Tc-99m DMSA
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ammar Ashraf had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ammar Ashraf's current disclosures- DMSA
- Technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA)
- Technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid
- Technetium-99m DMSA
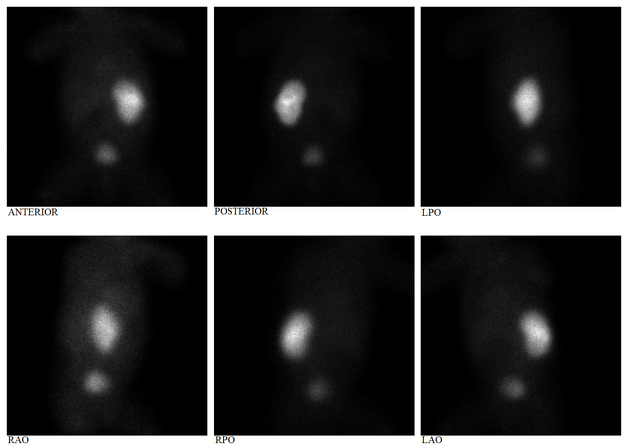
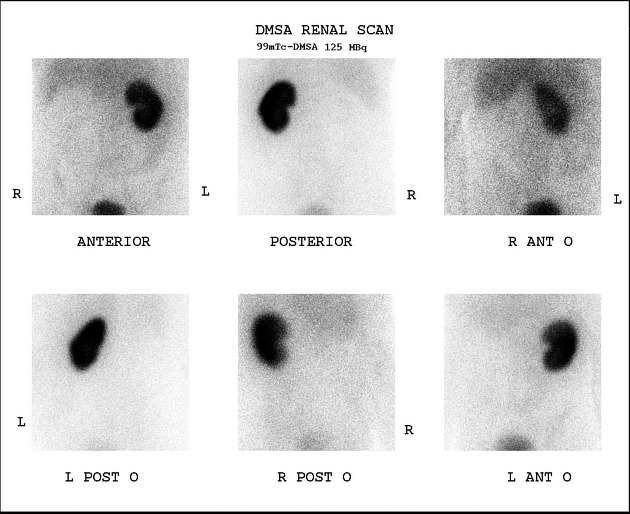
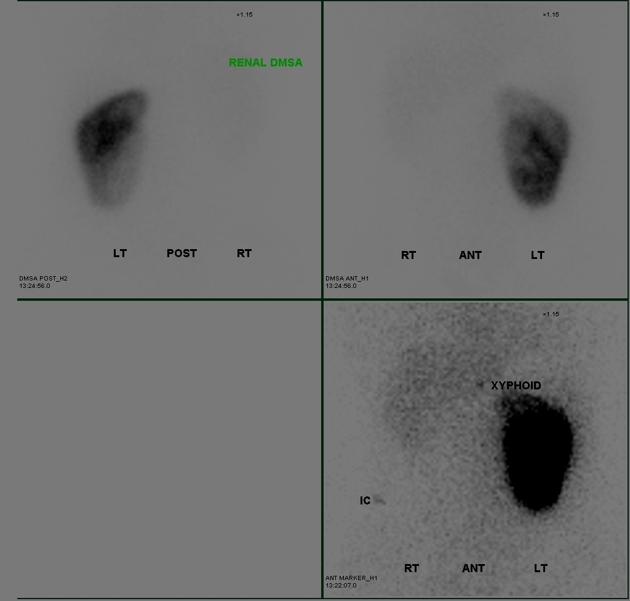
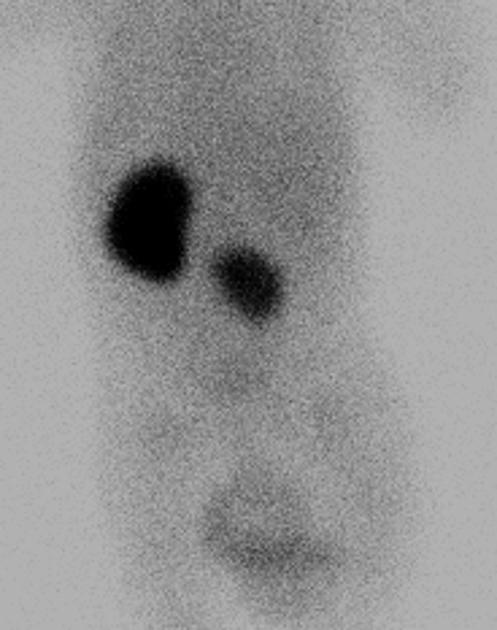
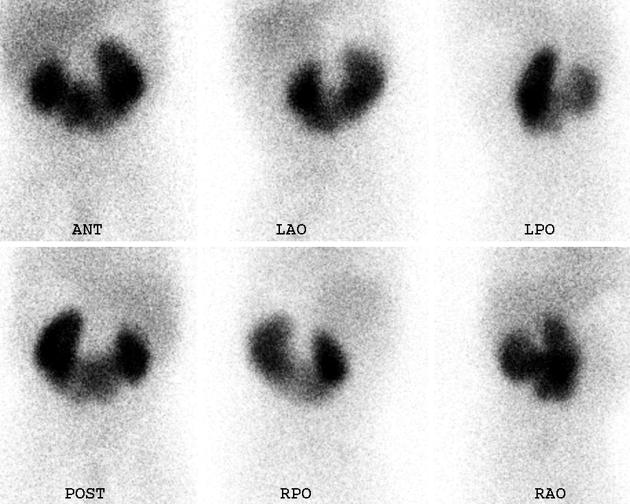
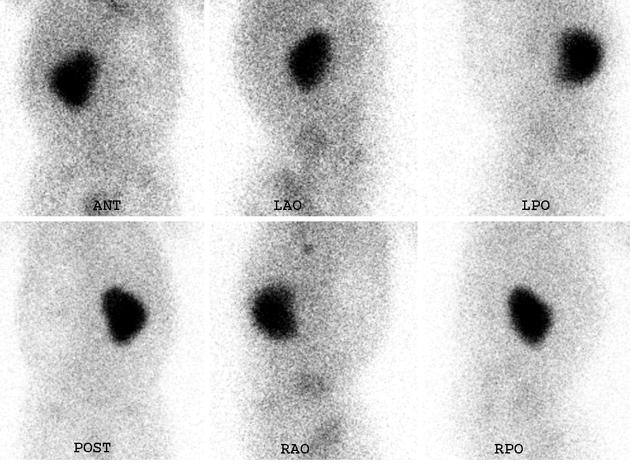
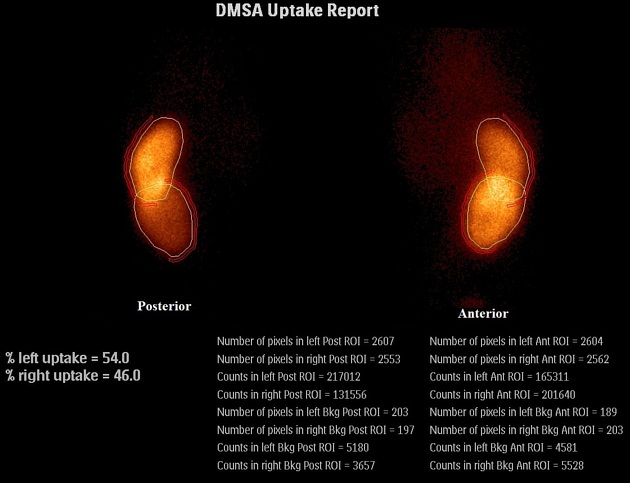
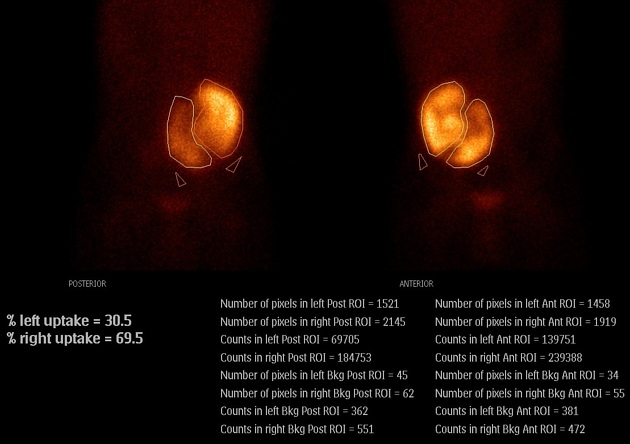
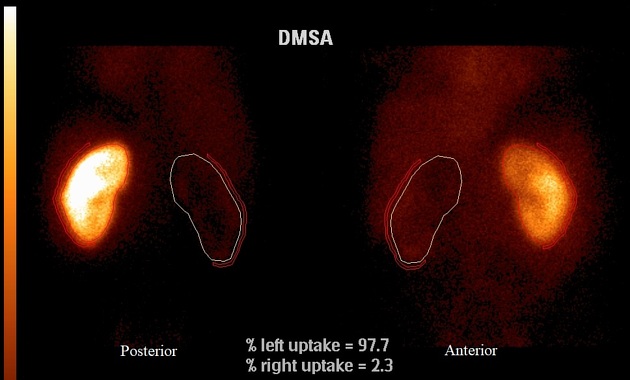
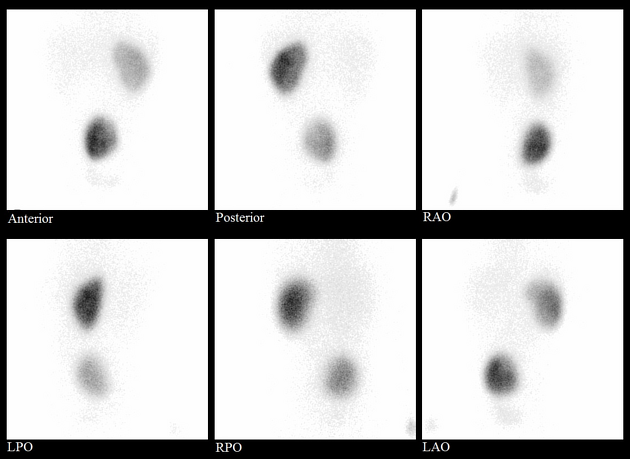
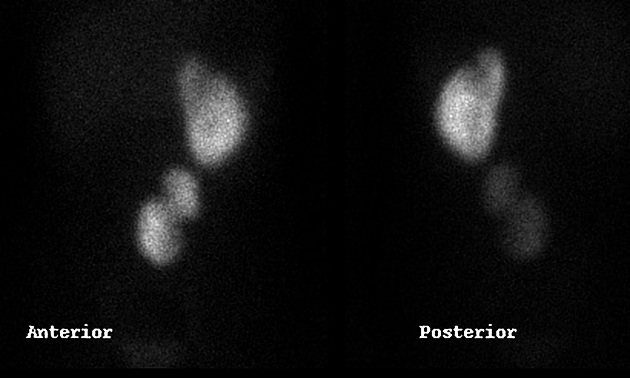
Tc-99m DMSA (2,3 dimercaptosuccinic acid) is a technetium radiopharmaceutical used in renal imaging to evaluate renal structure and morphology, particularly in paediatric imaging for detection of scarring and pyelonephritis. DMSA is an ideal agent for assessment of the renal cortex as it binds to the sulfhydryl groups in proximal tubules at the renal cortex with longer retention than other agents. This results in higher concentration and hence much higher resolution with pinhole SPECT. Also, it allows better assessment of differential renal function. It is a static scan as opposed to dynamic DTPA or MAG3 scans.
Characteristics
photon energy: 140 keV
physical half-life: 6 hours
biological half-life: 2.5-3.5 hours
2.3 < pH < 3.5 3,4
normal distribution: kidneys (100%)
excretion: renal
target organ: kidneys
-
pharmacokinetics:
after the injection 90% of the 2,3 dimercaptosuccinic acid is bound to plasma proteins 3,4
40-50% fixed to cortex (greater than glucoheptonate)
maximal cortical uptake within 3 hours
-
miscellaneous facts:
high-resolution imaging with pinhole collimators and SPECT is not possible with DTPA, MAG3 or OIH because of rapid transit times
diseases affecting the proximal convoluted tubules such as renal tubular acidosis, Fanconi syndrome and nephrotoxic drugs such as gentamicin and cisplatin also inhibit the DMSA uptake
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Uses, doses and timings
Renal cortical imaging
References
- 1. Ziessman HA, O'Malley JP, Thrall JH. Nuclear medicine. Saunders. ISBN:0323082998. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Gelfand MJ, Parisi MT, Treves ST. Pediatric radiopharmaceutical administered doses: 2010 North American consensus guidelines. (2011) Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 52 (2): 318-22. doi:10.2967/jnumed.110.084327 - Pubmed
- 3. M. P. Natale. P&C 5.1. Tecnico di radiologia. Guida completa alla preparazione di test preselettivi e prove pratiche per TSRM. Con software di simulazione. (2019) ISBN: 9788865846483
- 4. Maurizio Dondi, Raffaele Giubbini. Medicina nucleare nella pratica clinica. Con CD-ROM. (2019) ISBN: 9788855527286
Incoming Links
- Crossed renal ectopia
- Renal scarring (DMSA scan)
- Pelvic kidney
- Unilateral renal agenesis
- Unilateral renal agenesis
- Primary renal lymphoma
- Cross fused renal ectopia
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Transitional cell carcinoma of the ureter
- Horseshoe kidney
- Renal cortical scarring
- Normal DMSA scan
- Non-functioning kidney (DMSA scan)
- Crossed fused renal ectopia
- Horseshoe kidney
- Multicystic dysplastic kidney
- Ectopic kidney
Related articles: Imaging technology
- imaging technology
- imaging physics
- imaging in practice
-
x-rays
- x-ray physics
- x-ray in practice
- x-ray production
- x-ray tube
- filters
- automatic exposure control (AEC)
- beam collimators
- grids
- air gap technique
- cassette
- intensifying screen
- x-ray film
- image intensifier
- digital radiography
- digital image
- mammography
- x-ray artifacts
- radiation units
- radiation safety
- radiation detectors
- fluoroscopy
-
computed tomography (CT)
- CT physics
- CT in practice
- CT technology
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
- agents
- water soluble
- water insoluble
- vicarious contrast material excretion
- iodinated contrast media adverse reactions
- agents
- non-iodinated contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT safety
- history of CT
-
MRI
- MRI physics
- MRI in practice
- MRI hardware
- signal processing
-
MRI pulse sequences (basics | abbreviations | parameters)
- T1 weighted image
- T2 weighted image
- proton density weighted image
- chemical exchange saturation transfer
- CSF flow studies
- diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
- echo-planar pulse sequences
- fat-suppressed imaging sequences
- gradient echo sequences
- inversion recovery sequences
- metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS)
-
perfusion-weighted imaging
- techniques
- derived values
- saturation recovery sequences
- spin echo sequences
- spiral pulse sequences
- susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)
- T1 rho
- MR angiography (and venography)
-
MR spectroscopy (MRS)
- 2-hydroxyglutarate peak: resonates at 2.25 ppm
- alanine peak: resonates at 1.48 ppm
- choline peak: resonates at 3.2 ppm
- citrate peak: resonates at 2.6 ppm
- creatine peak: resonates at 3.0 ppm
- functional MRI (fMRI)
- gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- glutamine-glutamate peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- Hunter's angle
- lactate peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- lipids peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- myoinositol peak: resonates at 3.5 ppm
- MR fingerprinting
- N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak: resonates at 2.0 ppm
- propylene glycol peak: resonates at 1.13 ppm
-
MRI artifacts
- MRI hardware and room shielding
- MRI software
- patient and physiologic motion
- tissue heterogeneity and foreign bodies
- Fourier transform and Nyquist sampling theorem
- MRI contrast agents
- MRI safety
-
ultrasound
- ultrasound physics
-
transducers
- linear array
- convex array
- phased array
- frame averaging (frame persistence)
- ultrasound image resolution
- imaging modes and display
- pulse-echo imaging
- real-time imaging
-
Doppler imaging
- Doppler effect
- colour Doppler
- power Doppler
- B flow
- colour box
- Doppler angle
- pulse repetition frequency and scale
- wall filter
- colour write priority
- packet size (dwell time)
- peak systolic velocity
- end-diastolic velocity
- resistive index
- pulsatility index
- Reynolds number
- panoramic imaging
- compound imaging
- harmonic imaging
- elastography
- scanning modes
- 2D ultrasound
- 3D ultrasound
- 4D ultrasound
- M-mode
-
ultrasound artifacts
- acoustic shadowing
- acoustic enhancement
- beam width artifact
- reverberation artifact
- ring down artifact
- mirror image artifact
- side lobe artifact
- speckle artifact
- speed displacement artifact
- refraction artifact
- multipath artifact
- anisotropy
- electrical interference artifact
- hardware-related artifacts
- Doppler artifacts
- aliasing
- tissue vibration
- spectral broadening
- blooming
- motion (flash) artifact
- twinkling artifact
- acoustic streaming
- biological effects of ultrasound
- history of ultrasound
-
nuclear medicine
- nuclear medicine physics
- detectors
- tissue to background ratio
-
radiopharmaceuticals
- fundamentals of radiopharmaceuticals
- radiopharmaceutical labelling
- radiopharmaceutical production
- nuclear reactor produced radionuclides
- cyclotron produced radionuclides
- radiation detection
- dosimetry
- specific agents
- carbon-11
- chromium-51
- fluorine agents
- gallium agents
- Ga-67 citrate
- Ga-68
- iodine agents
-
I-123
- I-123 iodide
- I-123 ioflupane (DaTSCAN)
- I-123 ortho-iodohippurate
- I-131
-
MIBG scans
- I-123 MIBG
- I-131 MIBG
-
I-123
- indium agents
- In-111 Octreoscan
- In-111 OncoScint
- In-111 Prostascint
- In-111 oxine labelled WBC
- krypton-81m
- nitrogen-13
- oxygen-15
- phosphorus-32
- selenium-75
-
technetium agents
- Tc-99m DMSA
- Tc-99m DTPA
- Tc-99m DTPA aerosol
- Tc-99m HMPAO
- Tc-99m HMPAO labelled WBC
- Tc-99m MAA
- Tc-99m MAG3
- Tc-99m MDP
- Tc-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine
- Tc-99m pertechnetate
- Tc-99m labelled RBC
- Tc-99m sestamibi
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid (oral)
- thallium-201 chloride
- xenon agents
- in vivo therapeutic agents
- pharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine
-
emerging methods in medical imaging
- radiography
- phase-contrast imaging
- CT
- deep-learning reconstruction
- photon counting CT
- virtual non-contrast imaging
- ultrasound
- magnetomotive ultrasound (MMUS)
- superb microvascular imaging
- ultrafast Doppler imaging
- ultrasound localisation microscopy
- MRI
- nuclear medicine
- total body PET system
- immuno-PET
- miscellaneous
- radiography






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.