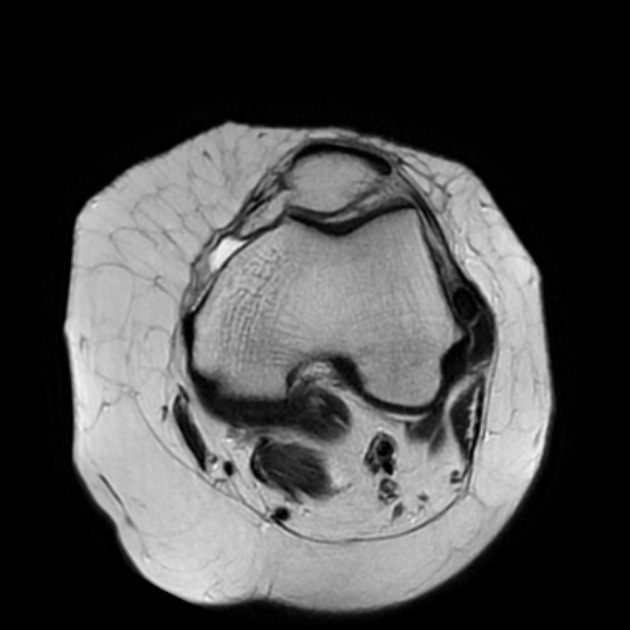
MRI
It appears as a low signal lesion in the lateral collateral ligament in comparison with the high attenuation area on the plain radiograph and may be associated with surrounding soft tissue edematous changes 1.
Treatment and prognosis
The management is usually conservative.
Differential diagnosis
Post-traumatic calcification changes and crystal-induced arthropathies (calcium pyrophosphate deposition and gout) are in differential diagnosis 2.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.