Thoracic spine
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Dinesh Palipana had no recorded disclosures.
View Dinesh Palipana's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- T-spine
- T spine
- D spine
- D-spine
- Thoracic spines
- T spines
- T-spines
- D-spines
- Dorsal spines
- Dorsal spine
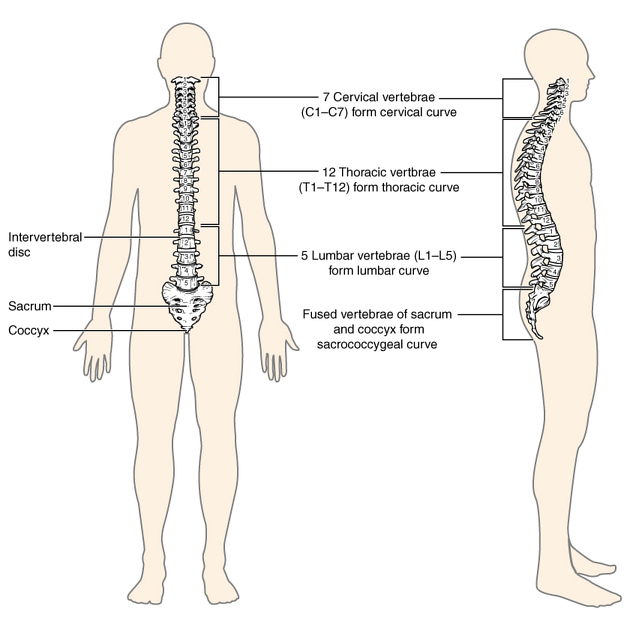
The thoracic spine (often shortened to T-spine) forms the middle part of the vertebral column. It extends from below C7 of the cervical spine to above L1 of the lumbar spine. There are 12 thoracic vertebra, termed T1-T12.
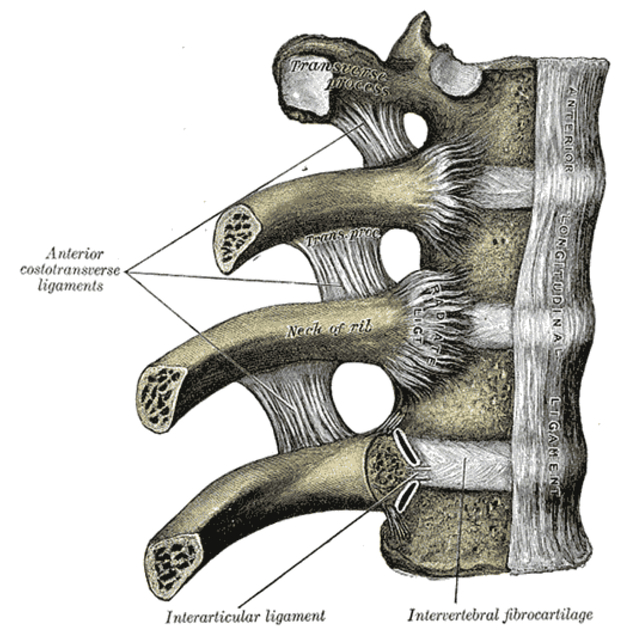
The thoracic spine is unique due to its articulation with ribs via costal facets. The ribs restrict the movement of the thoracic spine somewhat. The thoracic spine is otherwise the most mobile of all spinal column segments.
For a basic description of the anatomy of typical vertebrae, see vertebrae.
Terminology
In medical English, some doctors and texts refer to the dorsal spine, D-spine and D1-D12, however, we discourage this usage on Radiopaedia preferring thoracic spine, T-spine and T1-T12. This is consistent with Terminologia Anatomica, which solely employs the thoracic designator to refer to this part of the spine. However, in French-speaking parts of the world, D1-D12 are commonly used interchangeably with T1-T12 2.
Gross anatomy
Most thoracic vertebrae have similar features with the exception of some atypical ones. Relative to cervical and lumbar vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae have:
- medium-sized, heart shaped vertebral bodies
- medium-sized round vertebral canals
- prominent transverse processes with costal facets
- long spinous processes angulating downwards
For more detailed information, see typical thoracic vertebrae.
References
- 1. FRCS CSS. Last's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0702033952. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Ann Wiles. 2016. Ann's Acronyms: T versus D. https://sites.google.com/site/caduceusnewsletter/medical-reference/ann-s-acronyms-t-versus-d---by-ann-wiles . Caduceus [accessed 10 March 2020].
Incoming Links
- Interspinales muscles
- Thoracic spine protocol (MRI)
- Spinal anatomy
- Vertebra
- Intertransverse ligaments
- Oblique fissure
- Intervertebral joint
- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
- Spinal cord abscess
- Thoracic spine (AP view)
- Scheuermann disease
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (skeletal manifestations)
- Trauma CT thorax review areas (mnemonic)
- Thoracic spine series
- Thoracolumbar spine fracture
- Thoracic spine (lateral view)
- Mediastinum (ITMIG classification)
- Hemiazygos vein
- Words we never use
- Thorax
Related articles: Anatomy: Spine
-
osteology
- vertebrae
- spinal canal
- cervical spine
- thoracic spine
- lumbar spine
- sacrum
- coccyx
-
anatomical variants
- vertebral body
- neural arch
- transitional vertebrae
- ossicles
- ossification centres
- intervertebral disc
- articulations
- ligaments
- musculature of the vertebral column
- muscles of the neck
- muscles of the back
-
suboccipital muscle group
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- splenius capitis muscle
- splenius cervicis muscle
- erector spinae group
- transversospinalis group
- quadratus lumborum muscle
-
suboccipital muscle group
- spinal meninges and spaces
-
spinal cord
- gross anatomy
-
white matter tracts (white matter)
- corticospinal tract
- anterolateral columns
- lateral columns
-
dorsal columns
- fasiculus gracilis (column of Goll)
- fasiculus cuneatus (column of Burdach)
- grey matter
- nerve root
- central canal
- functional anatomy
- spinal cord blood supply
- sympathetic chain
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- oesophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax
- innervation of the thorax







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.