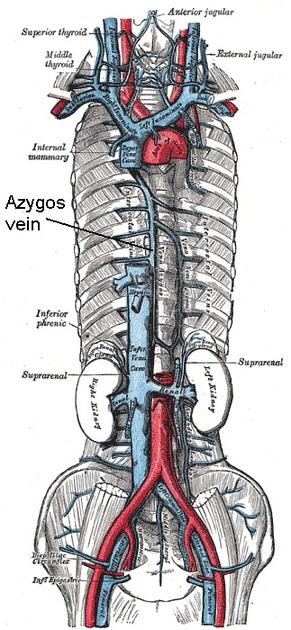
The azygos vein is a unilateral vessel that ascends in the thorax to the right of the vertebral column, carrying deoxygenated blood from the posterior chest and abdominal walls. It forms part of the azygos venous system.
On this page:
Terminology
The spelling azygous when referring to the vein is incorrect, regardless of whether British or American English is used 1. Azygous is a word in English meaning 'without pair', but in the context of this vein, azygos is the sole correct spelling (see Terminologia Anatomica). Azygous is allowable for an azygos anterior cerebral artery as in this sense it is being used to mean an unpaired ACA.
Gross anatomy
Origin
The azygos vein is formed by the union of the right ascending lumbar vein and right subcostal veins at around the T12-L2 vertebral level.
Course
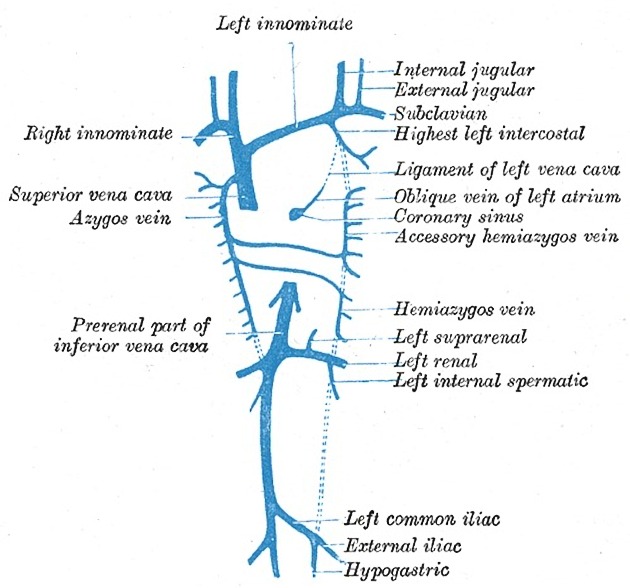
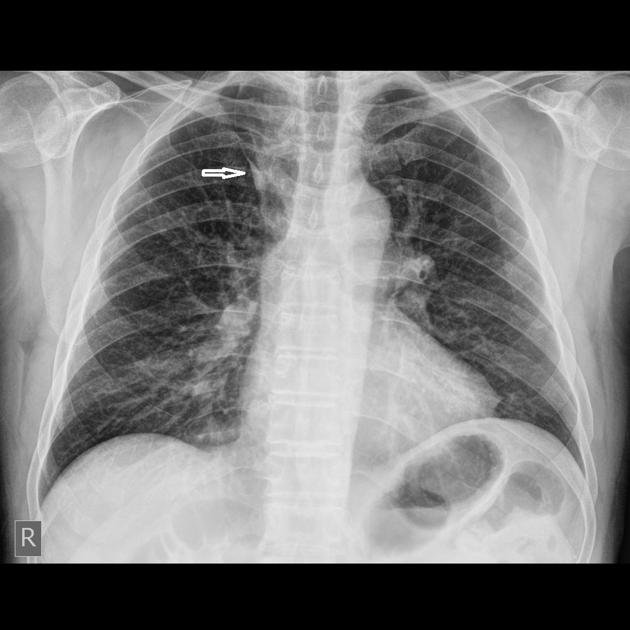
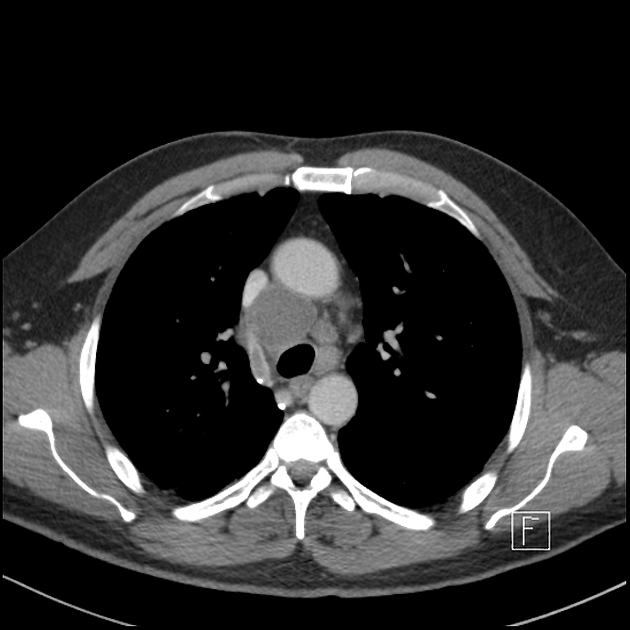
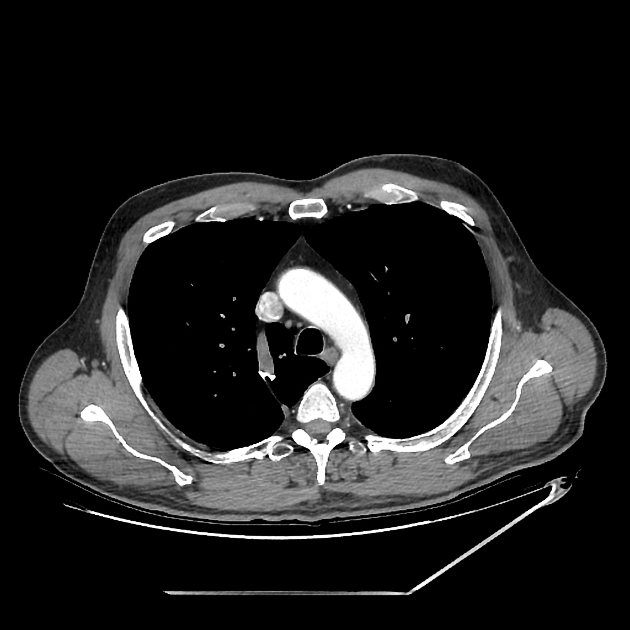
If originating at a lumbar level, the azygos vein typically enters the chest through the aortic hiatus (T12 vertebral level), although may enter by piercing the right crus of the diaphragm. It then ascends in the posterior mediastinum before arching over the right main bronchus posteriorly at the root of the right lung (at the level of T5-T6), where it joins the superior vena cava at the azygovenous junction. This arch of the azygos vein (arcus venae azygos) is an important anatomical landmark.
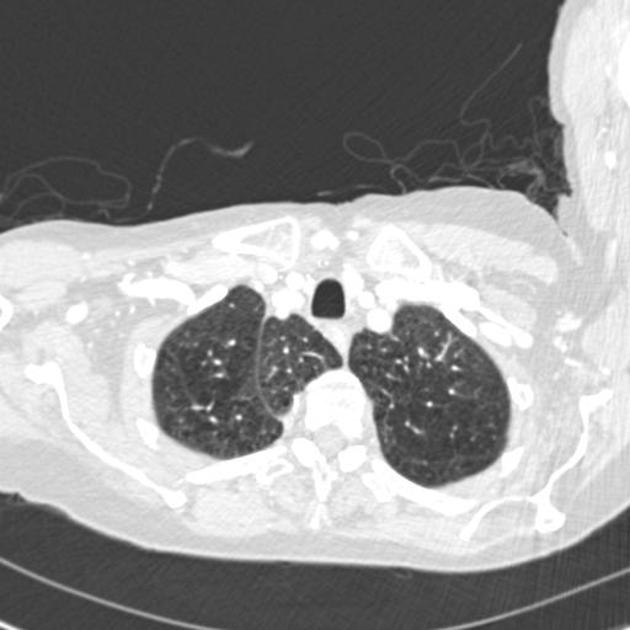
Often there is a valve in the arch within 4 cm of its orifice in the SVC, which can be seen in about two-thirds of CT cases with reflux of contrast into the azygos arch 2. When present and seen with contrast reflux, the valve is often (82%) associated with a bulge of the valve sinus 2. Contrast isolated in the sinuses of this valve may be mistaken for hyperattenuating foci in the vicinity, such as calcified lymph nodes, surgical clips or tracheal calcification.
Tributaries
hemiazygos vein is a similar structure on the opposite side of the vertebral column and drains into the azygos vein
right superior intercostal vein
right posterior intercostal veins
right superior phrenic vein
right bronchial vein
tracheal veins
oesophageal veins
pericardial veins
The azygos vein freely anastomoses with the vertebral venous plexus.
Relations
posterior: vertebral bodies of at least T5-T12, anterior longitudinal ligament, right posterior intercostal arteries
right lateral: right greater splanchnic nerve, pleura, lung
left: thoracic duct, aorta, oesophagus, trachea, right vagus nerve
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
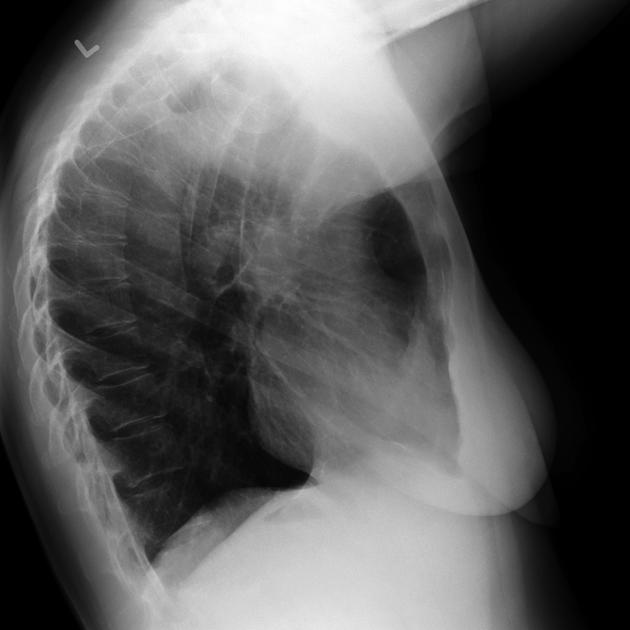
It forms part of the normal cardiomediastinal contour on chest x-rays and normally measures <7 mm (erect projection).
Variant anatomy
azygos fissure and azygos lobe 3
absence of the azygos vein (rare) 3
may drain into the SVC, or rarely into the right brachiocephalic or subclavian vein, intrapericardial SVC, or directly into the right atrium 3
History and etymology
The Ancient Greek root "ζυγόν" (zygon) means a yoke, as holds two oxen together, and thus came to mean a pair, and the prefix "α-" (a) means not; hence, azygos means a non-paired structure.
Related pathology
malpositioned central venous catheter in the azygos vein







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.