Vestibulocochlear nerve
Updates to Article Attributes
The vestibulocochlear nerve is the eighth cranial nerve and has two roles:
Gross anatomy
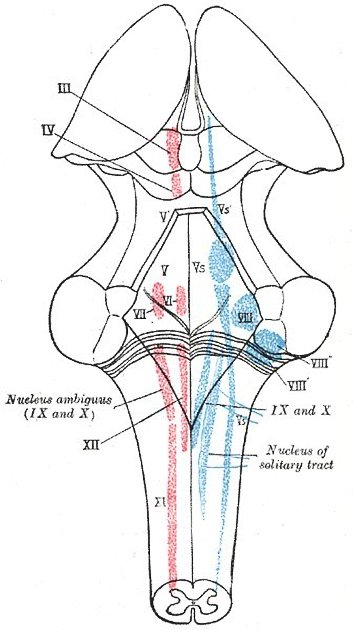
It emerges between the pons and the medulla, lateral to the facial nerve and nervus intermedius, passing laterally through the cerebellopontine angle to the internal acoustic meatus (IAM) with the aforementioned two other nerves.
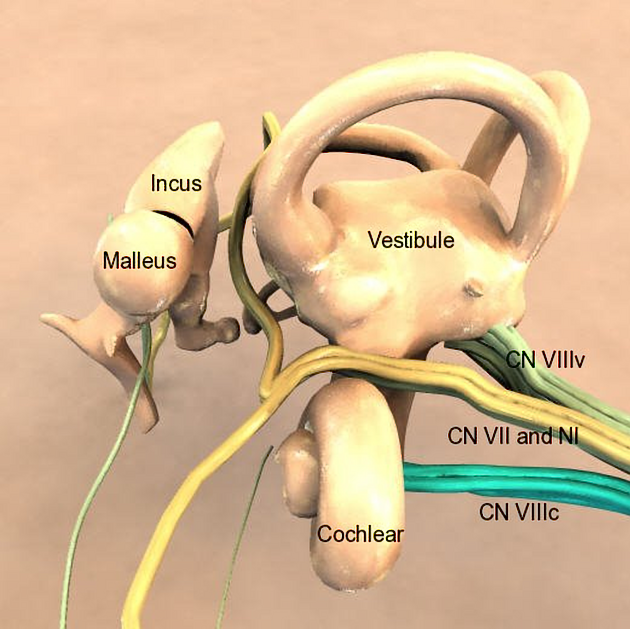
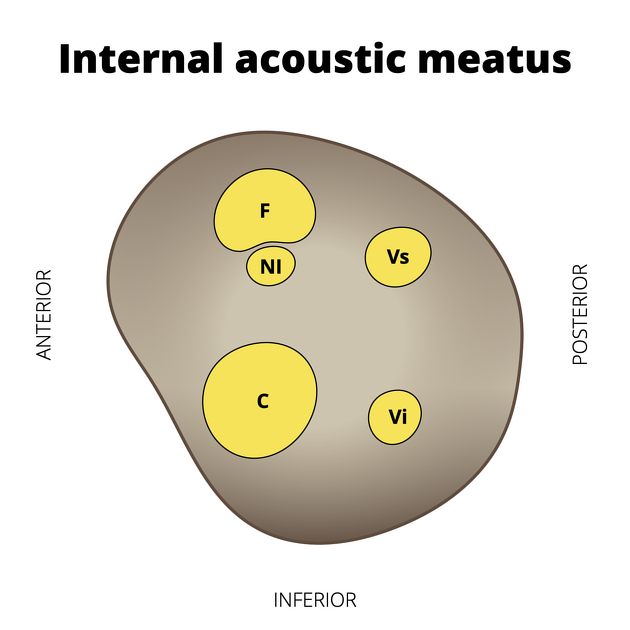
In the IAM the nerve splits into 4 bundles: cochlear nerve, superior and inferior division of the vestibular nerve and nerve from the posterior semicircular canal, separated from each other by the falciform crest and Bill's bar (see figure 2).
Cochlear nerve
The cochlear nerve relays with the first order sensory cells in the spiral ganglion, which is in the base of the spiral lamina.
Vestibular nerve
The vestibular nerve relays in the vestibular ganglion (aka ganglion of Scarpa) From here, from there three bundles emerge:
- The superior division of the vestibular nerve carries sensory fibres from the hair cells of the anterior and lateral semicircular canals and utricle. It is located in the posterosuperior quadrant
. - The inferior division carries sensory fibres from the saccule. It is located in the posteroinferior quadrant, along with
; - The nerve from the posterior semicircular canal, also in the posteroinferior quadrant passes through the foramen singulare
Related pathology
Tags changed:
- refs
Image ( update )
Image 5 Photograph ( update )
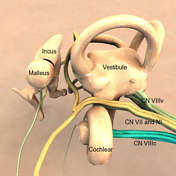
Image 9 MRI (T2) ( update )
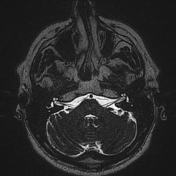
Image 10 MRI (T1 labelled) ( update )
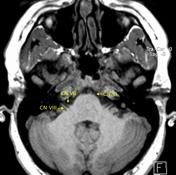
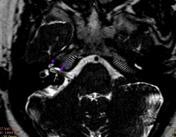
Image 11 Annotated image (CN VIII) ( update )












 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.