Posterior cranial fossa tumors have a very different differential in an adult as opposed to a child.
Adult
-
intraventricular
-
usually group B
usually arises from the floor of the 4th ventricle
-
most frequently near the obex
often in older patients
-
strikingly vividly enhancing
-
-
intra-axial
-
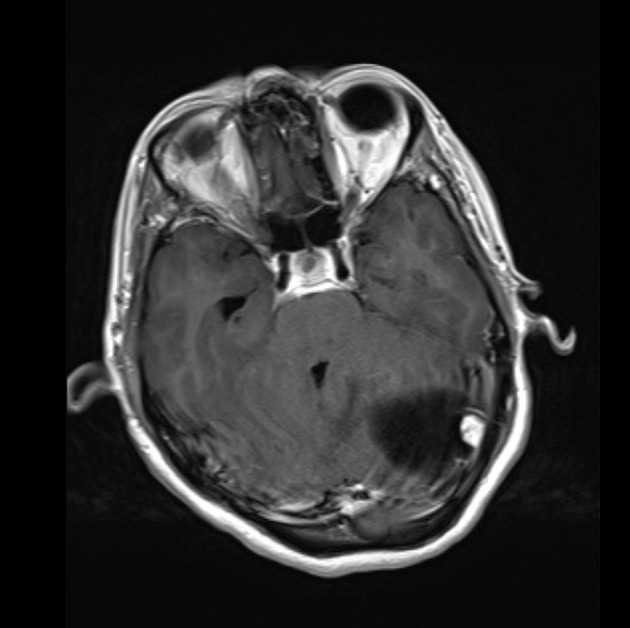
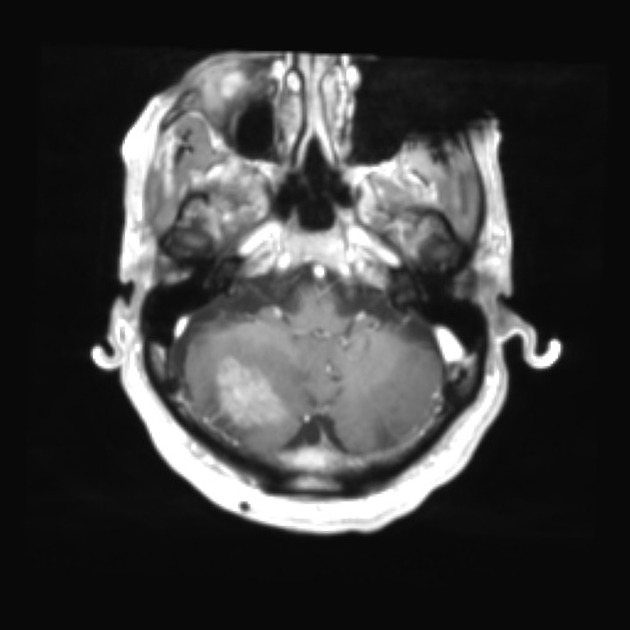
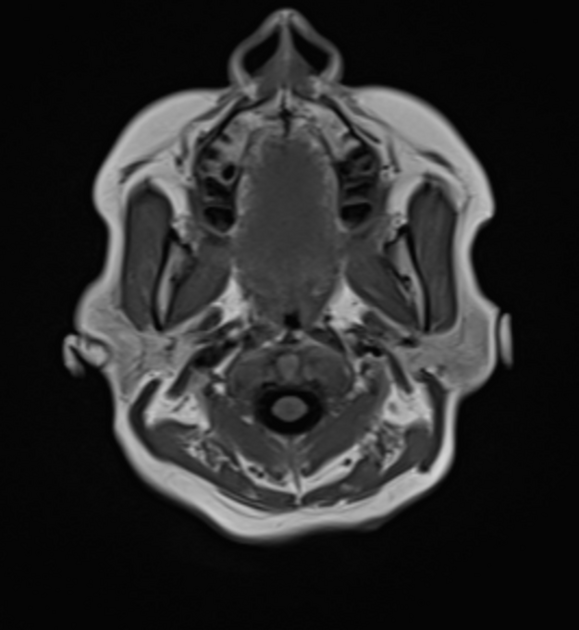
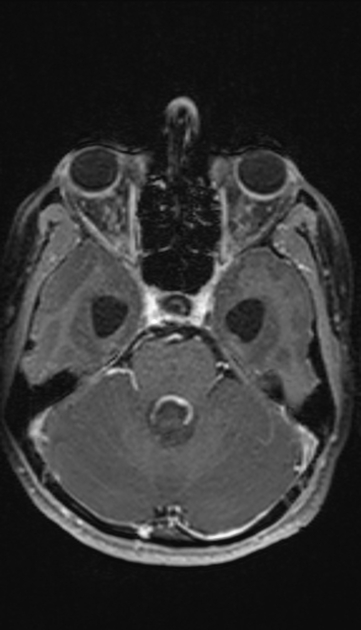
most common parenchymal posterior fossa tumor in adults
especially lung cancer and breast cancer
also melanoma, thyroid malignancies, and renal cell cancer
gastrointestinal stromal tumor (very rare) 5
-
most common parenchymal posterior fossa primary brain tumor in adults
prominent flow voids are often present
lymphoma 4
-
most often SHH-activated
heterogeneous tumors in the cerebellar hemisphere
-
rosette-forming glioneuronal tumor (RGNT)
frequently in the superior vermis
-
-
extra-axial
schwannoma: most commonly of the vestibular nerve
lipoma 4
An important space-occupying lesion (the most common in fact) to remember is that of a stroke, which when subacute can mimic a tumor.
Child
-
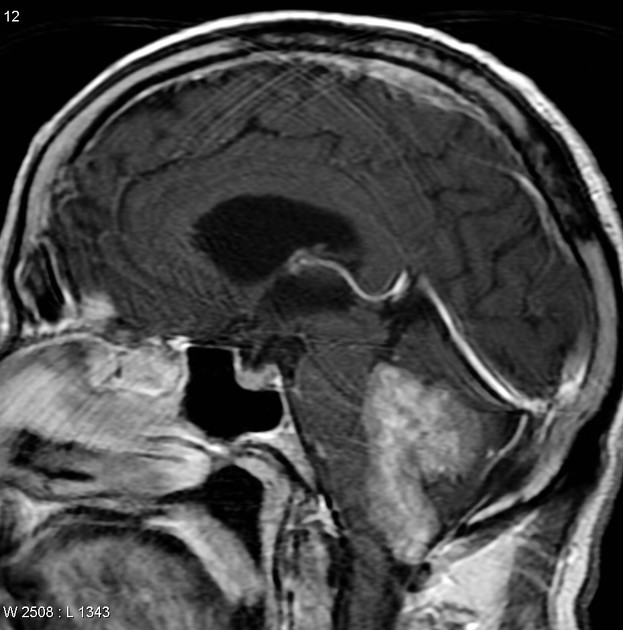
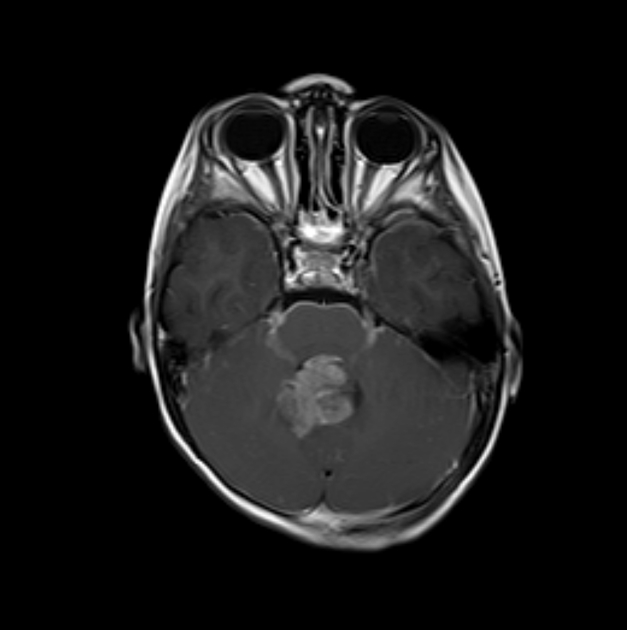
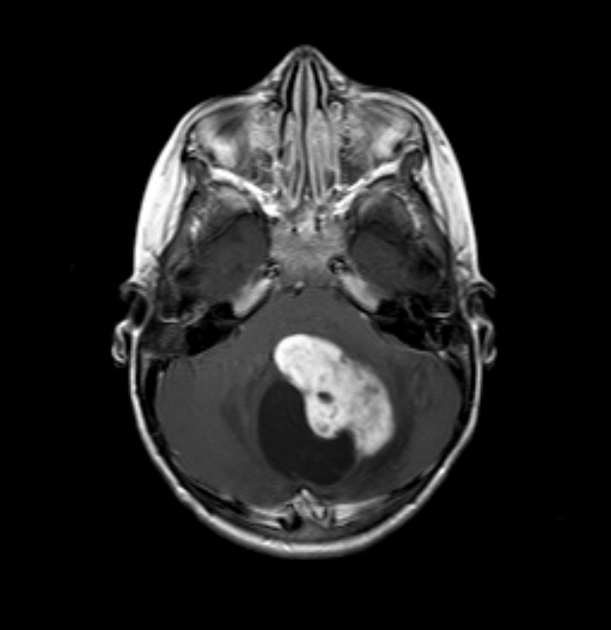
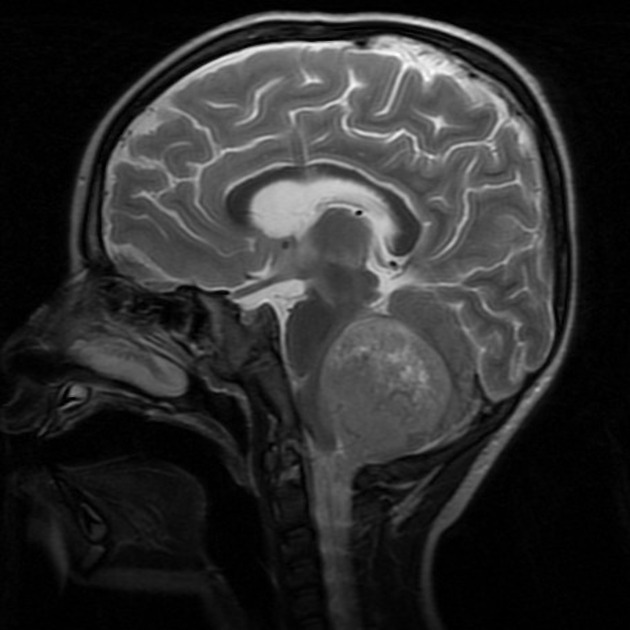
medulloblastoma: most common (30-40%) 7
hypercellular tumor (diffusion restriction with low ADC values ~550 x 10-6 mm2/s, hyperdense on non-contrast CT)
they do not usually extend into the basal cisterns through the foramina of Luschka and foramen of Magendie
drop metastases and leptomeningeal spread are common at presentation
-
pilocytic astrocytoma: second most common (25-35%) 7
large cystic component
brightly enhancing mural nodule
brainstem glioma (20-25%) 7
-
posterior fossa ependymoma (10-15%) 7
usually group A
usually arises from the lateral recess of the 4th ventricle
protrudes out of the foramina of Luschka and foramen of Magendie
does not usually cause significant diffusion restriction
-
atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT) (1-2%) 7
young children - median age is less than 2-3 years 8
very agressive
hemangioblastoma (uncommon except in patients with vHL)
teratoma (in infants)
A quick and handy mnemonic for posterior fossa tumors in children is BEAM.
Distribution
Although it is true that posterior fossa tumors are much more common in children than in adults the distribution does vary with age 2:
0 to 3 years of age: supratentorial > infratentorial
4 to 10 years of age: infratentorial > supratentorial
10 to early adulthood: infratentorial = supratentorial
adults: supratentorial > infratentorial
Overall 50-55% of all brain tumors in children are found in the posterior fossa 3.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.