The pons (TA: pons; plural: pontes 3), also less commonly known as pons Varolii, is the middle portion of the three contiguous parts of the brainstem, sitting above the medulla and below the midbrain. It acts as a relay between the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
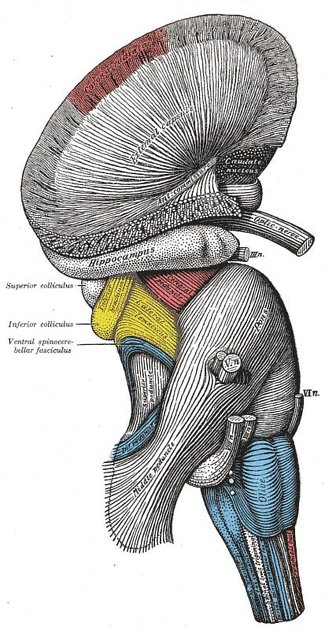
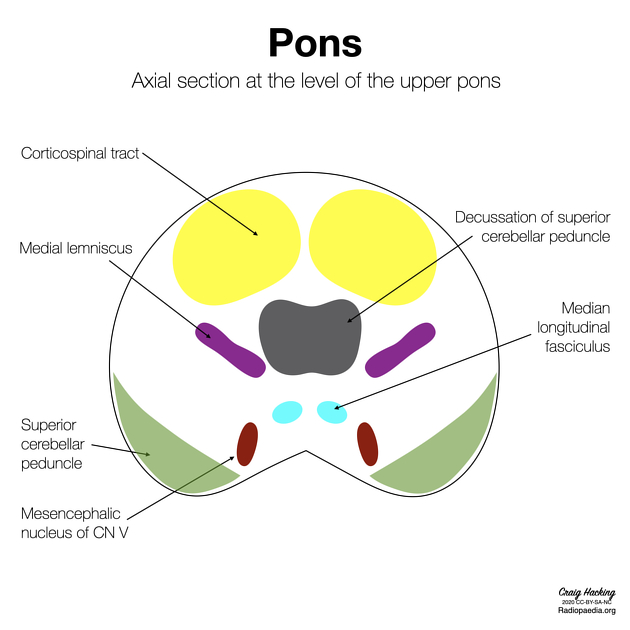
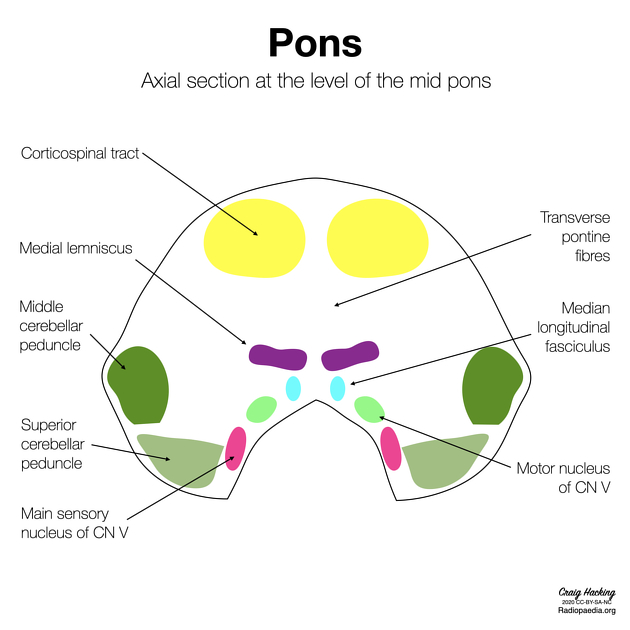
The pons has a bulbous shape and has two main components - the basis pontis (basal/ventral part) and the pontine tegmentum (dorsal part).
The basis pontis consists of white matter tracts (e.g. anterior and lateral corticospinal, corticobulbar and corticopontine tracts) with transverse fibres contributing to the bulk of the pons.
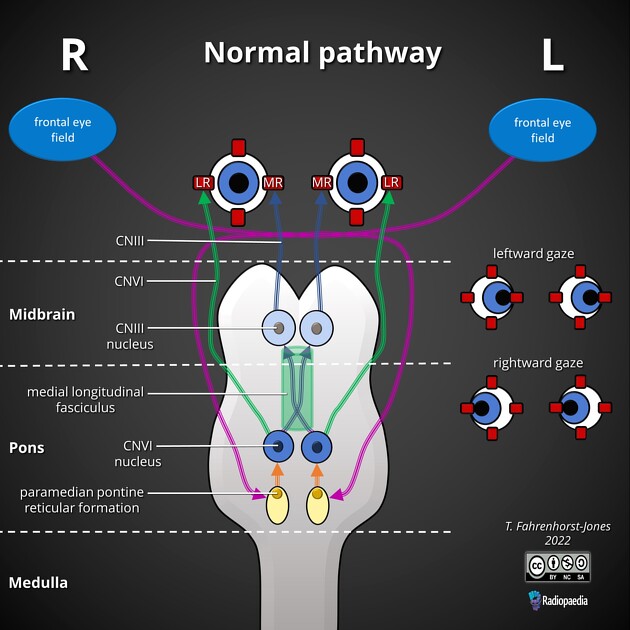
The pontine tegmentum is continuous with the tegmentum of the medulla and the midbrain. It contains multiple white matter tracts (e.g. medial longitudinal fasciculus, medial lemniscus, lateral lemniscus, etc.) and grey matter nuclei (e.g. cranial nerve nuclei). Within the dorsal tegmentum lie four cranial nerve nuclei:
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V): many motor, sensory and mesencephalic nuclei extending from the pons to the upper cervical cord
facial nerve (CN VII): including superior salivary, motor and solitary tract nuclei
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII): including vestibular and cochlear nuclei
Posteriorly, the pons is connected to the cerebellum by the middle cerebellar peduncle. Inferiorly the posterior surface of the pons is slightly depressed, forming the diamond-shaped rhomboid fossa which is the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Relations
anteriorly: prepontine cistern (contains CN V & VI)
laterally: cerebellopontine angle cistern (contains CN VII & VIII)
posteriorly: fourth ventricle (the pons makes up the anterior wall)
superiorly: continuous with the midbrain
inferiorly: continuous with the medulla
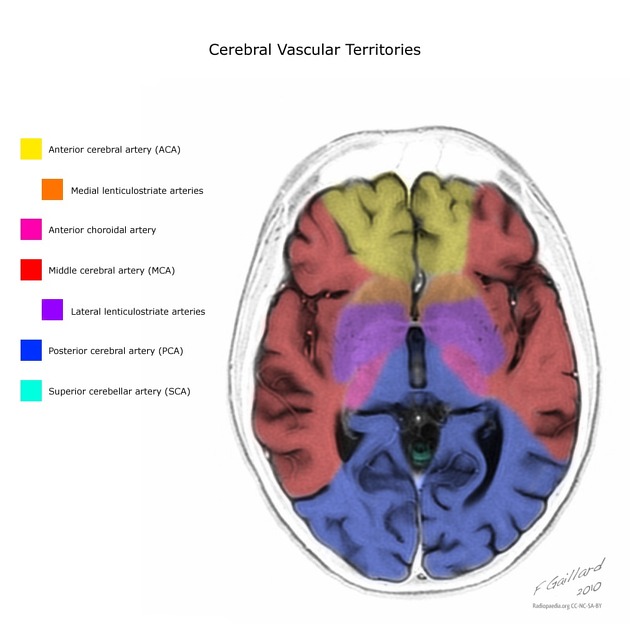
Arterial supply
Primarily by vertebrobasilar circulation:
medial branches of the superior cerebellar artery
pontine branches of basilar artery, thalamoperforator arteries
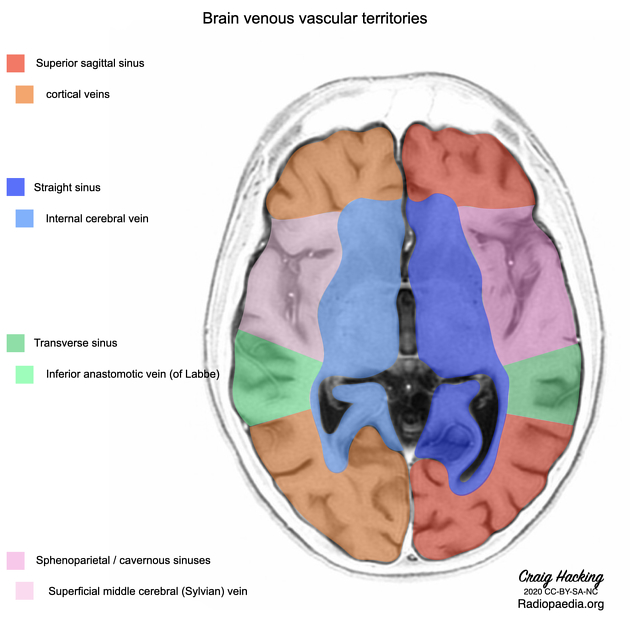
Venous drainage
The various pontine veins drain into the inferior petrosal sinuses and the basilar venous plexus 4.
History and etymology
Historically this structure was commonly called the pons Varolii, as the structure was first described by Costanzo Varolius (1543-1575), an Italian anatomist 2.
Pons is the Latin word for bridge 3.
Related pathology
Related conditions include:
-
pontine infarct
Gasperini syndrome: basilar artery or AICA
inferior medial pontine syndrome (Foville syndrome): basilar artery
lateral pontine syndrome (Marie-Foix syndrome): basilar artery or AICA
locked-in syndrome: basilar artery
Millard-Gubler syndrome: basilar artery
Raymond syndrome: basilar artery
rhombencephalitis and causes thereof
Related radiological signs include:










 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.