Subscapular artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Arriola P, Fahrenhorst-Jones T, Hapugoda S, et al. Subscapular artery. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 09 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-29048
Permalink:
rID:
29048
Article created:
30 Apr 2014,
Pablo E. Arriola
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Pablo E. Arriola had no recorded disclosures.
View Pablo E. Arriola's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Travis Fahrenhorst-Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Travis Fahrenhorst-Jones's current disclosures
Revisions:
9 times, by
5 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Tags:
Synonyms:
- Circumflex scapular artery
- Thoracodorsal artery
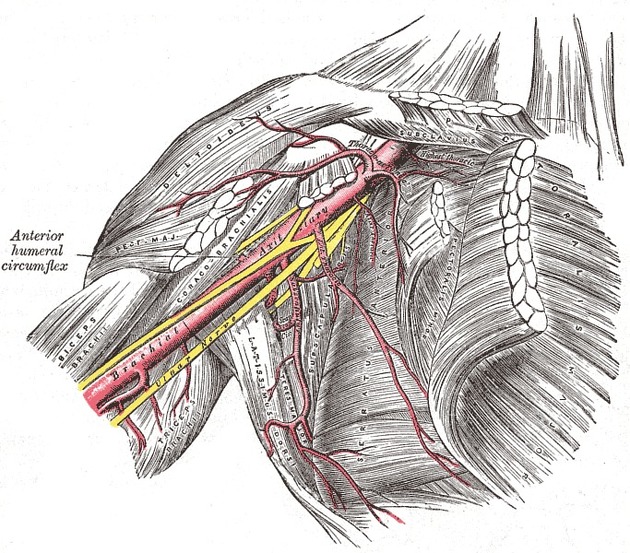
The subscapular artery is the largest branch of the axillary artery.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The subscapular artery originates from the medial surface of the third part of the axillary artery. It passes along the inferior border of the subscapularis muscle and it divides into two branches 1,2:
- Thoracodorsal artery: courses inferiorly along the serratus anterior muscle and posterior to the lateral thoracic artery supplying the intercostal muscles, serratus anterior and latissimus dorsi muscles as well as the skin of the lateral surface of the thorax.
- Circumflex scapular artery (scapular circumflex artery or dorsalis scapulae artery but not to be confused with the dorsal scapular artery): divides into three branches to supply the pectoral girdle.
Supply
- subscapularis, supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
- latissimus dorsi muscle
- serratus anterior muscle
Variant anatomy
The subscapular artery is quite stable with ~85% demonstrating classical anatomy as described above 3, 4. Common variation in anatomy includes:
- arises from second-part of axillary artery (~15%) 3
- absent in ~3% - thoracodorsal and circumflex scapular arteries arise separately from the axillary artery 3
- posterior humeral circumflex artery arising from the subscapular or thoracodorsal arteries 4
- lateral thoracic artery arising from the subscapular artery 4
References
- 1. Rouviere H. Anatomia Humana. Tronco - Tomo 2. Masson. ISBN:8445813145. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Latarjet M, Liard AR. Anatomia humana/ Human Anatomy. Media Panamericana. ISBN:9500613689. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Jesus RC, Lopes MC, Demarchi GT et-al. The subscapular artery and the thoracodorsal branch: an anatomical study. Folia Morphol. (Warsz). 2008;67 (1): 58-62. Pubmed citation
- 4. Garry N & Marquez S. The Subscapular Artery in the Axillary Region: Tracking Its Anatomical Distribution for Clinical Application. FASEB J. 2008;22(S1). doi:10.1096/fasebj.22.1_supplement.586.5
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Latissimus dorsi muscle
- Infraspinatus muscle
- Medial triangular space
- Thoracodorsal nerve
- Lower subscapular nerve
- Axillary artery branches (mnemonic)
- Teres minor muscle
- Deltoid muscle
- Shoulder
- Langer’s axillary arch
- Teres major muscle
- Lateral thoracic artery
- Scapular anastomosis
- Subscapularis muscle
- Acromion
- Glenohumeral joint
- Axillary artery
- Scapula
Related articles: Anatomy: Upper limb
-
skeleton of the upper limb
- clavicle
- scapula
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- hand
- accessory ossicles of the upper limb
- accessory ossicles of the shoulder
- accessory ossicles of the elbow
-
accessory ossicles of the wrist (mnemonic)
- os centrale carpi
- os epilunate
- os epitriquetrum
- os styloideum
- os hamuli proprium
- lunula
- os triangulare
- trapezium secondarium
- os paratrapezium
- os radiostyloideum (persistent radial styloid)
- joints of the upper limb
-
pectoral girdle
-
shoulder joint
- articulations
- associated structures
- joint capsule
- bursae
- ligaments
- movements
- scapulothoracic joint
-
glenohumeral joint
- arm flexion
- arm extension
- arm abduction
- arm adduction
- arm internal rotation (medial rotation)
- arm external rotation (lateral rotation)
- circumduction
- arterial supply - scapular anastomosis
- ossification centers
-
shoulder joint
-
elbow joint
- proximal radioulnar joint
- ligaments
- associated structures
- movements
- alignment
- arterial supply - elbow anastomosis
- development
-
wrist joint
- articulations
-
ligaments
- intrinsic ligaments
- extrinsic ligaments
- radioscaphoid ligament
- dorsal intercarpal ligament
- dorsal radiotriquetral ligament
- dorsal radioulnar ligament
- volar radioulnar ligament
- radioscaphocapitate ligament
- long radiolunate ligament
- Vickers ligament
- short radiolunate ligament
- ulnolunate ligament
- ulnotriquetral ligament
- ulnocapitate ligament
- ulnar collateral ligament
- associated structures
- extensor retinaculum
- flexor retinaculum
- joint capsule
- movements
- alignment
- ossification centers
-
hand joints
- articulations
- carpometacarpal joint
-
metacarpophalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
-
interphalangeal joints
- palmar ligament (plate)
- collateral ligament
- movements
- ossification centers
- articulations
-
pectoral girdle
- spaces of the upper limb
- muscles of the upper limb
- shoulder girdle
- anterior compartment of the arm
- posterior compartment of the arm
-
anterior compartment of the forearm
- superficial
- intermediate
- deep
-
posterior compartment of the forearm (extensors)
- superficial
- deep
- muscles of the hand
-
accessory muscles
- elbow
- volar wrist midline
- palmaris longus profundus
- aberrant palmaris longus
- volar wrist radial-side
- accessory flexor digitorum superficialis indicis
- flexor indicis profundus
- flexor carpi radialis vel profundus
- accessory head of the flexor pollicis longus (Gantzer muscle, common)
- volar wrist ulnar-side
- dorsal wrist
- blood supply to the upper limb
-
arteries
- subclavian artery (mnemonic)
- axillary artery
- brachial artery (proximal portion)
- ulnar artery
- radial artery
- veins
-
arteries
- innervation of the upper limb
- intercostobrachial nerve
-
brachial plexus (mnemonic)
- branches from the roots
- branches from the trunks
- branches from the cords
- lateral cord
- posterior cord
- medial cord
- terminal branches
- lymphatic drainage of the upper limb





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.