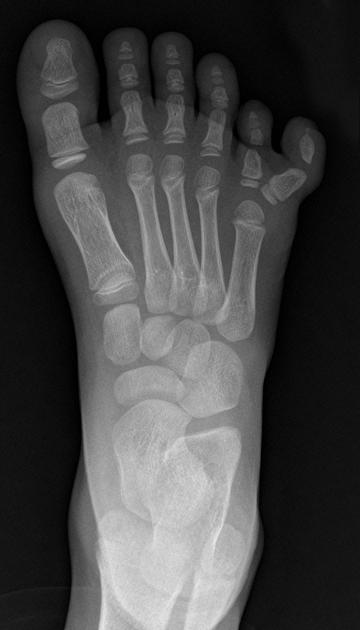
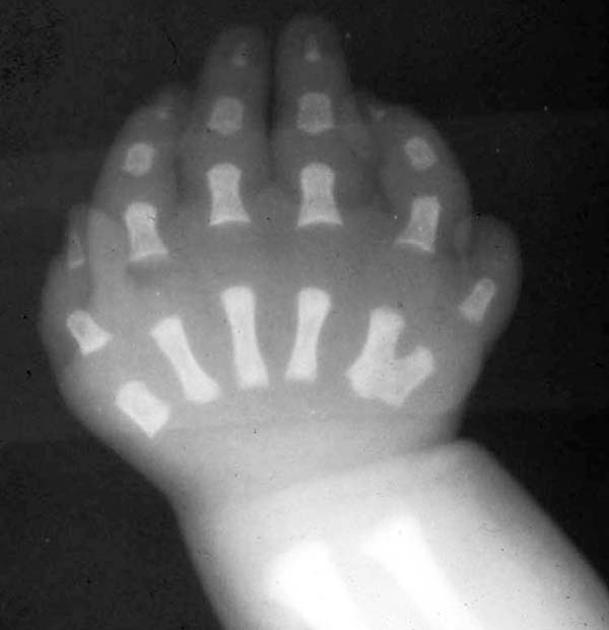
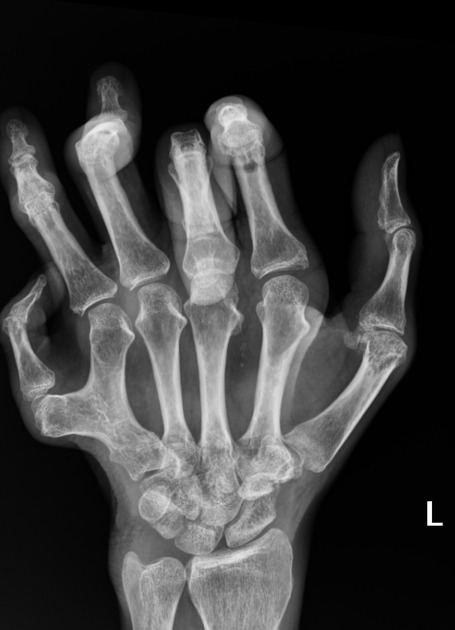
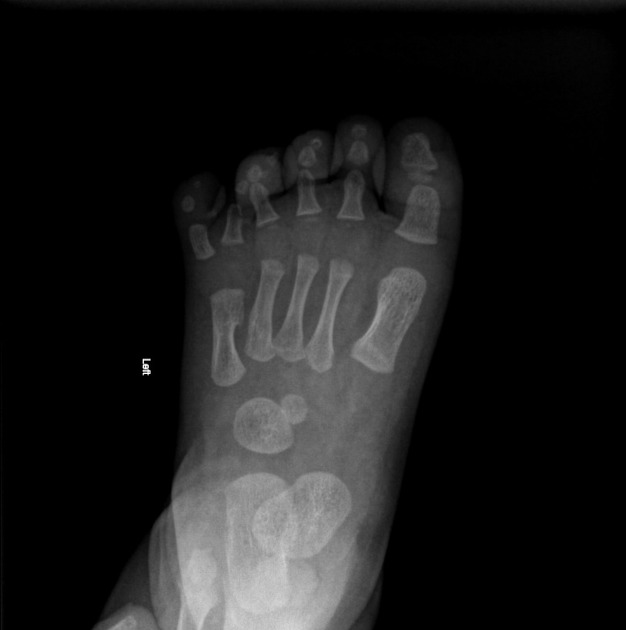
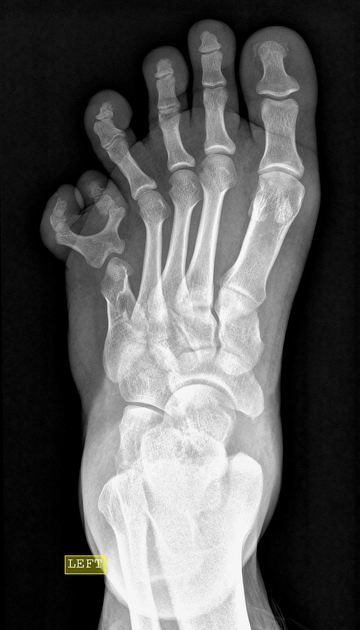
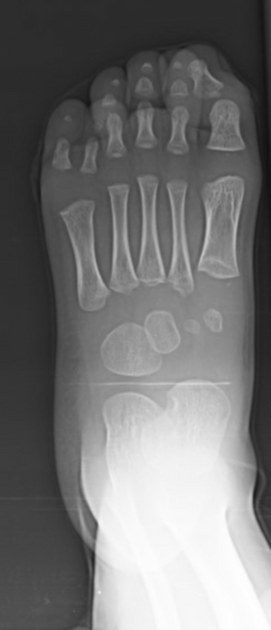
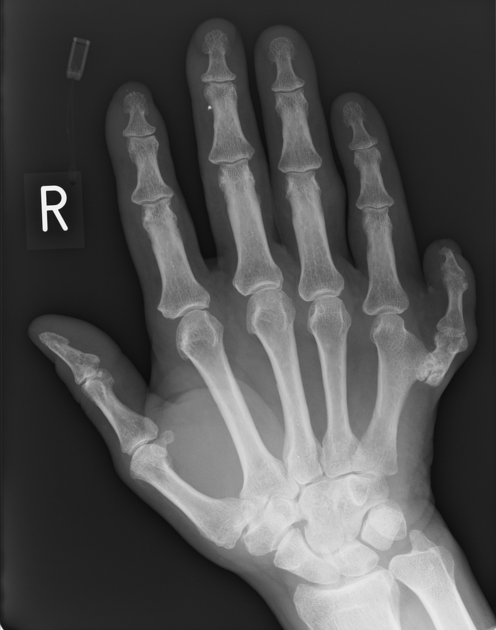
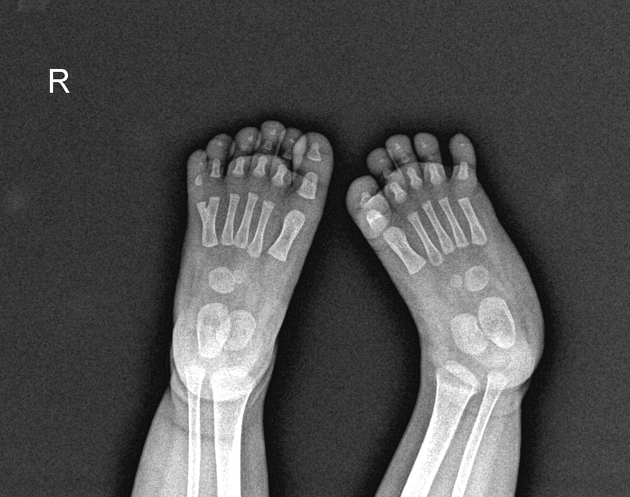
Postaxial polydactyly refers to polydactyly where the additional digit is on the ulnar margin of the hand, or lateral to the 5th (little) toe.
Epidemiology
Postaxial polydactyly is more common than preaxial polydactyly, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 3000 5.
Associations
-
following oral-facial-digital syndromes (OFDS)
-
certain skeletal dysplasias
certain short rib polydactyly syndromes: e.g. types I and III
Pathology
The majority of cases are idiopathic. Associations with mutations to the GLI3 gene on chromosome 7 as well as a second locus mapped to chromosome 13 have been implicated in postaxial polydactyly 5.
Classification
Several different classification systems exist for postaxial polydactyly of the hands, including the Pritsch, Rayan and Al-Qattan, and Duran classification systems.
Duran et al. introduced their classification system for post-axial polydactyly in 2015 6. This classification was created as it was felt that the previous systems in use were not comprehensive for coverage of the different post-axial forms.
type I: skin nub without nail or bone elements
type II: hypoplastic proximal phalanx
-
type III: proximal phalangeal malformations
IIIa: bifid proximal phalanx
IIIb: duplicated proximal phalanx
-
type IV: metacarpal malformations
IVa: fusion of the metacarpal
IVb: bifid metacarpal
IVc: duplication of the metacarpal
type V: (complicated type) with triplication of the small finger, polysyndactyly, or both





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.