Pseudocirrhosis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Maxime St-Amant had no recorded disclosures.
View Maxime St-Amant's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Pseudo cirrhosis
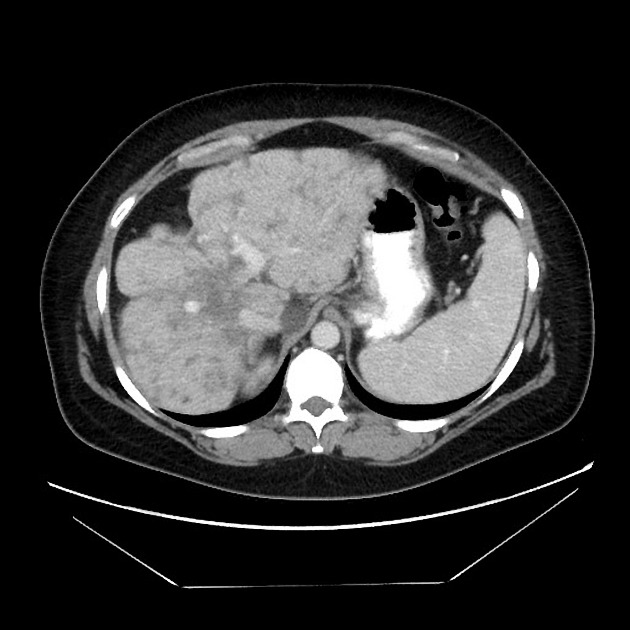
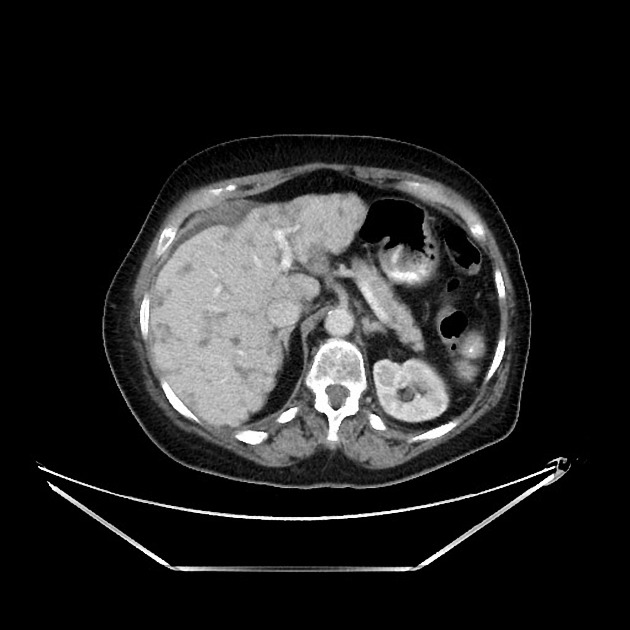
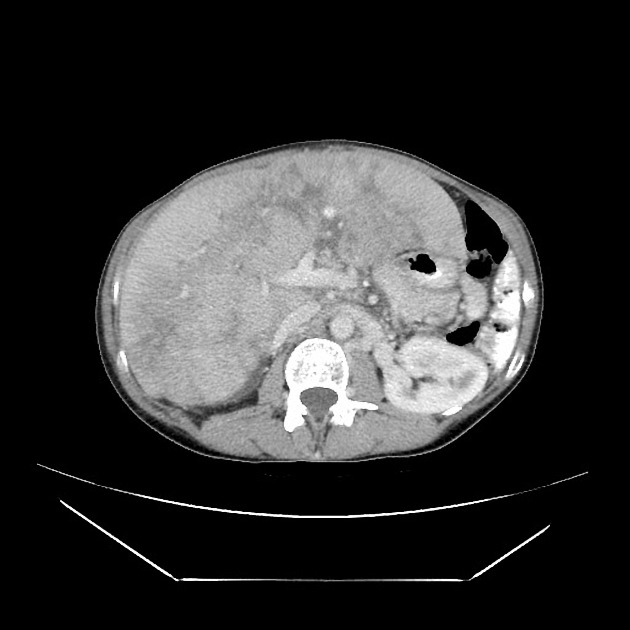
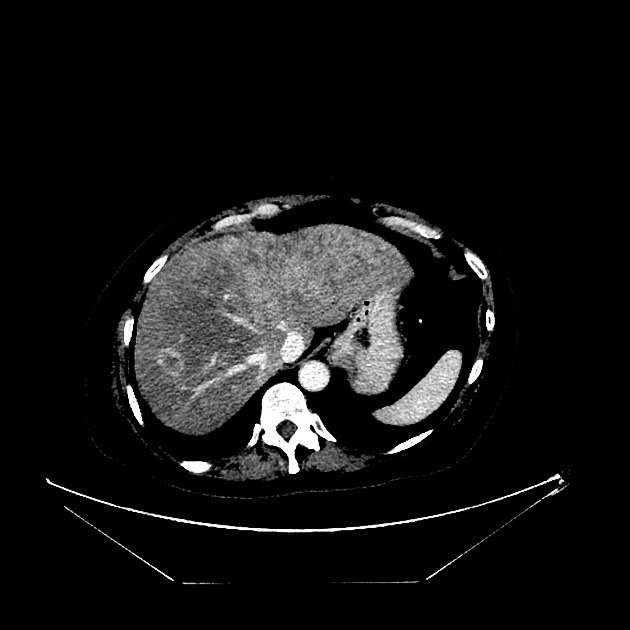
Pseudocirrhosis is a radiological term used to convey the imaging findings of cirrhosis but emphasises that it occurs in the setting of hepatic metastases. It is most commonly reported following chemotherapeutic treatment of breast cancer metastases, although it has also been reported before treatment and with other malignancies, including pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, medullary thyroid cancer and oesophageal cancer 5.
On this page:
Terminology
The term "pseudocirrhosis" is intended to convey a different disease process compared with cirrhosis of chronic liver disease.
Clinical presentation
Although most cases are mainly identified on an imaging basis, particularly found on post-treatment surveillance scans, patients may have symptoms related to liver failure and portal hypertension, including abdominal distension due to ascites.
Pathology
Two pathophysiologic correlates of pseudocirrhosis have been described 4:
hepatic capsular retraction in response to chemotherapeutic agents, with nodular regenerative hyperplasia and absence of bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis on histopathology
extensive fibrosis representing a profound desmoplastic response to an infiltrating tumour, occurring prior to chemotherapy
Radiographic features
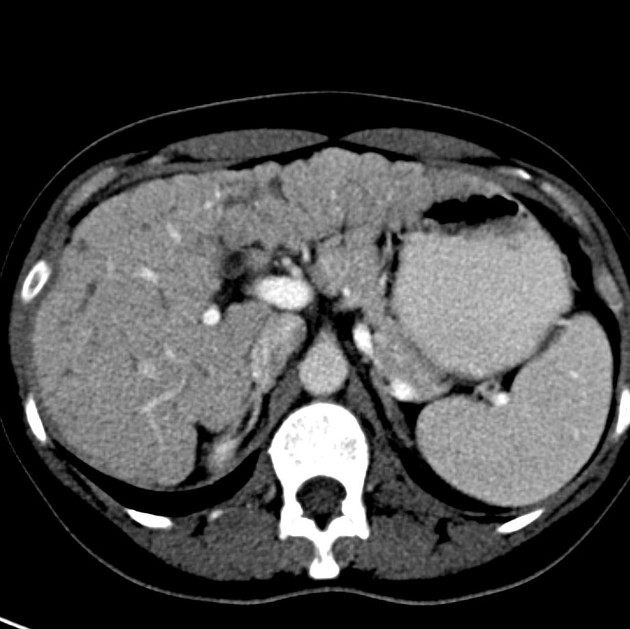
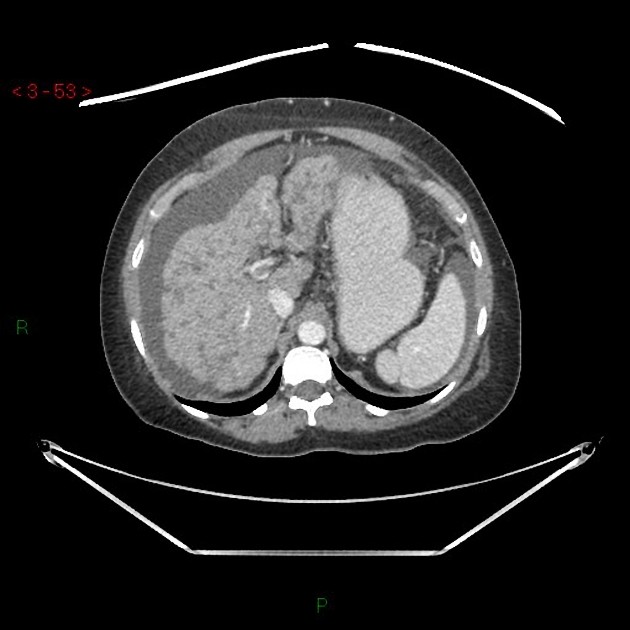
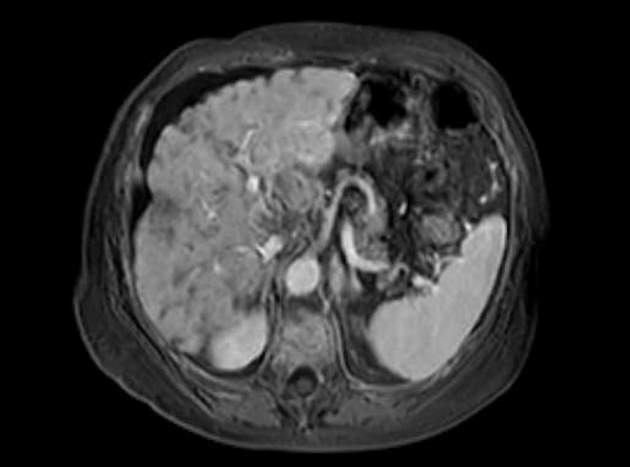
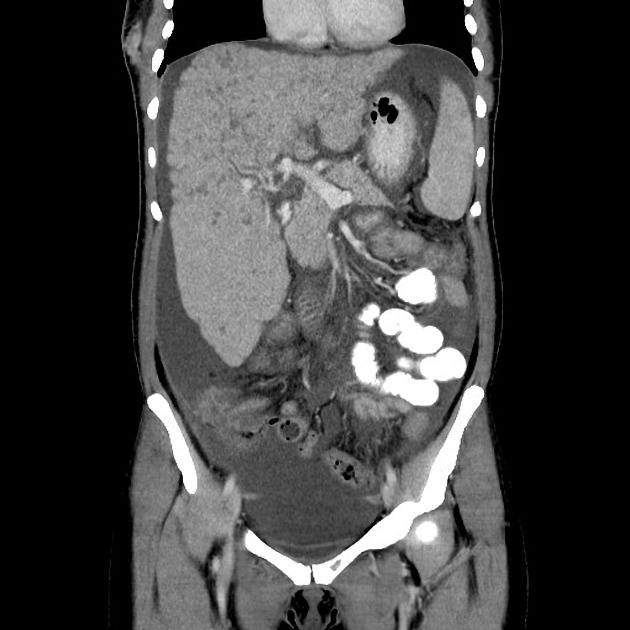
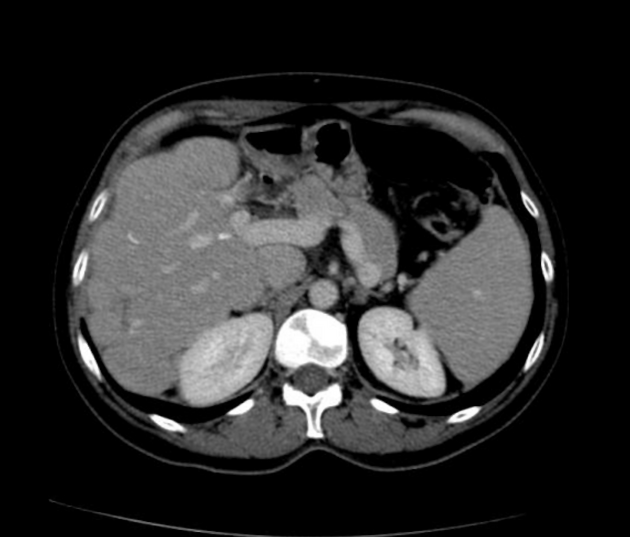
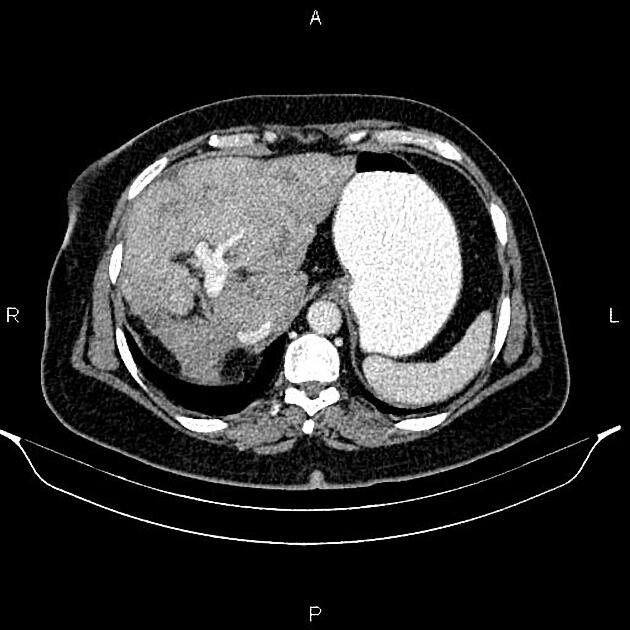
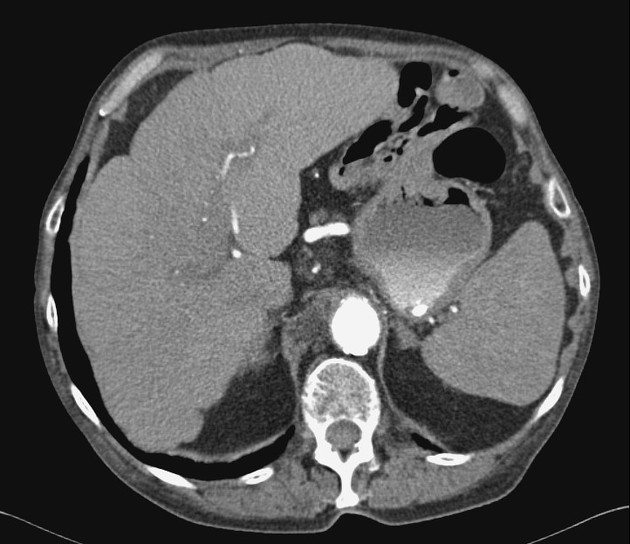
Imaging manifestations on CT, ultrasound, and MRI may be identical to liver cirrhosis, and consist of:
variable capsular retraction and liver nodularity
hepatic segmental volume loss
nodular contour
confluent fibrosis
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Lee SL, Chang ED, Na SJ et-al. Pseudocirrhosis of breast cancer metastases to the liver treated by chemotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2014;46 (1): 98-103. doi:10.4143/crt.2014.46.1.98 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 2. Jeong WK, Choi SY, Kim J. Pseudocirrhosis as a complication after chemotherapy for hepatic metastasis from breast cancer. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2013;19 (2): 190-4. doi:10.3350/cmh.2013.19.2.190 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 3. Jha P, Poder L, Wang ZJ et-al. Radiologic mimics of cirrhosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194 (4): 993-9. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.3409 - Pubmed citation
- 4. David A. Sass, Kenneth Clark, Dana Grzybicki, Mordechai Rabinovitz, Thomas A. Shaw-Stiffel. Diffuse Desmoplastic Metastatic Breast Cancer Simulating Cirrhosis with Severe Portal Hypertension: A Case of “Pseudocirrhosis”. (2007) Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 52 (3): 749. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-9332-9 - Pubmed
- 5. Adike A, Karlin N, Menias C, Carey EJ. Pseudocirrhosis: A Case Series and Literature Review. (2016) Case reports in gastroenterology. 10 (2): 381-391. doi:10.1159/000448066 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- benign epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumours
- primary malignant epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumours
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumours
- haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumours
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumours
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic haemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumour
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumour
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumour
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (inflammatory pseudotumour)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumours
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumours
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms
- gallbladder and biliary
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.