Precuneus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Dayu Gai had no recorded disclosures.
View Dayu Gai's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Fabio Macori had no recorded disclosures.
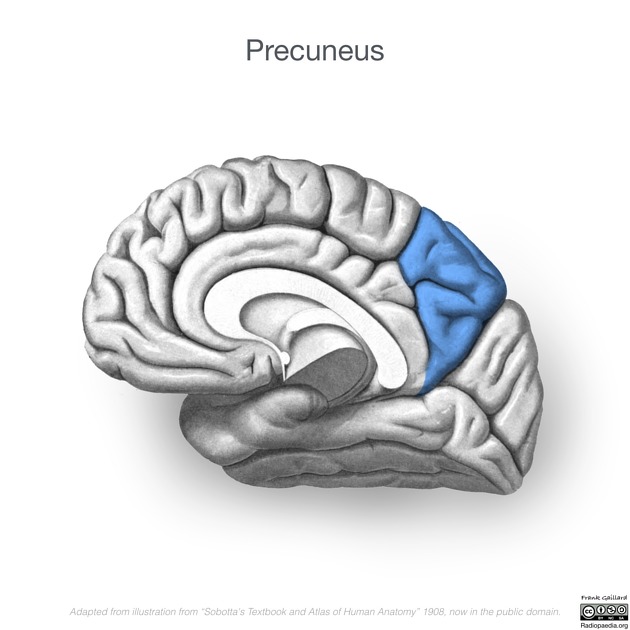
View Fabio Macori's current disclosuresThe precuneus is a part of the parietal lobe of the brain, lying on the medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere. It plays a role in visuospatial imagery, episodic memory retrieval and self-processing operations 1.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Relations
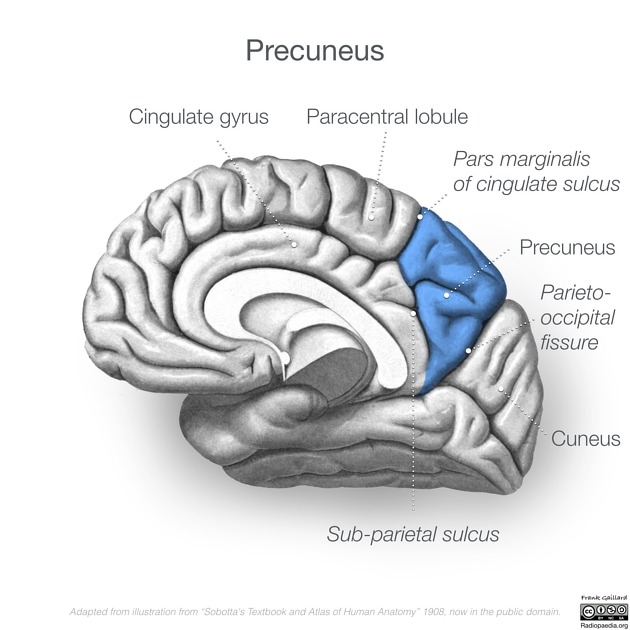
Posterior to the precuneus lies the cuneus, separated from it by the medial portion of the parieto-occipital sulcus 1,2.
Anteriorly lies the paracentral lobule, separated from it by the pars marginalis (ascending branch of the cingulate sulcus) 1,2.
Inferiorly is located the cingulate gyrus, separated from it by the subparietal sulcus 1,2.
Blood supply
While highly variable, the main arterial supply arises from the posterior cerebral artery, predominantly the P2 segment. The precuneus derives blood supply from the occipito-parietal artery, a terminal branch of the internal occipital artery.
Practical points
The parieto-occipital sulcus joins with the anterior end of the calcarine sulcus to form a 'lazy Y' configuration, sometimes referred to as the parieto-occipito-calcarine sign 2. The precuneus lies superior to the upper limb of the Y (parieto-occipital sulcus), whereas the cuneus lies in between the two limbs, and the lingual gyrus below the lower limb.
Clinical significance
Along with the posterior cingulate cortex and posterior temporoparietal areas, the precuneus is one of the key areas involved in Alzheimer disease. Characteristic hypometabolic patterns of FDG-PET maps involving precuneus and posterior cingulate gyrus (without occipital involvement) helps to distinguish Alzheimer disease from other kinds of dementia 3.
References
- 1. Cavanna A & Trimble M. The Precuneus: a Review of Its Functional Anatomy and Behavioural Correlates. Brain. 2006;129(Pt 3):564-83. doi:10.1093/brain/awl004
- 2. Thomas P. Naidich, Mauricio Castillo, Soonmee Cha et al. Imaging of the Brain, Expert Radiology Series,1. (2012-10-31) ISBN: 9781416050094
- 3. Schwarz A, Yu P, Miller B et al. Regional Profiles of the Candidate Tau PET Ligand18F-AV-1451 Recapitulate Key Features of Braak Histopathological Stages. Brain. 2016;139(5):1539-1550. doi:10.1093/brain/aww023
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.