The posterior interosseous nerve, also known as the dorsal interosseous nerve, is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve after it penetrates the supinator muscle. It carries fibers from the C7 and C8 spinal nerves and supplies the majority of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm. When compressed, the patient can present with posterior interosseous nerve syndrome.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Origin
The posterior interosseous nerve continues from the deep branch of the radial nerve and derives fibers from spinal nerve root levels C7 and C8.
Course
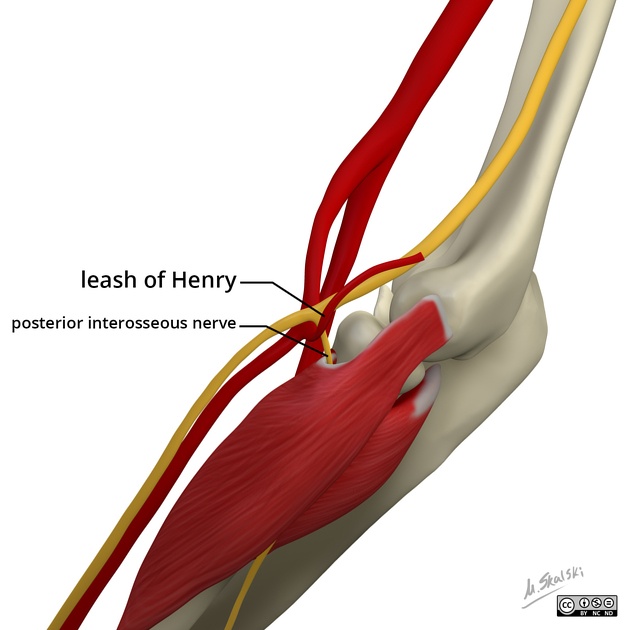
After spiraling laterally around the radial head, the deep branch of the radial nerve pierces and innervates the supinator muscle, becoming the posterior interosseous nerve.
The posterior interosseous nerve officially originates from the deep branch of the radial nerve under the arcade of Frosche (supinator arch), a fibrous arch at the superior aspect of the supinator muscle. The nerve then runs in a fascial plane between the superficial and deep extensor muscles and eventually reaches the interosseous membrane.
Along its course the posterior interosseous branch supplies motor innervation to all the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm and finally provides sensory fibers to the dorsal aspect of the carpus.
Branches and supply
The posterior interosseous nerve supplies multiple muscles, four superficial extensors and five deep extensors in the posterior compartment of the forearm:
-
superficial
extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB): deep branch of radial nerve
extensor digiti minimi (EDM)
extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
-
deep
supinator: deep branch of radial nerve
abductor pollicis longus (APL)
extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
The posterior interosseous nerve provides sensory fibers to the dorsal aspect of the wrist capsule, arising in a separate fascicle sheath from the deep radial aspect in the fourth extensor compartment. The nerve does not provide cutaneous branches.
Relations
The posterior interosseous nerve runs in close proximity to the posterior interosseous artery, which also passes along the posterior aspect of the interosseous membrane. The posterior interosseous artery is the principle artery supplying the middle third of the posterior compartment of the forearm. The posterior interosseous artery is eventually replaced by the anterior interosseous artery that pierces the interosseous membrane at the proximal aspect of the pronator quadratus muscle.
Variant anatomy
The posterior interosseous nerve may exit the supinator muscle from two sites, both under the distal edge of the muscle and piercing the supinator muscle distal to the articular surface of the radial head. The two origins of the nerve join and then course between the superficial and deep muscle layers of the posterior compartment.
Related pathology
The posterior interosseous nerve may be compressed at multiple points along its course, most commonly under the arcade of Frohse, the fibrotendinous proximal edge of the supinator muscle. The nerve may also become compressed at the distal edge of the supinator muscle or under the medial edge of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.