Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Weerakkody Y, Knipe H, Sharma R, et al. Siderotic synovitis. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 25 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-11056
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees (past)
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to
not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
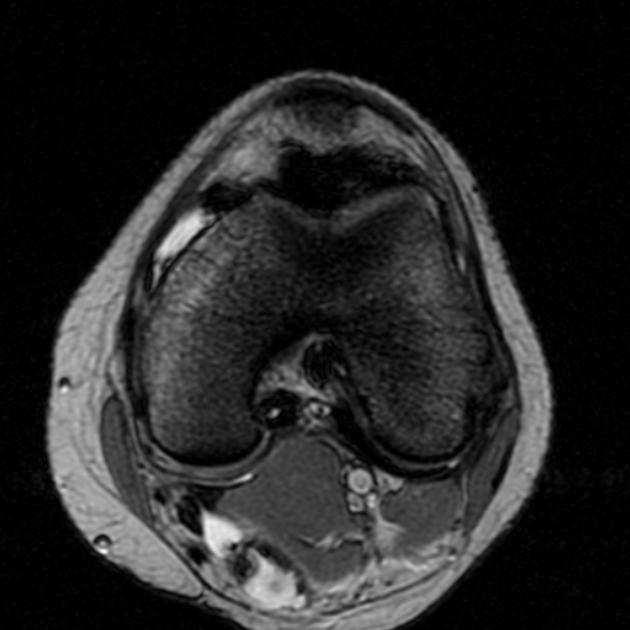
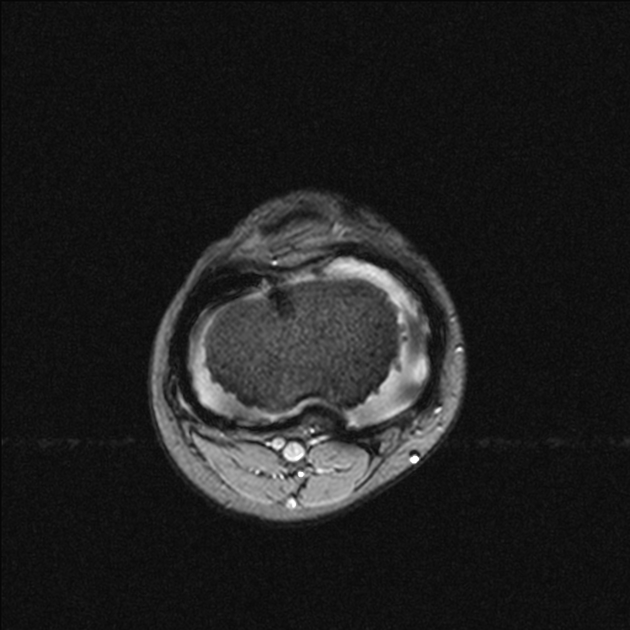
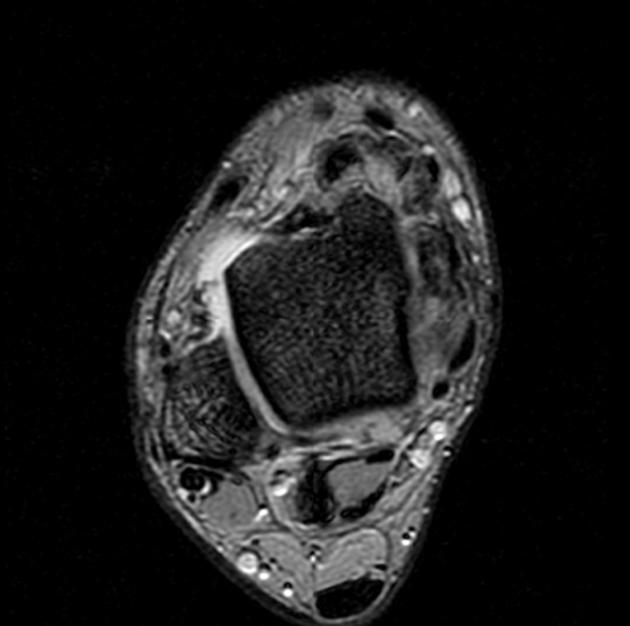
Siderotic synovitis is a condition that can occur with chronic haemarthroses.
Siderotic synovitis is characterized by rusty synovial pigmentation and hyperplasia but with an absence of foam cells and multinucleated giant cells which are seen in tenosynovial giant cell tumors.
Risk factors
MRI
May be seen as a focal or diffuse proliferation of the synovium. Signal characteristics can mimic tenosynovial giant cell tumors and include 1,4
On MRI consider:
-
1. Narváez J, Narváez J, Ortega R, De Lama E, Roca Y, Vidal N. Hypointense Synovial Lesions on T2-Weighted Images: Differential Diagnosis with Pathologic Correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181(3):761-9. doi:10.2214/ajr.181.3.1810761 - Pubmed
-
2. France M & Gupta S. Nonhemophilic Hemosiderotic Synovitis of the Shoulder. A Case Report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(262):132-6. - Pubmed
-
3. O'Connell J. Pathology of the Synovium. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;114(5):773-84. doi:10.1309/LWW3-5XK0-FKG9-HDRK - Pubmed
-
4. Boles C & Ward W. Loose Fragments and Other Debris: Miscellaneous Synovial and Marrow Disorders. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2000;8(2):371-90. - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.