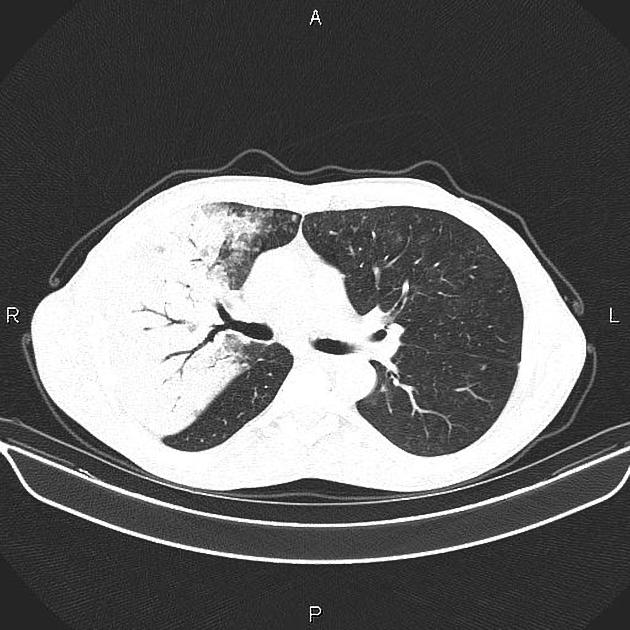
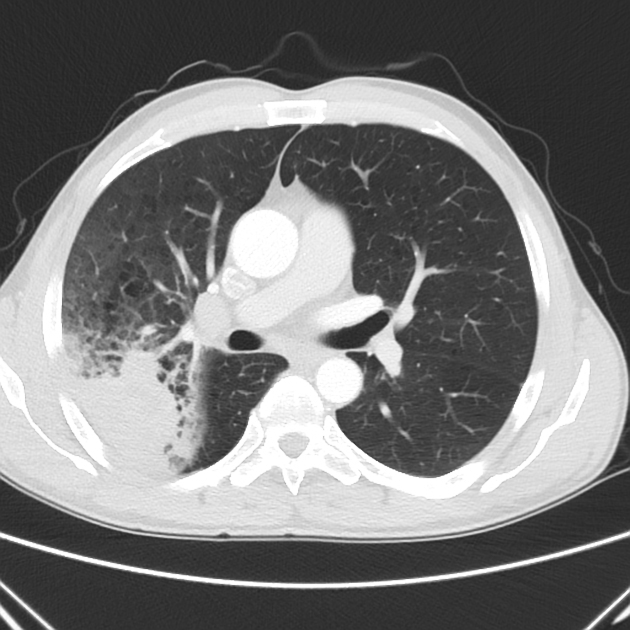
The term pneumonia is most commonly used to mean acute infection of the lung parenchyma. Sometimes chronic infections are included.
On this page:
Images:
Terminology
the term consolidation is often erroneously misinterpreted as a synonym for pneumonia
-
some interstitial lung diseases have been classified as interstitial pneumonias
some would argue that it would be less confusing to use the term pneumonitis for these inflammatory/fibrotic diseases
-
the word ‘pneumonia’ is derived from the Greek pneumon and literally means lung disease
although pneumonia has been recognized for millennia, the cause was a mystery until the 1880s when Streptococcus pneumoniae was first identified
60% of community acquired pneumonia is diagnosed clinically without identification of a causative organism or imaging studies
Epidemiology
Pneumonia ranks 8th as a cause of death in the USA and is the most deadly of the infectious diseases. Poverty, age and access to vaccination and antibiotics are the main causes of global variation. In 2019, 2.5 million people died of ‘clinical’ pneumonia and pneumonia was the leading cause of death for children under 5. The COVID-19 pandemic is responsible for over 7 millions deaths 3.
Classification
Pneumonias can be classified by:
-
etiology
-
infective agent
-
setting of infection
lipid: lipoid pneumonia
-
-
method of spread (a pathological description)
lobar pneumonia, single or multilobar pneumonia
interstitial pneumonia
-
radiographic appearance




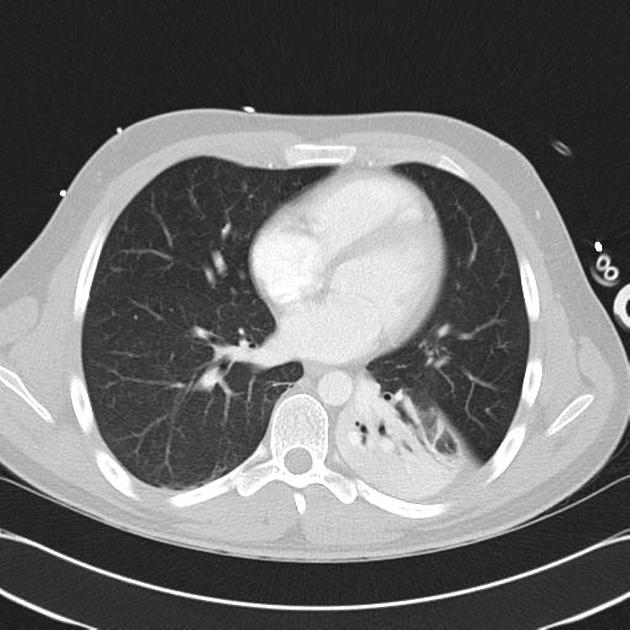

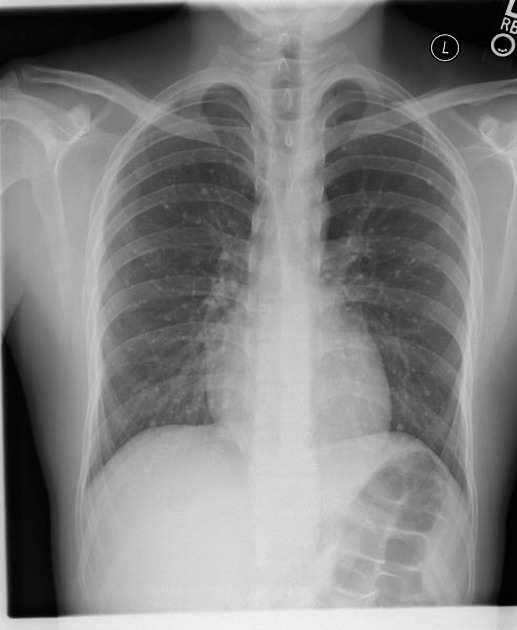
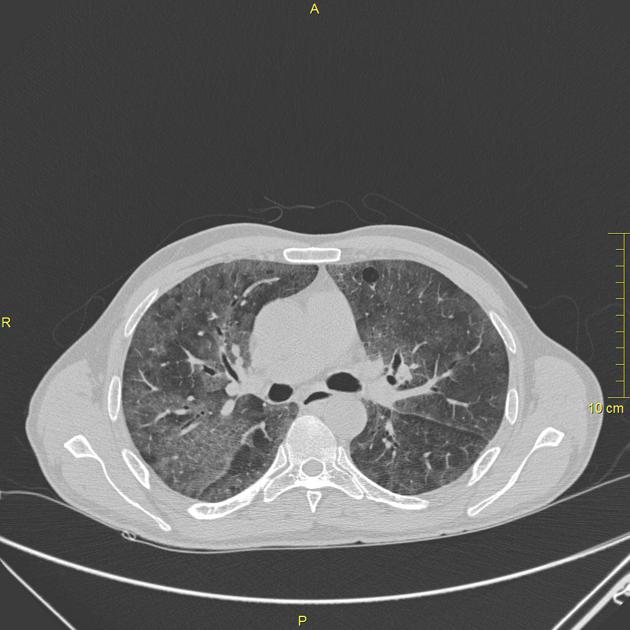
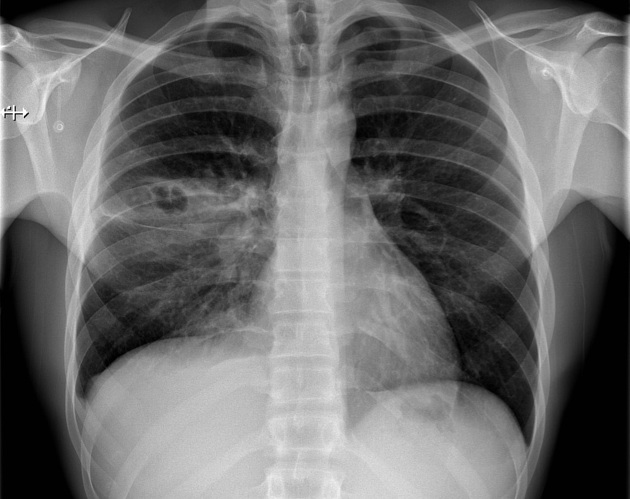




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.